Heat Capacity (C)
... For this process we are interested in the amount of heat that flows from surroundings into the system. Remember, heat can be tricky. When there is no chemical change or phase change, then energy flowing into a system in the form of heat will lead to a temperature change only. However, when there is ...
... For this process we are interested in the amount of heat that flows from surroundings into the system. Remember, heat can be tricky. When there is no chemical change or phase change, then energy flowing into a system in the form of heat will lead to a temperature change only. However, when there is ...
Matter Test Review Sheet
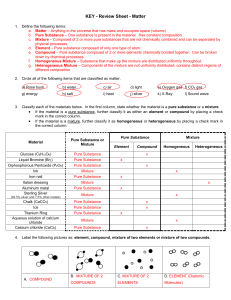
... a. Matter – Anything in the universe that has mass and occupies space (volume) b. Pure Substance – One substance is present in the material. Has constant composition. c. Mixture – Composed of 2 or more pure substances that are not chemically combined and can be separated by physical processes. d. El ...
... a. Matter – Anything in the universe that has mass and occupies space (volume) b. Pure Substance – One substance is present in the material. Has constant composition. c. Mixture – Composed of 2 or more pure substances that are not chemically combined and can be separated by physical processes. d. El ...
Paired with Lecture
... If DG is negative then there is a probability that a reaction will occur. The more negative DG becomes, the more driving force there is for the reaction Thermodynamics tells us the probability of a reaction but not the rate – the rate of a reaction is determined by Kinetics ...
... If DG is negative then there is a probability that a reaction will occur. The more negative DG becomes, the more driving force there is for the reaction Thermodynamics tells us the probability of a reaction but not the rate – the rate of a reaction is determined by Kinetics ...
Physical and Chemical Changes Worksheet
... In baking biscuits and other quick breads, the baking powder reacts to release carbon dioxide bubbles. The carbon dioxide bubbles cause the dough to rise. ...
... In baking biscuits and other quick breads, the baking powder reacts to release carbon dioxide bubbles. The carbon dioxide bubbles cause the dough to rise. ...
ΔG - Lemon Bay High School
... Plan We need to think about whether each process is consistent with our experience about the natural direction of events or whether we expect the reverse process to occur. Solve (a) This process is spontaneous. Whenever two objects at different temperatures are brought into contact, heat is transfer ...
... Plan We need to think about whether each process is consistent with our experience about the natural direction of events or whether we expect the reverse process to occur. Solve (a) This process is spontaneous. Whenever two objects at different temperatures are brought into contact, heat is transfer ...
Slide 1
... Plan We need to think about whether each process is consistent with our experience about the natural direction of events or whether we expect the reverse process to occur. Solve (a) This process is spontaneous. Whenever two objects at different temperatures are brought into contact, heat is transfer ...
... Plan We need to think about whether each process is consistent with our experience about the natural direction of events or whether we expect the reverse process to occur. Solve (a) This process is spontaneous. Whenever two objects at different temperatures are brought into contact, heat is transfer ...
KINETICS AND EQUILIBRIUM
... 1. In general for a closed system there will exist an equilibrium between phases where the rate of escape (from the phase) = the rate of return (to that phase) 2. Equilibrium existing between a solid and liquid phase at a substances melting point. At the melting point the rate at which a solid melts ...
... 1. In general for a closed system there will exist an equilibrium between phases where the rate of escape (from the phase) = the rate of return (to that phase) 2. Equilibrium existing between a solid and liquid phase at a substances melting point. At the melting point the rate at which a solid melts ...
_______1. solution a. capable of being dissolved _______2. solute
... If the temperature is decreased on the above system, which reaction increases, (forward / reverse)? There will be (more / less) SO3. 101. 2CO2 + heat 2 CO + O2 If the temperature is decreased on the above system, which reaction is increased? (forward / reverse) There will be (more / less) CO2. The ...
... If the temperature is decreased on the above system, which reaction increases, (forward / reverse)? There will be (more / less) SO3. 101. 2CO2 + heat 2 CO + O2 If the temperature is decreased on the above system, which reaction is increased? (forward / reverse) There will be (more / less) CO2. The ...
