esa`s magnetic field mission
... OUR PLANET In simple terms, Earth’s magnetic field behaves as if there were a powerful bar magnet at the centre of the planet, tilted at about 11° to the axis of rotation. In reality, however, the processes involved in generating the field are far more complex. The magnetic field is thought to be la ...
... OUR PLANET In simple terms, Earth’s magnetic field behaves as if there were a powerful bar magnet at the centre of the planet, tilted at about 11° to the axis of rotation. In reality, however, the processes involved in generating the field are far more complex. The magnetic field is thought to be la ...
Characterizing Si: P quantum dot qubits with spin resonance
... Silicon is an excellent host for spin qubits as it is a spin-free environment with the added advantage of weak spin-orbit coupling. The coherence time of single electron spins bound to phosphorus donors in enriched silicon-28 was measured to be 0.6 s with Hahn echo in bulk1. Recent advances in scann ...
... Silicon is an excellent host for spin qubits as it is a spin-free environment with the added advantage of weak spin-orbit coupling. The coherence time of single electron spins bound to phosphorus donors in enriched silicon-28 was measured to be 0.6 s with Hahn echo in bulk1. Recent advances in scann ...
Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 070602
... such phases have not, thus far, been seen experimentally outside of the quantum Hall regime. Is this because topological phases are very rare and these models are adiabatically connected only to very small regions of the phase diagrams of real experimental systems? In this Letter, we take a first st ...
... such phases have not, thus far, been seen experimentally outside of the quantum Hall regime. Is this because topological phases are very rare and these models are adiabatically connected only to very small regions of the phase diagrams of real experimental systems? In this Letter, we take a first st ...
URL - StealthSkater
... spaceships so that they would behave very much like a light system (as observations indeed suggest). Plasmoids could be living spaceships able to draw their energy from environment by the time mirror mechanism. It seems, however, that the highly-developed civilizations would probably not see the tro ...
... spaceships so that they would behave very much like a light system (as observations indeed suggest). Plasmoids could be living spaceships able to draw their energy from environment by the time mirror mechanism. It seems, however, that the highly-developed civilizations would probably not see the tro ...
Chapter 28: Problems
... Finally, the spin angular momentum can take on one of only two values, conventionally referred to as “spin up” and “spin down.” The spin angular momentum is characterized by the spin quantum number, which can take on values of +1/2 or –1/2. Understanding the periodic table of elements One key to und ...
... Finally, the spin angular momentum can take on one of only two values, conventionally referred to as “spin up” and “spin down.” The spin angular momentum is characterized by the spin quantum number, which can take on values of +1/2 or –1/2. Understanding the periodic table of elements One key to und ...
CHE 106 Chapter 6
... In atoms with more than one electron, there are two forces acting on each electron at the same time: 1. Attraction to the protons in the nuclear 2. Repulsion by other electrons To understand the energy of the electron, we have to know the net “feeling” each electron experiences in it’s environment. ...
... In atoms with more than one electron, there are two forces acting on each electron at the same time: 1. Attraction to the protons in the nuclear 2. Repulsion by other electrons To understand the energy of the electron, we have to know the net “feeling” each electron experiences in it’s environment. ...
Document
... Hamiltonian provides an upper bound to the exact energy the lower the energy, the better it is! It also follows that increasing the number of elements in a basis will improve (or at least not worsen) the result • Also applies to excited states • NOT all electronic structure methods are variational ...
... Hamiltonian provides an upper bound to the exact energy the lower the energy, the better it is! It also follows that increasing the number of elements in a basis will improve (or at least not worsen) the result • Also applies to excited states • NOT all electronic structure methods are variational ...
First-principles calculations of long-range intermolecular dispersion forces Auayporn Jiemchooroj Link¨
... and gravitational—are believed to explain all physical processes and structures observed in nature. In view of the microscopic world of atoms and molecules, electromagnetic forces are responsible for chemical bonds that keep atoms together in molecules and also intermolecular interactions such as io ...
