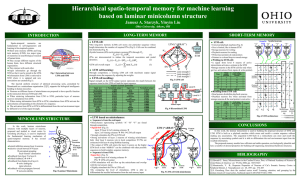
Simulating in vivo-like Synaptic Input Patterns in Multicompartmental
... synchan element called AMPA is shown below. The synchan object also allows the user to set a frequency of activation, but we don’t use this mechanism, so the frequency field of all of our synchan elements is set to 0. We begin by making a single, template synchan element and placing it into a neutra ...
... synchan element called AMPA is shown below. The synchan object also allows the user to set a frequency of activation, but we don’t use this mechanism, so the frequency field of all of our synchan elements is set to 0. We begin by making a single, template synchan element and placing it into a neutra ...
Running Improves Pattern Separation during Novel Object
... Physical exercise was reported to increase hippocampal stem cell proliferation and adult neurogenesis [15]. As a consequence hippocampus-dependent learning and memory formation is improved by voluntary wheel running in mice [16, 17]. In particular, pattern separation in a touch screen task was shown ...
... Physical exercise was reported to increase hippocampal stem cell proliferation and adult neurogenesis [15]. As a consequence hippocampus-dependent learning and memory formation is improved by voluntary wheel running in mice [16, 17]. In particular, pattern separation in a touch screen task was shown ...
Neural changes underlying the development of
... To our knowledge, only a handful of published studies have examined the relationship between hippocampal volume and episodic memory in typically developing children (e.g., Østby et al., 2011; Sowell et al., 2001; Yurgelun-Todd et al., 2003). In immediate memory tasks, several studies reported weakly ...
... To our knowledge, only a handful of published studies have examined the relationship between hippocampal volume and episodic memory in typically developing children (e.g., Østby et al., 2011; Sowell et al., 2001; Yurgelun-Todd et al., 2003). In immediate memory tasks, several studies reported weakly ...
Synaptic and extrasynaptic traces of long-term memory
... 30,000 excitatory synapses (Megías et al., 2001); in the mouse cerebral cortex, the corresponding number is 8000 (Braitenberg and Schüz, 1998). The continual shower of spikes arriving to all these synapses differs in an essential way from the input streams to gates in a digital computer, which are ...
... 30,000 excitatory synapses (Megías et al., 2001); in the mouse cerebral cortex, the corresponding number is 8000 (Braitenberg and Schüz, 1998). The continual shower of spikes arriving to all these synapses differs in an essential way from the input streams to gates in a digital computer, which are ...
to get the file
... Encoding concerns perceiving, recognizing, and further processing an object so that it can be later remembered. Storage refers to transferring information from short-term memory to long-term memory. Retrieval concerns searching long-term memory and finding the event that has been stored and retrieve ...
... Encoding concerns perceiving, recognizing, and further processing an object so that it can be later remembered. Storage refers to transferring information from short-term memory to long-term memory. Retrieval concerns searching long-term memory and finding the event that has been stored and retrieve ...
Spike-Timing Theory of Working Memory
... the other synapses in the network (Figure 4A, ‘‘short-term synaptic change’’ curves). Upon termination of the stimulation, the temporarily facilitated intra-PNG synapses and the noisy synaptic inputs resulted in sporadic reactivations of different segments of the target PNG, often leading to the rea ...
... the other synapses in the network (Figure 4A, ‘‘short-term synaptic change’’ curves). Upon termination of the stimulation, the temporarily facilitated intra-PNG synapses and the noisy synaptic inputs resulted in sporadic reactivations of different segments of the target PNG, often leading to the rea ...
Action Potential Riddle Quiz
... Please take out 1 piece of notebook paper & label it “Action Potential Riddle Quiz”. Write your NAME, DATE & PERIOD in the top right! For the 10 questions of the quiz, you will see screens for 30 secs. with “riddles” about Action Potentials. Write JUST THE ANSWER to the riddle next to the number (do ...
... Please take out 1 piece of notebook paper & label it “Action Potential Riddle Quiz”. Write your NAME, DATE & PERIOD in the top right! For the 10 questions of the quiz, you will see screens for 30 secs. with “riddles” about Action Potentials. Write JUST THE ANSWER to the riddle next to the number (do ...
