Environmental science Conservation bio questions
... What is conservation biology? What are the three levels of diversity (genetic, species and ecosystem) What are some major threats to biodiversity on our planet? What are some problems with captive breeding programs (species approach)? What is the difference between species, population, and ...
... What is conservation biology? What are the three levels of diversity (genetic, species and ecosystem) What are some major threats to biodiversity on our planet? What are some problems with captive breeding programs (species approach)? What is the difference between species, population, and ...
population
... • Genetic drift occurs when # of reproducing individuals in a population is too small to ensure all alleles in the gene pool will be passed on to next generation in their existing frequencies • Genetic drift may result in one allele becoming fixed and one allele disappearing in a population ...
... • Genetic drift occurs when # of reproducing individuals in a population is too small to ensure all alleles in the gene pool will be passed on to next generation in their existing frequencies • Genetic drift may result in one allele becoming fixed and one allele disappearing in a population ...
Genes and Evolution - Mad River Local Schools
... Sequencing Neanderthal DNA 1. Why is comparing human DNA to Neanderthal DNA difficult in the lab? 2. How can the bases of DNA change overtime? 3. Where was the sample taken from Pääbo found and how old was it? ...
... Sequencing Neanderthal DNA 1. Why is comparing human DNA to Neanderthal DNA difficult in the lab? 2. How can the bases of DNA change overtime? 3. Where was the sample taken from Pääbo found and how old was it? ...
Conservation Genetics
... Frankham (1998): reported high levels of inbreeding in island populations, but found that endemic island populations were more inbred than non-endemic island populations. A survey of deliberately inbred lab and domestic populations found a negative correlation between survival and inbreeding: The p ...
... Frankham (1998): reported high levels of inbreeding in island populations, but found that endemic island populations were more inbred than non-endemic island populations. A survey of deliberately inbred lab and domestic populations found a negative correlation between survival and inbreeding: The p ...
Natural Selection ppt
... coloration, which allows the beetle to have more offspring, becomes more common in the population. If this process continues, eventually, all individuals in the population will be brown. ...
... coloration, which allows the beetle to have more offspring, becomes more common in the population. If this process continues, eventually, all individuals in the population will be brown. ...
BiologyReferences_files/Evolution 2012 with study guide
... •Guiding QuestionsWhat are selective forces?Why is natural selection the mechanism for evolution?What is an adaptation?How do behavioral, physiological, and structural adaptations differ? In terms of evolution, can an individual organism adapt?What defines a species?How do selective forces guide evo ...
... •Guiding QuestionsWhat are selective forces?Why is natural selection the mechanism for evolution?What is an adaptation?How do behavioral, physiological, and structural adaptations differ? In terms of evolution, can an individual organism adapt?What defines a species?How do selective forces guide evo ...
Genetics Cram EOC Session
... 22. BW means Black and white at same time 23. The heterozygote shows a blending phenotype 24. written as AA’ 25. When red flowering plants mate with white flowering plants to make pink offspring ...
... 22. BW means Black and white at same time 23. The heterozygote shows a blending phenotype 24. written as AA’ 25. When red flowering plants mate with white flowering plants to make pink offspring ...
Document
... How does sexual reproduction produce variation? Mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA. 2 How can genetic variation be measu‑ red? DNA sequence variation. DNA fragment size variation. Protein varia‑ tion. Phenotypic variation. 3 Genetic structure in natural popula‑ tions. What is a population? How are al ...
... How does sexual reproduction produce variation? Mitochondrial and chloroplast DNA. 2 How can genetic variation be measu‑ red? DNA sequence variation. DNA fragment size variation. Protein varia‑ tion. Phenotypic variation. 3 Genetic structure in natural popula‑ tions. What is a population? How are al ...
Evolution of Populations
... • All members of a population can interbreed, they share a common group of genes, called a gene pool. – A gene pool is the combined genetic information of all the members of a particular population. • Typically contains two or more alleles—or forms of a certain gene—for each inheritable trait. ...
... • All members of a population can interbreed, they share a common group of genes, called a gene pool. – A gene pool is the combined genetic information of all the members of a particular population. • Typically contains two or more alleles—or forms of a certain gene—for each inheritable trait. ...
Concepts of Genetics
... ….the structure of DNA was described as a double helix by Watson and Crick ...
... ….the structure of DNA was described as a double helix by Watson and Crick ...
Hardy Weinberg
... real world, evolution is inevitable. Hardy and Weinberg went on to develop a simple equation that can be used to discover the probable genotype frequencies in a population and to track their changes from one generation to ...
... real world, evolution is inevitable. Hardy and Weinberg went on to develop a simple equation that can be used to discover the probable genotype frequencies in a population and to track their changes from one generation to ...
II-10 to II-16
... • random changes in allele frequencies occur until p = 0 or 1 is reached; no further change occurs after that. (b) Across replicate populations. • Replicate population allele frequencies diverge through time. – Relation between the two views: • overall statistical properties across replicate populat ...
... • random changes in allele frequencies occur until p = 0 or 1 is reached; no further change occurs after that. (b) Across replicate populations. • Replicate population allele frequencies diverge through time. – Relation between the two views: • overall statistical properties across replicate populat ...
Differences in the concept of fitness between artificial
... the predictions of biological models of cooperation, a corn the case of a non-proportionate selection. Alternatively, one ...
