ChBE 11: Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
... – If the system is free from forced flows, it will eventually achieve equilibrium – The Pliq = Pvap and Tliq = Tvap with more than one phase present with no tendency to change ...
... – If the system is free from forced flows, it will eventually achieve equilibrium – The Pliq = Pvap and Tliq = Tvap with more than one phase present with no tendency to change ...
CHAPTER 1 CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS 1 CHAPTER ONE
... calculation. For addition/subtraction, the result has the same number of decimal places as the least precise number used in the calculation (not necessarily the number with the fewest significant figures). ...
... calculation. For addition/subtraction, the result has the same number of decimal places as the least precise number used in the calculation (not necessarily the number with the fewest significant figures). ...
Document
... An exothermic reaction is exothermic, no matter what the temperature is. An endothermic reaction is endothermic at all temperatures. You should think of heat as ________________for endothermic reactions and as ________________ for exothermic reactions. B. Le Châtelier's principle - add hea ...
... An exothermic reaction is exothermic, no matter what the temperature is. An endothermic reaction is endothermic at all temperatures. You should think of heat as ________________for endothermic reactions and as ________________ for exothermic reactions. B. Le Châtelier's principle - add hea ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... • The equilibrium constant (K) is the ratio of the mathematical product of the concentrations of substances formed at equilibrium to the mathematical product of the concentrations of reacting substances. Each concentration is raised to a power equal to the coefficient of that substance in the chemic ...
... • The equilibrium constant (K) is the ratio of the mathematical product of the concentrations of substances formed at equilibrium to the mathematical product of the concentrations of reacting substances. Each concentration is raised to a power equal to the coefficient of that substance in the chemic ...
2008 local exam - American Chemical Society
... on that sheet, not written in the booklet. Each student should be provided with an answer sheet and scratch paper, both of which must be turned in with the test booklet at the end of the examination. Local Sections may use an answer sheet of their own choice. The full examination consists of 60 mult ...
... on that sheet, not written in the booklet. Each student should be provided with an answer sheet and scratch paper, both of which must be turned in with the test booklet at the end of the examination. Local Sections may use an answer sheet of their own choice. The full examination consists of 60 mult ...
Chapter 1.1 –Chemistry is a Physical Science Chemistry is one of
... The building blocks of matter are atoms. An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical identity of that element. An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, stable substances and is made of only one type of atom. A compound is a substance that c ...
... The building blocks of matter are atoms. An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical identity of that element. An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, stable substances and is made of only one type of atom. A compound is a substance that c ...
KEY
... boundaries prevent the flow of matter into and out of it (they are impermeable), whereas in an open system the boundaries permit such flow. The portion of the remainder of the universe that can exchange energy and matter with the system is the surroundings. Heat, q, is the amount of kinetic energy t ...
... boundaries prevent the flow of matter into and out of it (they are impermeable), whereas in an open system the boundaries permit such flow. The portion of the remainder of the universe that can exchange energy and matter with the system is the surroundings. Heat, q, is the amount of kinetic energy t ...
chem100c1f
... • Physical change: • A change in the state of matter. It does not involve a change in the substances. E.g. melting of wax and water. • Chemical change: • A change involving at least one of the substances making the matter. E.g. Electrolysis of water, formation of rust: reaction of iron and oxygen to ...
... • Physical change: • A change in the state of matter. It does not involve a change in the substances. E.g. melting of wax and water. • Chemical change: • A change involving at least one of the substances making the matter. E.g. Electrolysis of water, formation of rust: reaction of iron and oxygen to ...
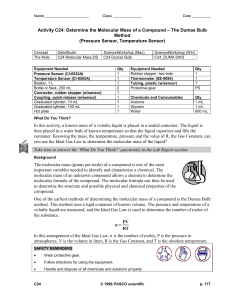
Determine the Molecular Mass of a Compound
... Take time to answer the ‘What Do You Think?’ question(s) in the Lab Report section. Background ...