Paper - Edexcel
... A The student used a higher temperature than in the other experiments. B The student used less copper(II) carbonate than in the other experiments. C The student heated the crucible without a lid on. D The student used a spirit burner instead of a Bunsen burner. (d) In another experiment, the student ...
... A The student used a higher temperature than in the other experiments. B The student used less copper(II) carbonate than in the other experiments. C The student heated the crucible without a lid on. D The student used a spirit burner instead of a Bunsen burner. (d) In another experiment, the student ...
Document
... because it is done by the system. (c) The work done by the gas represents energy leaving the system. If this were the only energy exchange between the system and its surroundings, the internal energy of the system would decrease, and so would the temperature. However, because the temperature remains ...
... because it is done by the system. (c) The work done by the gas represents energy leaving the system. If this were the only energy exchange between the system and its surroundings, the internal energy of the system would decrease, and so would the temperature. However, because the temperature remains ...
Lecture 7. Fundamentals of atmospheric chemistry: Part 2 1
... These terms are sometimes confusing since the reduction process involves adding an electron. Keep in mind it's the charge that's being reduced in this case. Oxidation receives its name because almost all reactions with oxygen involve some other element losing electrons to the oxygen. Only fluorine w ...
... These terms are sometimes confusing since the reduction process involves adding an electron. Keep in mind it's the charge that's being reduced in this case. Oxidation receives its name because almost all reactions with oxygen involve some other element losing electrons to the oxygen. Only fluorine w ...
Class: 11 Subject: Chemistry Topic: Equilibrium No. of
... 16. The equilibrium N2 + O2 ƒ 2NO is established in a reaction vessel of 2.5 litres capacity. The amounts of nitrogen and oxygen taken at the start were 2 moles and 4 moles respectively. Half a mole of nitrogen has been used up a equilibrium. The molar concentration of nitric oxide is A. 0.2 B. 0.4 ...
... 16. The equilibrium N2 + O2 ƒ 2NO is established in a reaction vessel of 2.5 litres capacity. The amounts of nitrogen and oxygen taken at the start were 2 moles and 4 moles respectively. Half a mole of nitrogen has been used up a equilibrium. The molar concentration of nitric oxide is A. 0.2 B. 0.4 ...
Chapter 17 lecture notes on Chemical Equilibria
... stress by moving away from it. We apply the same notion to chemical equilibria. In a system at equilibrium, when a change occurs a stress is imposed on the system. The system then responds by adopting new equilibrium conditions that relieve the stress. This is the definition of LeChatlier’s Principl ...
... stress by moving away from it. We apply the same notion to chemical equilibria. In a system at equilibrium, when a change occurs a stress is imposed on the system. The system then responds by adopting new equilibrium conditions that relieve the stress. This is the definition of LeChatlier’s Principl ...
Chemical Dynamics, Thermochemistry, and Quantum Chemistry
... Plot the temperature versus time data on a full scale graph. Draw straight lines (not necessarily flat) through both the initial and final temperature baselines. These need not be parallel to one another or have zero slope. ...
... Plot the temperature versus time data on a full scale graph. Draw straight lines (not necessarily flat) through both the initial and final temperature baselines. These need not be parallel to one another or have zero slope. ...
AP Chem Chapter 16 Review Packet
... will be spontaneous at high temperatures. c. will be spontaneous at low temperatures. d. will not be spontaneous at any temperature. e. will never happen. (ΔS is +, because there are more possible positions in the products than in the reactants.) (ΔH is + because it will require added energy to brea ...
... will be spontaneous at high temperatures. c. will be spontaneous at low temperatures. d. will not be spontaneous at any temperature. e. will never happen. (ΔS is +, because there are more possible positions in the products than in the reactants.) (ΔH is + because it will require added energy to brea ...
Slide 1
... 19.6 Free Energy and Temperature Although, we calculated G at 25°C using Gfo values, we often encounter reaction occurring at other than standard temperature conditions. How do we handle this? How T affects the sign of G? • There are two parts to the free energy equation: H— the enthalpy ter ...