The Role of Working Memory in Reading Disability
... Shankweiler, Liberman, Fowler, & Fischer, 1977; because in the nonrhyming case the internal ...
... Shankweiler, Liberman, Fowler, & Fischer, 1977; because in the nonrhyming case the internal ...
Building silicon nervous systems with dendritic tree neuromorphs
... PSPs at the soma. However, the utility of the dendritic tree as a spike processor mainly derives from the fundamental non−linearity alluded to in the last section. Because synaptic activation opens a conductance to a voltage source, the charge flowing into the compartment is proportional to the diff ...
... PSPs at the soma. However, the utility of the dendritic tree as a spike processor mainly derives from the fundamental non−linearity alluded to in the last section. Because synaptic activation opens a conductance to a voltage source, the charge flowing into the compartment is proportional to the diff ...
Scaling self-organizing maps to model large cortical networks
... The scaling equations and GLISSOM are based on the RFLISSOM (Receptive-Field Laterally Interconnected Synergetically Self-Organizing Map) computational model of cortical maps. RF-LISSOM has been successfully used to model the development of ocular dominance and orientation maps, as well as low-level ...
... The scaling equations and GLISSOM are based on the RFLISSOM (Receptive-Field Laterally Interconnected Synergetically Self-Organizing Map) computational model of cortical maps. RF-LISSOM has been successfully used to model the development of ocular dominance and orientation maps, as well as low-level ...
From/To LTM - Ohio University
... •Storage neurons in the STM cell fire only when get two activations (from inputs & write pointer) ...
... •Storage neurons in the STM cell fire only when get two activations (from inputs & write pointer) ...
Artificial Intelligence
... through the process of introducing variations into successive generations and selectively eliminating less fit individuals, adaptations of increasing capability and diversity emerge in a population evolution and emergence occur in populations of embodied individuals, whose actions affect others and ...
... through the process of introducing variations into successive generations and selectively eliminating less fit individuals, adaptations of increasing capability and diversity emerge in a population evolution and emergence occur in populations of embodied individuals, whose actions affect others and ...
Document
... through the process of introducing variations into successive generations and selectively eliminating less fit individuals, adaptations of increasing capability and diversity emerge in a population evolution and emergence occur in populations of embodied individuals, whose actions affect others and ...
... through the process of introducing variations into successive generations and selectively eliminating less fit individuals, adaptations of increasing capability and diversity emerge in a population evolution and emergence occur in populations of embodied individuals, whose actions affect others and ...
Simulation of myelinated neuron with focus on conduction speed
... because we didn’t find a whole set of parameters for a soma with the same membrane dynamics working at the same temperature as the axon in [1]. For the dendrites we used passive mechanism implemented in NEURON and set the reversal potential Epas to be -80mV, which was the same as the rest potential ...
... because we didn’t find a whole set of parameters for a soma with the same membrane dynamics working at the same temperature as the axon in [1]. For the dendrites we used passive mechanism implemented in NEURON and set the reversal potential Epas to be -80mV, which was the same as the rest potential ...
Methods for reducing interference in the Complementary Learning
... learning tunes a subset of the hidden units to respond more strongly to that stimulus. As these units respond more and more strongly to the stimulus, they start to inhibit other units. Thus, the neural response to a stimulus transitions from a diffuse overall response (where no units are tuned to re ...
... learning tunes a subset of the hidden units to respond more strongly to that stimulus. As these units respond more and more strongly to the stimulus, they start to inhibit other units. Thus, the neural response to a stimulus transitions from a diffuse overall response (where no units are tuned to re ...
BCM Theory
... background input from MFs. This disconnection of the CFs removed any variability in PCs, such as the complex spikes, making it possible to lump the activity of the PC population together. We also verified the equivalence of the two models by following the trajectory of the PC population output and ...