... Take time to answer the ‘What Do You Think?’ question(s) in the Lab Report section. Background ...
Ductility-the ability to be stretched into wires
... Solubility- The ability to dissolve in another substance—how well the substance dissolves. (__.P) ...
... Solubility- The ability to dissolve in another substance—how well the substance dissolves. (__.P) ...
Shifting Equilibrium
... because changing the temperature changes the relative amounts of reactants and products. Increasing the temperature is, in effect, the addition of energy in the form of heat. According to Le Châtelier’s principle, the stress of the added heat will be lessened by shifting the equilibrium in the direc ...
... because changing the temperature changes the relative amounts of reactants and products. Increasing the temperature is, in effect, the addition of energy in the form of heat. According to Le Châtelier’s principle, the stress of the added heat will be lessened by shifting the equilibrium in the direc ...
chem – mixtures elements compounds for ib 1 10-10
... Give an example of a physical change that water can undergo. ...
... Give an example of a physical change that water can undergo. ...
Equilibrium 5
... 10. Arsenic can be extracted from its ores by first reacting the ore with oxygen (called Roasting) to from solid As4O6, which is then reduced using carbon: As4O6 (s) + ...
... 10. Arsenic can be extracted from its ores by first reacting the ore with oxygen (called Roasting) to from solid As4O6, which is then reduced using carbon: As4O6 (s) + ...
Cheat Sheet for Chemical Equilibrium
... values. They therefore need different concentrations of one anion for precipitation to occur. • ∆G = ∆G° + RTlnQ ‐ formula used to relate Gibbs Free Energy at standard and non‐standard ...
... values. They therefore need different concentrations of one anion for precipitation to occur. • ∆G = ∆G° + RTlnQ ‐ formula used to relate Gibbs Free Energy at standard and non‐standard ...
Chapter 1
... U = q + w = (-82) + (-622) = -704 kJ We see that the person ‘s internal energy falls by 704 kJ. 2). An electric battery is charged by supplying 250 kJ of energy to it as electrical work, but in the process it loses 25 kJ of energy as heat to the surroundings. What is the change in internal energy o ...
... U = q + w = (-82) + (-622) = -704 kJ We see that the person ‘s internal energy falls by 704 kJ. 2). An electric battery is charged by supplying 250 kJ of energy to it as electrical work, but in the process it loses 25 kJ of energy as heat to the surroundings. What is the change in internal energy o ...
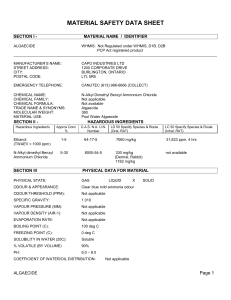
section i
... PHYSICIAN – Probable mucosal damage may contraindicate the use of gastric lavage. Measures against circulatory shock, respiratory depression and convulsion may be needed. ...
... PHYSICIAN – Probable mucosal damage may contraindicate the use of gastric lavage. Measures against circulatory shock, respiratory depression and convulsion may be needed. ...
Introduction to Chemistry
... gas, liquid, or solid Generally, as you add energy, particles move faster and farther apart As you remove energy, particles move closer and become attracted to each other ...
... gas, liquid, or solid Generally, as you add energy, particles move faster and farther apart As you remove energy, particles move closer and become attracted to each other ...
Avogadro`s Law is relation between
... 3- Given the same number of moles of two gases at STP conditions, how do the volumes of two gases compare? How do the masses of the two gas samples compare? 4- How many moles of helium are contained in each volume at STP: (a) 5.0 L; (b) 11.2 L; (c) 50.0 mL? 5- How many moles of argon are contained i ...
... 3- Given the same number of moles of two gases at STP conditions, how do the volumes of two gases compare? How do the masses of the two gas samples compare? 4- How many moles of helium are contained in each volume at STP: (a) 5.0 L; (b) 11.2 L; (c) 50.0 mL? 5- How many moles of argon are contained i ...
