Slides - Professor Laura Ruetsche
... quantized has only finitely many degrees of freedom, fails to apply to these quantizations. So When we apply the quantization recipe to a classical field theory, we can obtain unitarily inequivalent representations of the CCRs encapsulating its quantization. Each purports to be the QFT that quantize ...
... quantized has only finitely many degrees of freedom, fails to apply to these quantizations. So When we apply the quantization recipe to a classical field theory, we can obtain unitarily inequivalent representations of the CCRs encapsulating its quantization. Each purports to be the QFT that quantize ...
Glasgow2004
... The main application of MUBs pertains to secure quantum key exchange (quantum cryptography). This is because any attempt by an eavesdropper (say Eve) to distinguish between two nonorthogonal quantum states shared by two remote parties (say Alice and Bob) will occur at the price of introducing a dist ...
... The main application of MUBs pertains to secure quantum key exchange (quantum cryptography). This is because any attempt by an eavesdropper (say Eve) to distinguish between two nonorthogonal quantum states shared by two remote parties (say Alice and Bob) will occur at the price of introducing a dist ...
Hamiltonian of the quantum and classical Ising model with skew
... spin S matrices, with norm ||S|| The chain has N spatial sites and satisfies periodic spatial boundary conditions. The coupling strength J between first-neighbor z-components of spin can either be positive (antiferromagnetic case) or negative (ferromagnetic case). Due to the rotational symmetry of t ...
... spin S matrices, with norm ||S|| The chain has N spatial sites and satisfies periodic spatial boundary conditions. The coupling strength J between first-neighbor z-components of spin can either be positive (antiferromagnetic case) or negative (ferromagnetic case). Due to the rotational symmetry of t ...
Nick-Evans
... After renormalization (trust us) this leads to a negative shift in the mass spectrum… ...
... After renormalization (trust us) this leads to a negative shift in the mass spectrum… ...
Entanglement and Distinguishability of Quantum States
... Entanglement is an algebraic property of quantum states. Its physical interpretation is typically related to non-locality. In our talk we will show that entanglement is physically related also with the concept of distinguishability of quantum states. Lets consider two systems differing by a unitary ...
... Entanglement is an algebraic property of quantum states. Its physical interpretation is typically related to non-locality. In our talk we will show that entanglement is physically related also with the concept of distinguishability of quantum states. Lets consider two systems differing by a unitary ...
Essentials of Particle Physics
... Understanding more theoretically •Just as the equation x2=4 can have two possible solutions (x=2 OR x=-2), so Dirac's equation could have two solutions, one for an electron with positive energy, and one for an electron with negative energy. •Dirac interpreted this to mean that for every particle th ...
... Understanding more theoretically •Just as the equation x2=4 can have two possible solutions (x=2 OR x=-2), so Dirac's equation could have two solutions, one for an electron with positive energy, and one for an electron with negative energy. •Dirac interpreted this to mean that for every particle th ...
KS-DFT formalism
... independent particle wave functions. The degree to which this limitation has invaded our thinking is marked by our constant use of concepts which have meaning only in terms of independent particle wave functions: shell structure, the occupation number, the Fermi sea and the Fermi surface, the repres ...
... independent particle wave functions. The degree to which this limitation has invaded our thinking is marked by our constant use of concepts which have meaning only in terms of independent particle wave functions: shell structure, the occupation number, the Fermi sea and the Fermi surface, the repres ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint - INAF - OA
... (This is non true when p=p(T,Θ) , that’s to say: when pressure is not only function of the temperature.This is what happens for example during phase transition at a temperature different from the critical one) ...
... (This is non true when p=p(T,Θ) , that’s to say: when pressure is not only function of the temperature.This is what happens for example during phase transition at a temperature different from the critical one) ...
Slide 1
... oWhen an e- occupies an orbit greater than the lowest possible energy level it is said to be in an “excited state” oΔE=-Rhc(1/nf2 - 1/ni2) Rhc=1312 kJ/mol Wave/particle duality oTaken from idea that light, usually considered to exhibit wave properties, actually consists of particles (photons) oSim ...
... oWhen an e- occupies an orbit greater than the lowest possible energy level it is said to be in an “excited state” oΔE=-Rhc(1/nf2 - 1/ni2) Rhc=1312 kJ/mol Wave/particle duality oTaken from idea that light, usually considered to exhibit wave properties, actually consists of particles (photons) oSim ...
The Differential Geometry and Physical Basis for the Application of
... turned from trying to unify electromagnetism and gravity to introducing as a phase factor an exponential in which the phase α is preceded by the imaginary unit i, e.g., e+iqα(x), in the wave function for the wave equations (for instance, the Dirac equation is (iγμ∂μ −m)ψ = 0). It is here that Weyl c ...
... turned from trying to unify electromagnetism and gravity to introducing as a phase factor an exponential in which the phase α is preceded by the imaginary unit i, e.g., e+iqα(x), in the wave function for the wave equations (for instance, the Dirac equation is (iγμ∂μ −m)ψ = 0). It is here that Weyl c ...
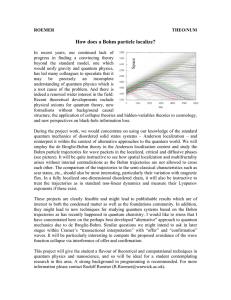
How does a Bohm particle localize?
... employ the de Broglie-Bohm theory in the Anderson localization context and study the Bohm particle trajectories for wave packets in the localized, critical and diffusive phases (see picture). It will be quite instructive to see how spatial localization and multifractality arises without internal con ...
... employ the de Broglie-Bohm theory in the Anderson localization context and study the Bohm particle trajectories for wave packets in the localized, critical and diffusive phases (see picture). It will be quite instructive to see how spatial localization and multifractality arises without internal con ...
Document
... De’Broglie, Schroedinger and Heisenberg De’Broglie relates particle and wave =h/p - provides a description for Bohr’s atomic model Schroedinger’s equation of matter wave - wave functions encapsulate probability…success ...
... De’Broglie, Schroedinger and Heisenberg De’Broglie relates particle and wave =h/p - provides a description for Bohr’s atomic model Schroedinger’s equation of matter wave - wave functions encapsulate probability…success ...