... background input from MFs. This disconnection of the CFs removed any variability in PCs, such as the complex spikes, making it possible to lump the activity of the PC population together. We also verified the equivalence of the two models by following the trajectory of the PC population output and ...
to receive a reprint - Institute for Learning and Brain Sciences
... component linguistic processes in parallel while storing intermediate representations. Thus, indices of verbal working memory capacity such as the Reading Span Test (Daneman and Carpenter 1980) that measure the ability to simultaneously process sentences and maintain information in memory correlate ...
... component linguistic processes in parallel while storing intermediate representations. Thus, indices of verbal working memory capacity such as the Reading Span Test (Daneman and Carpenter 1980) that measure the ability to simultaneously process sentences and maintain information in memory correlate ...
in search of memory traces
... for the storage of memories (see Shors & Matzel 1997, Wilson & Tonegawa ...
... for the storage of memories (see Shors & Matzel 1997, Wilson & Tonegawa ...
Habituation, sensitization and Pavlovian conditioning
... of events as the animal moves and/or the environment changes. For example, one can smell an apple before/without tasting it, but not vice versa. In general, biologically important objects (e.g., food, predators, aggressive opponents, potential mates, sharp objects) are detectable via distal cues (i. ...
... of events as the animal moves and/or the environment changes. For example, one can smell an apple before/without tasting it, but not vice versa. In general, biologically important objects (e.g., food, predators, aggressive opponents, potential mates, sharp objects) are detectable via distal cues (i. ...
The Bifurcating Neuron Network 1q
... reproduce the actual behavior of a neuron as closely as possible. Choosing a model neuron of the proper complexity is not an easy task because the nature of the approximation implied by a certain model is often unclear until the model is tested in a network. An obvious minimum requirement would be t ...
... reproduce the actual behavior of a neuron as closely as possible. Choosing a model neuron of the proper complexity is not an easy task because the nature of the approximation implied by a certain model is often unclear until the model is tested in a network. An obvious minimum requirement would be t ...
Nervous System - Neuron and Nerve Impulse PowerPoint
... – Dendrites receive impulses from other neurons and carry impulses to the cell body. ...
... – Dendrites receive impulses from other neurons and carry impulses to the cell body. ...
PDF - Oxford Academic - Oxford University Press
... cooperativity factor which was used to fit the model with physiological data (see below), and was set to one for all the model simulations. D is bounded below at Dmin, which determines the maximum disinhibition and biophysically corresponds to the maximum number of synapses that are cannabinoid sensi ...
... cooperativity factor which was used to fit the model with physiological data (see below), and was set to one for all the model simulations. D is bounded below at Dmin, which determines the maximum disinhibition and biophysically corresponds to the maximum number of synapses that are cannabinoid sensi ...
Selective cognitive dysfunction in acetylcholine M
... M1–/– mice performed normally on the training phase, but were severely impaired on the working memory phase. The mice also tended to be impaired at the 2-min delay (data not plotted). (b) Social discrimination memory was assessed by exposing mutant or WT male mice to ovarectomized female mice and as ...
... M1–/– mice performed normally on the training phase, but were severely impaired on the working memory phase. The mice also tended to be impaired at the 2-min delay (data not plotted). (b) Social discrimination memory was assessed by exposing mutant or WT male mice to ovarectomized female mice and as ...
The Molecular Biology of Memory Storage: A Dialog
... learning more about the biology of the brain, and became interested in knowing how learning produces changes in the neural networks of the brain and how a transient short-term memory is converted to an enduring long-term memory. From the beginning, my purpose in translating questions about the psych ...
... learning more about the biology of the brain, and became interested in knowing how learning produces changes in the neural networks of the brain and how a transient short-term memory is converted to an enduring long-term memory. From the beginning, my purpose in translating questions about the psych ...
Eichenbaum et al., 2012a, #15 - Fortin Lab @ UCI
... A major challenge in the development of an animal model of episodic memory concerns the question of whether animals have this capacity and how to measure it. In humans, episodic memory is readily observed in the verbal recall of specific experiences, but this approach is obviously not possible in an ...
... A major challenge in the development of an animal model of episodic memory concerns the question of whether animals have this capacity and how to measure it. In humans, episodic memory is readily observed in the verbal recall of specific experiences, but this approach is obviously not possible in an ...