30 - Edgemead High School
... Draw free-body diagrams. (This is a diagram that shows the relative magnitudes and directions of forces acting on a body/particle that has been isolated from its surroundings) Resolve a two-dimensional force (such as the weight of an object on an inclined plane) into its parallel (x) and perpendicul ...
... Draw free-body diagrams. (This is a diagram that shows the relative magnitudes and directions of forces acting on a body/particle that has been isolated from its surroundings) Resolve a two-dimensional force (such as the weight of an object on an inclined plane) into its parallel (x) and perpendicul ...
Exam Review Chapter 18-Equilibrium
... c. neither a nor b b. chemical equilibrium. d. both a and b 8. According to collision theory, in order for a chemical reaction to occur, the reactant atoms must: a. make contact with each other. b. have a minimum level of kinetic energy. c. form an activated complex. d. all of the above ...
... c. neither a nor b b. chemical equilibrium. d. both a and b 8. According to collision theory, in order for a chemical reaction to occur, the reactant atoms must: a. make contact with each other. b. have a minimum level of kinetic energy. c. form an activated complex. d. all of the above ...
AS Paper 1 Practice Paper 4 - A
... The student decided to use a measuring cylinder to obtain 25.0 cm3 of the supplier’s solution. This was poured into a 250 cm3 graduated flask and the liquid level was made up to the mark with de-ionised water. The student filled a burette with the acid solution. The following results were obtained w ...
... The student decided to use a measuring cylinder to obtain 25.0 cm3 of the supplier’s solution. This was poured into a 250 cm3 graduated flask and the liquid level was made up to the mark with de-ionised water. The student filled a burette with the acid solution. The following results were obtained w ...
nomenclature review
... If 7.40g of calcium hydroxide reacts with excess nitric acid, how many grams of calcium nitrate are formed?(16.4grams) ...
... If 7.40g of calcium hydroxide reacts with excess nitric acid, how many grams of calcium nitrate are formed?(16.4grams) ...
AP Chemistry: Chapter 13 Gaseous Equilibrium Section 1: Multiple
... A rigid container holds a mixture of graphite pellets (C(s)), H2O(g), CO(g), and H2(g) at equilibrium. State whether the number of moles of CO(g) in the container will increase, decrease, or remain the same after each of the following disturbances is applied to the original mixture. For each case, a ...
... A rigid container holds a mixture of graphite pellets (C(s)), H2O(g), CO(g), and H2(g) at equilibrium. State whether the number of moles of CO(g) in the container will increase, decrease, or remain the same after each of the following disturbances is applied to the original mixture. For each case, a ...
FINAL EXAM Spring 2012
... The last page of this examination is a periodic table [Gas constant = 8.314 J/mol K; 0.08206 L*atm/mole*K,1 faraday = 96500 J/V mol e-; at 25oC] 1) The reaction has the rate law, Rate = k[A][B]2. Which will cause the rate to increase the most? A) doubling [A] B) doubling [B] C) tripling [B] D) quadr ...
... The last page of this examination is a periodic table [Gas constant = 8.314 J/mol K; 0.08206 L*atm/mole*K,1 faraday = 96500 J/V mol e-; at 25oC] 1) The reaction has the rate law, Rate = k[A][B]2. Which will cause the rate to increase the most? A) doubling [A] B) doubling [B] C) tripling [B] D) quadr ...
Thermodynamics
... From knowing the value of ∆G, you may predict whether a process/reaction will be spontaneous at a certain temperature. A process is spontaneous if ∆G is negative (∆G < 0), nonspontaneous if ∆G is positive (∆G > 0), and at equilibrium if ∆G = 0. The enthalpy change, ∆Hrxn, is the heat gained or lost ...
... From knowing the value of ∆G, you may predict whether a process/reaction will be spontaneous at a certain temperature. A process is spontaneous if ∆G is negative (∆G < 0), nonspontaneous if ∆G is positive (∆G > 0), and at equilibrium if ∆G = 0. The enthalpy change, ∆Hrxn, is the heat gained or lost ...