... the predictions of biological models of cooperation, a corn the case of a non-proportionate selection. Alternatively, one ...
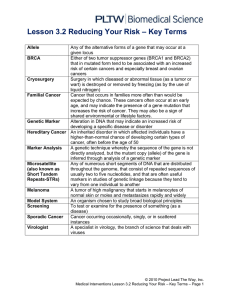
L3.2ReducingYourRisk - jj-sct
... Hereditary Cancer An inherited disorder in which affected individuals have a higher-than-normal chance of developing certain types of cancer, often before the age of 50 Marker Analysis A genetic technique whereby the sequence of the gene is not directly analyzed, but the mutant copy (allele) of the ...
... Hereditary Cancer An inherited disorder in which affected individuals have a higher-than-normal chance of developing certain types of cancer, often before the age of 50 Marker Analysis A genetic technique whereby the sequence of the gene is not directly analyzed, but the mutant copy (allele) of the ...
Evolution (18%) 11 Items Sample Test Prep Questions
... that natural selection is the mechanism of evolution. (pg 109 Science Framework) Summary: Charles Darwin explained his line of reasoning for natural selection as the primary mechanism for evolution. Darwin proposed that differences between offspring would occur randomly. Some of those differences wo ...
... that natural selection is the mechanism of evolution. (pg 109 Science Framework) Summary: Charles Darwin explained his line of reasoning for natural selection as the primary mechanism for evolution. Darwin proposed that differences between offspring would occur randomly. Some of those differences wo ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Photosynthesis Quiz
... Germination of the pollen grain usually takes place on the … ...
... Germination of the pollen grain usually takes place on the … ...
Chapter 23: Evolution of Populations - Biology E
... Extremely large population size: The smaller the population, the more likely it is that allele frequencies will fluctuate by chance from one generation to the next. No gene flow: By moving alleles into or out of populations, gene flow can alter allele frequencies. ...
... Extremely large population size: The smaller the population, the more likely it is that allele frequencies will fluctuate by chance from one generation to the next. No gene flow: By moving alleles into or out of populations, gene flow can alter allele frequencies. ...
Principles of Evolution
... • Nature “selects” the variations that provide greatest chance for survival - Adaptations • Descent with Modification – Darwin’s term for evolution –organisms share a common ancestor but descendants change over time ...
... • Nature “selects” the variations that provide greatest chance for survival - Adaptations • Descent with Modification – Darwin’s term for evolution –organisms share a common ancestor but descendants change over time ...
Natural selection articles for high school
... Natural selection moderates the disorganizing effects of these processes because it multiplies the incidence of beneficial mutations over the generations and. The theory of evolution is one of the great intellectual revolutions of human history, drastically changing our perception of the world and o ...
... Natural selection moderates the disorganizing effects of these processes because it multiplies the incidence of beneficial mutations over the generations and. The theory of evolution is one of the great intellectual revolutions of human history, drastically changing our perception of the world and o ...
Natural Selection Quiz
... d. causing the death of a significant proportion of the population. e. driving the species toward an eventual endpoint sometime in the future. 5. If the weather in Richmond, Virginia, changed to very cold (snow on the ground 8 months of each year) over the next few years, what change might occur? a. ...
... d. causing the death of a significant proportion of the population. e. driving the species toward an eventual endpoint sometime in the future. 5. If the weather in Richmond, Virginia, changed to very cold (snow on the ground 8 months of each year) over the next few years, what change might occur? a. ...
Print test
... 2 In a pond, the primary producer is a green alga, Spirogyra; the primary consumer is the crustacean, Daphnia; the secondary consumer is a small fish, the bluegill; and the tertiary consumer is a larger fish, the smallmouth bass. What changes can be expected in the pond if the Daphnia are killed wit ...
... 2 In a pond, the primary producer is a green alga, Spirogyra; the primary consumer is the crustacean, Daphnia; the secondary consumer is a small fish, the bluegill; and the tertiary consumer is a larger fish, the smallmouth bass. What changes can be expected in the pond if the Daphnia are killed wit ...
1. Assuming simple dominance, out of a total of 160 offspring, how
... Lesson Assessment: Genetics 6. What is the expected number of offspring phenotypes produced by a cross between heterozygotes for a gene that shows codominance? a) 2 b) 3 c) 1 d) 9 7. The allelic composition of an organism is called the _____. a) sequence b) phenotype c) genotype d) karyotype 8. What ...
... Lesson Assessment: Genetics 6. What is the expected number of offspring phenotypes produced by a cross between heterozygotes for a gene that shows codominance? a) 2 b) 3 c) 1 d) 9 7. The allelic composition of an organism is called the _____. a) sequence b) phenotype c) genotype d) karyotype 8. What ...
CYSTIC FIBROSIS
... world, but resembled those on South American coast. How did they become so well-suited to ...
... world, but resembled those on South American coast. How did they become so well-suited to ...
Population genetics

Population genetics is the study of the distribution and change in frequency of alleles within populations, and as such it sits firmly within the field of evolutionary biology. The main processes of evolution (natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and genetic recombination) form an integral part of the theory that underpins population genetics. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as adaptation, speciation, population subdivision, and population structure.Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics.Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, lab and field work. Computational approaches, often utilising coalescent theory, have played a central role since the 1980s.