Chapter 1 Reading Guide
... Units: g/cm or g/mL (for solids and liquids); g/L (often used for gases). Was originally based on mass (the density was defined as the mass of 1.00 mL of pure water at 25 ˚C). ...
... Units: g/cm or g/mL (for solids and liquids); g/L (often used for gases). Was originally based on mass (the density was defined as the mass of 1.00 mL of pure water at 25 ˚C). ...
Document
... An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion (at constant velocity) unless acted upon by an external force. Forces are the “causes” of changes in motion. forces on an object arise from interactions with other objects. The inertia of an object is its resistance ...
... An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion (at constant velocity) unless acted upon by an external force. Forces are the “causes” of changes in motion. forces on an object arise from interactions with other objects. The inertia of an object is its resistance ...
Material Safety Data Sheet For Wax Medium
... Eye Protection: Approved eye protection to safeguard against potential eye contact, irritation or injury is recommended. A Source of clean water should be available in the work area for flushing eyes and skin. Skin Protection: Not normally required for solid material. The use of thermally-resistant ...
... Eye Protection: Approved eye protection to safeguard against potential eye contact, irritation or injury is recommended. A Source of clean water should be available in the work area for flushing eyes and skin. Skin Protection: Not normally required for solid material. The use of thermally-resistant ...
Basic Concepts of the Gas Phase
... Alfons Buekens was born in Aalst, Belgium; he obtained his M.Sc. (1964) and his Ph.D (1967) at Ghent University (RUG) and received the K.V.I.V.-Award (1965), the Robert De Keyser Award (Belgian Shell Co., 1968), the Körber Foundation Award (1988) and the Coca Cola Foundation Award (1989). Dr. Bueken ...
... Alfons Buekens was born in Aalst, Belgium; he obtained his M.Sc. (1964) and his Ph.D (1967) at Ghent University (RUG) and received the K.V.I.V.-Award (1965), the Robert De Keyser Award (Belgian Shell Co., 1968), the Körber Foundation Award (1988) and the Coca Cola Foundation Award (1989). Dr. Bueken ...
Module 3 -- Lesson 4
... Each condition increases the yield by shifting the equilibrium to favor the product. LESSON 4, ASSIGNMENT 1 Answer the following questions. For each situation, predict the shift in equilibrium using Le Chatelier’s Principle and explain the shift using collision - rate theory. 1. When a few drops of ...
... Each condition increases the yield by shifting the equilibrium to favor the product. LESSON 4, ASSIGNMENT 1 Answer the following questions. For each situation, predict the shift in equilibrium using Le Chatelier’s Principle and explain the shift using collision - rate theory. 1. When a few drops of ...
Final Exam Practice
... ____ 48. There are many different ways to classify matter, but one way is to use only two categories for ALL matter. All matter can be classified as either: a. solids or liquids. b. mixtures or substances. c. atoms or molecules. d. elements or compounds. ____ 49. A substance made of two or more elem ...
... ____ 48. There are many different ways to classify matter, but one way is to use only two categories for ALL matter. All matter can be classified as either: a. solids or liquids. b. mixtures or substances. c. atoms or molecules. d. elements or compounds. ____ 49. A substance made of two or more elem ...
6-1 Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
... water freezes and flask sticks to wood. Lift the flask to show its hold on the wood. Exothermic: Put stir bar in Styrofoam cup and set on stir plate. Add 50 mL of water into cup. Turn on stir plate so that water is gently stirring. Take initial temperature reading, displaying thermometer reading on ...
... water freezes and flask sticks to wood. Lift the flask to show its hold on the wood. Exothermic: Put stir bar in Styrofoam cup and set on stir plate. Add 50 mL of water into cup. Turn on stir plate so that water is gently stirring. Take initial temperature reading, displaying thermometer reading on ...
Calculating Enthalpy Changes
... Actually, the change in the equilibrium constant is Not as bad as you might think. Obviously, this Has been studied quite carefully. The temperature 500 K was chosen since it is below the crossover Temperature (can you use DrxnHo and DrxnSo to calculate it?). We can see the effect of the change of e ...
... Actually, the change in the equilibrium constant is Not as bad as you might think. Obviously, this Has been studied quite carefully. The temperature 500 K was chosen since it is below the crossover Temperature (can you use DrxnHo and DrxnSo to calculate it?). We can see the effect of the change of e ...
Chapter 14…Kinetic Theory
... Write the equations for the following and indicate what is held constant: 1. Boyle’s Law: 2. Charles’ Law: 3. Gay-Lussac’s Law: 4. Combined Gas Law: 5. Ideal Gas Law: 6. Density: 7. Indicate the relationship between the variables in each of the equations above. 8. Indicate what each variable stands ...
