Holography, de Sitter space and SUSY breaking
... Holographic cosmology implies future of normal region is dS with c.c. determined by number of quantum states in initial defect (TB, Fischler) Will outline (incomplete) quantum theory of eternal dS space, which describes asymptotic state of our universe (cf. Poincare invariant string theory of partic ...
... Holographic cosmology implies future of normal region is dS with c.c. determined by number of quantum states in initial defect (TB, Fischler) Will outline (incomplete) quantum theory of eternal dS space, which describes asymptotic state of our universe (cf. Poincare invariant string theory of partic ...
Abstracts of the talks
... Given a surface S with a collection of special points on the boundary modulo isotopy, and a split reductive group G, we define a moduli space M (G, S) of G-local systems on S with some special data at the special points. We introduce a function W on M (G, S), the potential. It determines a set of W ...
... Given a surface S with a collection of special points on the boundary modulo isotopy, and a split reductive group G, we define a moduli space M (G, S) of G-local systems on S with some special data at the special points. We introduce a function W on M (G, S), the potential. It determines a set of W ...
Elements of a Physics Case for HE LHC
... Tevatron 95% exclusion 160 GeV < mh < 170 GeV Experiment Summary: 115 GeV < mh < 160 GeV or 170 GeV < mh < 180 GeV In other words, Higgs boson (or equivalent dynamics) is likely to be LIGHT and PERTURBATIVE electroweak interactions are expected. ...
... Tevatron 95% exclusion 160 GeV < mh < 170 GeV Experiment Summary: 115 GeV < mh < 160 GeV or 170 GeV < mh < 180 GeV In other words, Higgs boson (or equivalent dynamics) is likely to be LIGHT and PERTURBATIVE electroweak interactions are expected. ...
Link between the hierarchy of fractional quantum Hall states and
... Link between the hierarchy of fractional quantum Hall states and Haldane’s conjecture for quantum spin chains Masaaki Nakamura Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo 152-8551, Japan ...
... Link between the hierarchy of fractional quantum Hall states and Haldane’s conjecture for quantum spin chains Masaaki Nakamura Department of Physics, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo 152-8551, Japan ...
HWU4-21 QUESTION: The principal quantum number, n, describes
... The principal quantum number, n, describes the energy level of a particular orbital as a function of the distance from the center of the nucleus. Additional quantum numbers exist to quantify the other characteristics of the electron. The angular momentum quantum number (ℓ), the magnetic quantum numb ...
... The principal quantum number, n, describes the energy level of a particular orbital as a function of the distance from the center of the nucleus. Additional quantum numbers exist to quantify the other characteristics of the electron. The angular momentum quantum number (ℓ), the magnetic quantum numb ...
New Frontiers in Particle Physics.
... The Higgs Boson That’s almost the whole story…. But the gauge symmetries of the Standard Model do not permit particles to carry mass! Q. How is mass generated? A. By the non-trivial action of the vacuum! It grabs hold of things! ...
... The Higgs Boson That’s almost the whole story…. But the gauge symmetries of the Standard Model do not permit particles to carry mass! Q. How is mass generated? A. By the non-trivial action of the vacuum! It grabs hold of things! ...
PHYS6510/4510 Quantum Mechanics I Fall 2012 HW #5
... c. Calculate ∆S/h̄ for a particle which moves 1 mm in 1 ms for two cases. The particle is a nanoparticle made up of 100 carbon atoms in one case. The other case is an electron. For which of these would you consider the motion “quantum mechanical” and why? (2) Modern Quantum Mechanics, Problem 2.28. ...
... c. Calculate ∆S/h̄ for a particle which moves 1 mm in 1 ms for two cases. The particle is a nanoparticle made up of 100 carbon atoms in one case. The other case is an electron. For which of these would you consider the motion “quantum mechanical” and why? (2) Modern Quantum Mechanics, Problem 2.28. ...
CHAPTER 2. LAGRANGIAN QUANTUM FIELD THEORY §2.1
... Note that the discretized version of the QFT yields the mechanical interpretation of QFT as an infinite collection of quantum mechanical generalized coordinates. Before proceeding further let’s consider an example with which we are already familiar, the noninteracting, Hermitian, scalar (spin zero) ...
... Note that the discretized version of the QFT yields the mechanical interpretation of QFT as an infinite collection of quantum mechanical generalized coordinates. Before proceeding further let’s consider an example with which we are already familiar, the noninteracting, Hermitian, scalar (spin zero) ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... Prove that the square of the angular momentum commutes with its components. What is meant by degeneracy of an energy level? What is an orthonormal basis? With an example explain simultaneous eigenfunctions. If A and B are two operators, then show that [A-1[A,B]] = 2B. ...
... Prove that the square of the angular momentum commutes with its components. What is meant by degeneracy of an energy level? What is an orthonormal basis? With an example explain simultaneous eigenfunctions. If A and B are two operators, then show that [A-1[A,B]] = 2B. ...
Why there is Something rather than Nothing (from
... boson could serve as the inflaton for a scenario with ns» 0.93 and T/S» 0.0004 The mechanism is very different from F.Bezrukov and M.Shaposhnikov, Phys.Lett. 659B (2008) 703 because it is dominated by the quantum effects: CMB data probe quantum anomalous scaling induced by all heavy massive particle ...
... boson could serve as the inflaton for a scenario with ns» 0.93 and T/S» 0.0004 The mechanism is very different from F.Bezrukov and M.Shaposhnikov, Phys.Lett. 659B (2008) 703 because it is dominated by the quantum effects: CMB data probe quantum anomalous scaling induced by all heavy massive particle ...
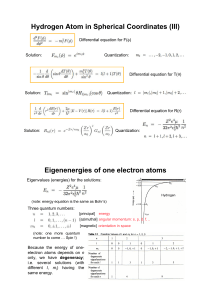
Hydrogen Atom in Spherical Coordinates (III) Eigenenergies of one
... [principal] energy [azimuthal] angular momentum: s, p, d, f, .. [magnetic] orientation in space (note: one more quantum number to come … Spin !) ...
... [principal] energy [azimuthal] angular momentum: s, p, d, f, .. [magnetic] orientation in space (note: one more quantum number to come … Spin !) ...
Chern-Simons theory and the fractional quantum Hall effect
... above formula corresponds to integer numbers. Surprisingly in 1983, Tsui and collaborators[2] observed the so called fractional quantum Hall effect (FQHE), for which ν = pq , p, q integers. In these notes we discuss how one can use the ChernSimons gauge theory to understand or to deal with the FQHE. ...
... above formula corresponds to integer numbers. Surprisingly in 1983, Tsui and collaborators[2] observed the so called fractional quantum Hall effect (FQHE), for which ν = pq , p, q integers. In these notes we discuss how one can use the ChernSimons gauge theory to understand or to deal with the FQHE. ...