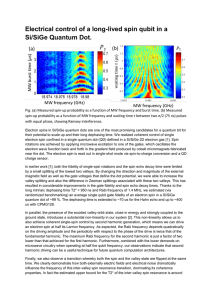
Hamiltonian of the quantum and classical Ising model with skew
... spin S matrices, with norm ||S|| The chain has N spatial sites and satisfies periodic spatial boundary conditions. The coupling strength J between first-neighbor z-components of spin can either be positive (antiferromagnetic case) or negative (ferromagnetic case). Due to the rotational symmetry of t ...
... spin S matrices, with norm ||S|| The chain has N spatial sites and satisfies periodic spatial boundary conditions. The coupling strength J between first-neighbor z-components of spin can either be positive (antiferromagnetic case) or negative (ferromagnetic case). Due to the rotational symmetry of t ...
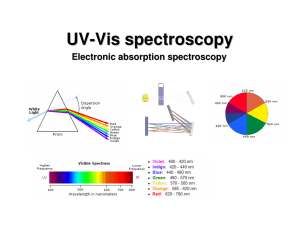
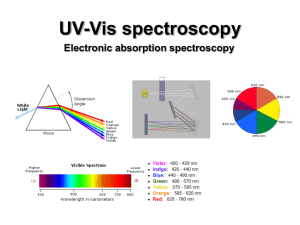
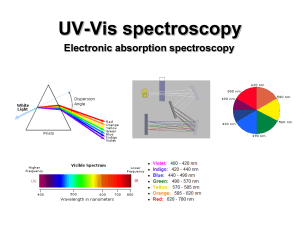
UV-Vis (electronic) spectroscopy
... Since the nuclei do not move during the excitation, the internuclear distances remain constant and “the most probable component of an electronic transition involves only the vertical transitions”. ...
... Since the nuclei do not move during the excitation, the internuclear distances remain constant and “the most probable component of an electronic transition involves only the vertical transitions”. ...
[30 pts] While the spins of the two electrons in a hydrog
... b) List the possible combinations of quantum numbers (ms1 , ms2 ). c) What is the degeracy of the ground state? d) The degeneracy of the ground state is broken into a single and triplet of states by magnetic ~ = ~s1 +~s2 coupling of s1 and s2 . List the possible quantum numbers (s, ms ) of the total ...
... b) List the possible combinations of quantum numbers (ms1 , ms2 ). c) What is the degeracy of the ground state? d) The degeneracy of the ground state is broken into a single and triplet of states by magnetic ~ = ~s1 +~s2 coupling of s1 and s2 . List the possible quantum numbers (s, ms ) of the total ...
Problem set VI Problem 6.1 Problem 6.2 Problem 6.3 Problem 6.4
... a) The first measurement accepts sz = h̄/2 atoms and rejects sz = −h̄/2 atoms. b) The second measurement accepts sn = h̄/2 atoms and rejects sn = −h̄/2 atoms, where sn is the eigenvalue of the operator S · n̂, with n̂ making an angle β in the xz-plane with respect to the z-axis. c) The third measure ...
... a) The first measurement accepts sz = h̄/2 atoms and rejects sz = −h̄/2 atoms. b) The second measurement accepts sn = h̄/2 atoms and rejects sn = −h̄/2 atoms, where sn is the eigenvalue of the operator S · n̂, with n̂ making an angle β in the xz-plane with respect to the z-axis. c) The third measure ...
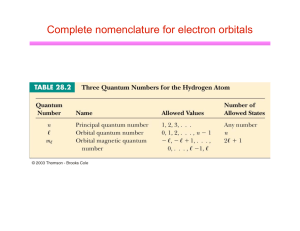
Complete nomenclature for electron orbitals
... What happens? Some of the electrons can accelerate and gain energy. This is possible because the conduction band is close in energy to the valence band and there are empty energy states to jump into. This can’t happen with insulators where there is too large of an energy gap between. ...
... What happens? Some of the electrons can accelerate and gain energy. This is possible because the conduction band is close in energy to the valence band and there are empty energy states to jump into. This can’t happen with insulators where there is too large of an energy gap between. ...
Searching for the Field-Induced Non-Magnetic Phase - ICAM
... In the strongly correlated electron systems, quantum phase transition realized at ~ 0 K can be induced by magnetic field, pressure or chemical substitution. In the vicinity of the transition point between magnetic ordered phases and paramagnetic phase, quantum critical behavior like non-Fermi liquid ...
... In the strongly correlated electron systems, quantum phase transition realized at ~ 0 K can be induced by magnetic field, pressure or chemical substitution. In the vicinity of the transition point between magnetic ordered phases and paramagnetic phase, quantum critical behavior like non-Fermi liquid ...
Temperature and sample dependence of spin echo in SiC
... Towards table (schematic rotated from photo) ...
... Towards table (schematic rotated from photo) ...
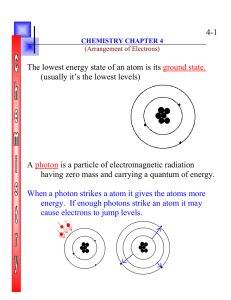
4-1 The lowest energy state of an atom is its ground state. (usually
... Rules for assigning students to dorm rooms: 1. Maximum of two students in any one room 2. There are no elevators->students must be as close to the 1st floor as possible 3. When filling a type of room, all rooms must be full before going onto a different type of room. 4. When filling rooms on a floor ...
... Rules for assigning students to dorm rooms: 1. Maximum of two students in any one room 2. There are no elevators->students must be as close to the 1st floor as possible 3. When filling a type of room, all rooms must be full before going onto a different type of room. 4. When filling rooms on a floor ...
Aufbau Diagram Directions
... Pauli Exclusion: an atomic orbital may describe at most 2 electrons (each electron will have a different spin) Hund’s Rule: When electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbital until all the orbitas contain one electron, then a second electron is added to each orbital. Ho ...
... Pauli Exclusion: an atomic orbital may describe at most 2 electrons (each electron will have a different spin) Hund’s Rule: When electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbital until all the orbitas contain one electron, then a second electron is added to each orbital. Ho ...
Nitrogen-vacancy center

The nitrogen-vacancy center (N-V center) is one of numerous point defects in diamond. Its most explored and useful property is photoluminescence, which can be easily detected from an individual N-V center, especially those in the negative charge state (N-V−). Electron spins at N-V centers, localized at atomic scales, can be manipulated at room temperature by applying a magnetic field, electric field, microwave radiation or light, or a combination, resulting in sharp resonances in the intensity and wavelength of the photoluminescence. These resonances can be explained in terms of electron spin related phenomena such as quantum entanglement, spin-orbit interaction and Rabi oscillations, and analysed using advanced quantum optics theory. An individual N-V center can be viewed as a basic unit of a quantum computer, and it has potential applications in novel, more efficient fields of electronics and computational science including quantum cryptography and spintronics.
![[30 pts] While the spins of the two electrons in a hydrog](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002487557_1-ac2bceae20801496c3356a8afebed991-300x300.png)