... Write the equations for the following and indicate what is held constant: 1. Boyle’s Law: 2. Charles’ Law: 3. Gay-Lussac’s Law: 4. Combined Gas Law: 5. Ideal Gas Law: 6. Density: 7. Indicate the relationship between the variables in each of the equations above. 8. Indicate what each variable stands ...
Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Solids 21 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
... a: Evaporation coefficient (0< a £ 1). pK: Vapor pressure as determined by the Knudsen method. The Knudsen cell is often used in combination with a mass spectrometer (Identification of the gaseous species). Knudsen-Effusion: Determination of the mass at room temperature before and after the experime ...
... a: Evaporation coefficient (0< a £ 1). pK: Vapor pressure as determined by the Knudsen method. The Knudsen cell is often used in combination with a mass spectrometer (Identification of the gaseous species). Knudsen-Effusion: Determination of the mass at room temperature before and after the experime ...
Chapter 14, Section 1, pages 494-501
... To describe chemical equilibrium To give examples of chemical equilibrium Demo Burn sulfur in oxygen as an example of a completion reaction. Input Completion Reactions and Reversible Reactions What does reversible mean? Completion Reactions are reactions that use up all or almost all of the reactant ...
... To describe chemical equilibrium To give examples of chemical equilibrium Demo Burn sulfur in oxygen as an example of a completion reaction. Input Completion Reactions and Reversible Reactions What does reversible mean? Completion Reactions are reactions that use up all or almost all of the reactant ...
Semester 2 Final Exam
... will the graph change? (A) A will increase, while B remains the same. (B) B will increase, while A remains the same. (C) Both A and B will increase. (D) Both A and B will remain the same. 19. If B decreases while A increases, which of the following may have happened? I. The reaction mixture was heat ...
... will the graph change? (A) A will increase, while B remains the same. (B) B will increase, while A remains the same. (C) Both A and B will increase. (D) Both A and B will remain the same. 19. If B decreases while A increases, which of the following may have happened? I. The reaction mixture was heat ...
document
... • Enthalpy is the macroscopic energy change (in the form of heat) that accompanies changes at the atomic level (bond formation or breaking) • Enthalpy has the same sign convention as work, q and U – If energy is released as heat during a chemical reaction the enthalpy has a ‘-’ sign – If energy is ...
... • Enthalpy is the macroscopic energy change (in the form of heat) that accompanies changes at the atomic level (bond formation or breaking) • Enthalpy has the same sign convention as work, q and U – If energy is released as heat during a chemical reaction the enthalpy has a ‘-’ sign – If energy is ...
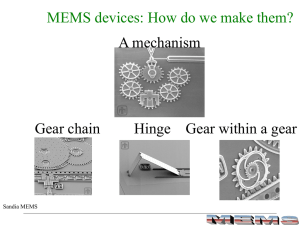
MEMS Processing
... using selective etching of sacrificial thin films to form freestanding/completely released thin-film microstructures ...
... using selective etching of sacrificial thin films to form freestanding/completely released thin-film microstructures ...
FHN - Chemical and Physical Changes
... Solid melting to a liquid Liquid evaporating to a gas Gas condensing to a liquid Liquid freezing into a solid Usually occur with a change in temperature Can also be when a substance dissolves in a liquid, but does ...
... Solid melting to a liquid Liquid evaporating to a gas Gas condensing to a liquid Liquid freezing into a solid Usually occur with a change in temperature Can also be when a substance dissolves in a liquid, but does ...
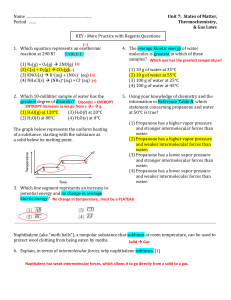
Name ………………………………………………… Unit 7: States of
... (1) Propanone has a higher vapor pressure and stronger intermolecular forces than water. (2) Propanone has a higher vapor pressure and weaker intermolecular forces than water. (3) Propanone has a lower vapor pressure and stronger intermolecular forces than water. (4) Propanone has a lower vapor pres ...
... (1) Propanone has a higher vapor pressure and stronger intermolecular forces than water. (2) Propanone has a higher vapor pressure and weaker intermolecular forces than water. (3) Propanone has a lower vapor pressure and stronger intermolecular forces than water. (4) Propanone has a lower vapor pres ...