... 19.6 Free Energy and Temperature Although, we calculated G at 25°C using Gfo values, we often encounter reaction occurring at other than standard temperature conditions. How do we handle this? How T affects the sign of G? • There are two parts to the free energy equation: H— the enthalpy ter ...
printable version
... stopped, in fact the products are still being made and used up-but at the same speed (rate). • Equilibrium is symbolized by the use of a double arrow ( ) or an equals sign (=) ...
... stopped, in fact the products are still being made and used up-but at the same speed (rate). • Equilibrium is symbolized by the use of a double arrow ( ) or an equals sign (=) ...
Advanced Placement Chemistry
... 43. A sample of 61.8 g of H3BO3, a weak acid is dissolvedin 1,000 g of water to make a 1.0molal solution. Which of the following would be the best procedure to determine to molarity of the solution? (Assume no additional information is available.) (A) Titration of the solution with standard acid (B) ...
... 43. A sample of 61.8 g of H3BO3, a weak acid is dissolvedin 1,000 g of water to make a 1.0molal solution. Which of the following would be the best procedure to determine to molarity of the solution? (Assume no additional information is available.) (A) Titration of the solution with standard acid (B) ...
MASS-INDEPENDENT ISOTOPE FRACTIONATION OF CHROMIUM
... in a chemical exchange system [2]. Since then, researchers have applied the new Bigeleisen theory to explain other unusual isotope effects (see, e.g. [3] and references therein). How such mass independent isotopic fractionation would affect interpretations of isotopic anomalies observed in the primi ...
... in a chemical exchange system [2]. Since then, researchers have applied the new Bigeleisen theory to explain other unusual isotope effects (see, e.g. [3] and references therein). How such mass independent isotopic fractionation would affect interpretations of isotopic anomalies observed in the primi ...
Internal energy
... The enthalpy change depends on pressure, temperature and also on the physical state of the reactants and products (s-solid, l-liquid, g-gas). Data corresponding to the standard state (p=100 kPa at constant temperature T=298 K), are published, e.g., by the National Institute of Standards and Technolo ...
... The enthalpy change depends on pressure, temperature and also on the physical state of the reactants and products (s-solid, l-liquid, g-gas). Data corresponding to the standard state (p=100 kPa at constant temperature T=298 K), are published, e.g., by the National Institute of Standards and Technolo ...
Question 1 - JustAnswer
... Which of the following statements is true? Answer If the reaction mixture initially contains only OF2(g), then the total pressure at equilibrium will be less than the total initial pressure. If the reaction mixture initially contains only O2(g) and F2(g), then at equilibrium, the reaction mixture wi ...
... Which of the following statements is true? Answer If the reaction mixture initially contains only OF2(g), then the total pressure at equilibrium will be less than the total initial pressure. If the reaction mixture initially contains only O2(g) and F2(g), then at equilibrium, the reaction mixture wi ...
Test - Angelfire
... with a QWERTY keyboard, and electronic writing pads will not be allowed. Students must not bring any external support devices such as manuals, printed or electronic cards, printers, memory expansion chips, or external keyboards. Students may have more than one calculator available during the examina ...
... with a QWERTY keyboard, and electronic writing pads will not be allowed. Students must not bring any external support devices such as manuals, printed or electronic cards, printers, memory expansion chips, or external keyboards. Students may have more than one calculator available during the examina ...
Document
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in M. In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M or in atm. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium ...
... 1. The concentrations of the reacting species in the condensed phase are expressed in M. In the gaseous phase, the concentrations can be expressed in M or in atm. 2. The concentrations of pure solids, pure liquids and solvents do not appear in the equilibrium constant expressions. 3. The equilibrium ...
Practice Test: Equilibrium
... 5. Do products or reactants dominate in this equilibrium? ____________________ 6. If the system is at equilibrium and 5.0 moles of chlorine are added, what will be the new Keq? ______ 7. If the system is at equilibrium and the container is doubled in size, what will be the new Keq? ______ 8. What wi ...
... 5. Do products or reactants dominate in this equilibrium? ____________________ 6. If the system is at equilibrium and 5.0 moles of chlorine are added, what will be the new Keq? ______ 7. If the system is at equilibrium and the container is doubled in size, what will be the new Keq? ______ 8. What wi ...