Tall: 1) The decomposition of CaCO3 is an endothermic process:
... The reaction below has an equilibrium constant, Keq, of 171 at 25oC. Using the reaction conditions given, determine if the reaction is product-favored, reactant-favored, or at equilibrium. Don’t forget to find Molarity first! 2 NO2(g) N2O4(g) a) 2.0x10-3 mol NO2, 1.5x10-5 mol N2O4, 10.0 L flask ...
... The reaction below has an equilibrium constant, Keq, of 171 at 25oC. Using the reaction conditions given, determine if the reaction is product-favored, reactant-favored, or at equilibrium. Don’t forget to find Molarity first! 2 NO2(g) N2O4(g) a) 2.0x10-3 mol NO2, 1.5x10-5 mol N2O4, 10.0 L flask ...
13AP General Equilibrium FR worksheet (missing 1988)
... CO2(g) + H2(g) H2O(g) + CO(g) When H2(g) is mixed with CO2(g) at 2,000 K, equilibrium is achieved according to the equation above. In one experiment, the following equilibrium concentrations were measured. [H2] = 0.20 mol/L [CO2] = 0.30 mol/L [H2O] = [CO] = 0.55 mol/L (a) What is the mole fraction ...
... CO2(g) + H2(g) H2O(g) + CO(g) When H2(g) is mixed with CO2(g) at 2,000 K, equilibrium is achieved according to the equation above. In one experiment, the following equilibrium concentrations were measured. [H2] = 0.20 mol/L [CO2] = 0.30 mol/L [H2O] = [CO] = 0.55 mol/L (a) What is the mole fraction ...
Phase, Q, Curves
... _________minutes and _________ joules of energy to vaporize this substance from its liquid phase. The math formula for the slant lines at B, F, and J is ____________________? This substance is a___________ at point J. At point K the temperature may continue to rise that is one reason why steam will ...
... _________minutes and _________ joules of energy to vaporize this substance from its liquid phase. The math formula for the slant lines at B, F, and J is ____________________? This substance is a___________ at point J. At point K the temperature may continue to rise that is one reason why steam will ...
Ch. 1 Introduction: Matter and Measurement
... Decide whether the following is a mixture or a pure substance. Tomato juice Iodine crystals Sand Baking soda ...
... Decide whether the following is a mixture or a pure substance. Tomato juice Iodine crystals Sand Baking soda ...
Equilibrium - District 196
... changes occur at equal rates in a closed system Ex. A phase change can be a physical condition that can be described to be in equilibrium Solid + ∆H Liquid ...
... changes occur at equal rates in a closed system Ex. A phase change can be a physical condition that can be described to be in equilibrium Solid + ∆H Liquid ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood (Pages 735
... *7. ________________ is the ___________ of the average _________ energy (energy of _________) of the particles (_________/molecules) *a. The ________ of matter depends on the ____________ between the __________ energy (energy of ___________) and the ____________ in the bonds (latent heat _________ ...
... *7. ________________ is the ___________ of the average _________ energy (energy of _________) of the particles (_________/molecules) *a. The ________ of matter depends on the ____________ between the __________ energy (energy of ___________) and the ____________ in the bonds (latent heat _________ ...
03 nanoparticles part 7 File - e-learning
... At 380°C, the titania will shift to the anatase phase. In presence of barium nitrate, at 540-650°C, finally barium titanate is produced: The advantages of this process are purity, spherical particles and no agglomeration; disadvantages are wide PSD, the necessity of high gas flow rates to avoid aggl ...
... At 380°C, the titania will shift to the anatase phase. In presence of barium nitrate, at 540-650°C, finally barium titanate is produced: The advantages of this process are purity, spherical particles and no agglomeration; disadvantages are wide PSD, the necessity of high gas flow rates to avoid aggl ...
LATENT HEAT AND ELECTRODE POTENTIAL
... come greater than X. Such results are contrary both to experience and to the principles of thermodynamics. Theory (7) and experiment indicate that at the mp of M, the liquid and solid forms of M must have the same potential. Although this potential, or the emf, E, of a cell of which M forms one elec ...
... come greater than X. Such results are contrary both to experience and to the principles of thermodynamics. Theory (7) and experiment indicate that at the mp of M, the liquid and solid forms of M must have the same potential. Although this potential, or the emf, E, of a cell of which M forms one elec ...
7.5.9 Compare physical properties of matter to the chemical property
... oThe boiling point for pure water at sea level is 100 degrees Celsius or 212 degrees Fahrenheit ...
... oThe boiling point for pure water at sea level is 100 degrees Celsius or 212 degrees Fahrenheit ...