... and gravitational—are believed to explain all physical processes and structures observed in nature. In view of the microscopic world of atoms and molecules, electromagnetic forces are responsible for chemical bonds that keep atoms together in molecules and also intermolecular interactions such as io ...
Simple Resonance Hierarchy for Surmounting Quantum Uncertainty
... noetic aspects of the continuous-state symmetry breaking of spacetime topology which requires further extension to include action of the noetic unitary field in additional dimensions. The Noetic Field [32,33,38-51] produces periodic symmetry vari-ations with long-range coherence [35-37] that can le ...
... noetic aspects of the continuous-state symmetry breaking of spacetime topology which requires further extension to include action of the noetic unitary field in additional dimensions. The Noetic Field [32,33,38-51] produces periodic symmetry vari-ations with long-range coherence [35-37] that can le ...
Introduction to Semiconductors
... • This is because the application of heat makes it possible for some electrons in the valence band to move to the conduction band. • Obviously the more heat applied the higher the number of electrons that can gain the required energy to make the conduction band transition and become available as cha ...
... • This is because the application of heat makes it possible for some electrons in the valence band to move to the conduction band. • Obviously the more heat applied the higher the number of electrons that can gain the required energy to make the conduction band transition and become available as cha ...
non equilibrium dynamics of quantum ising chains in the presence
... Chapter 2), makes it a good place to study ideas involving quantum phase transitions and out of equilibrium dynamics [18, 19, 20]. Since the early studies of this model in 1960s [9], it has been applied to a variety of problems [8, 21, 22], e.g. atoms in some magnetic materials such as Ho ions in Li ...
... Chapter 2), makes it a good place to study ideas involving quantum phase transitions and out of equilibrium dynamics [18, 19, 20]. Since the early studies of this model in 1960s [9], it has been applied to a variety of problems [8, 21, 22], e.g. atoms in some magnetic materials such as Ho ions in Li ...
properties of materials
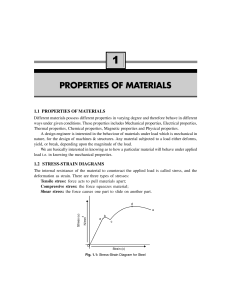
... The slow and continuous elongation of a material with time at constant stress and high temperature below elastic limit is called creep. At high temperatures, stresses even below the elastic limit can cause some permanent deformation on stress-strain diagram. There are three stages of creep. In the f ...
... The slow and continuous elongation of a material with time at constant stress and high temperature below elastic limit is called creep. At high temperatures, stresses even below the elastic limit can cause some permanent deformation on stress-strain diagram. There are three stages of creep. In the f ...
Euclidean Field Theory - Department of Mathematical Sciences
... instance by putting it on a lattice (which, in the quantum-mechanical model, means discretising time). As a result, all the systems that we are dealing with in these lectures are in a sense discrete systems, with a countable number N of degrees of freedom. The main question we are then interested in ...
... instance by putting it on a lattice (which, in the quantum-mechanical model, means discretising time). As a result, all the systems that we are dealing with in these lectures are in a sense discrete systems, with a countable number N of degrees of freedom. The main question we are then interested in ...
Realizing effective magnetic field for photons by controlling the
... systems is the existence of unidirectional edge modes3,4, which are topologically protected and characterized by a non-zero Chern number for the bulk band structure5,6. Photons are neutral particles. Accordingly, there are no naturally analogous magnetic fields. Nevertheless, with the development of ...
... systems is the existence of unidirectional edge modes3,4, which are topologically protected and characterized by a non-zero Chern number for the bulk band structure5,6. Photons are neutral particles. Accordingly, there are no naturally analogous magnetic fields. Nevertheless, with the development of ...
Ferromagnetism

Not to be confused with Ferrimagnetism; for an overview see Magnetism.Ferromagnetism is the basic mechanism by which certain materials (such as iron) form permanent magnets, or are attracted to magnets. In physics, several different types of magnetism are distinguished. Ferromagnetism (including ferrimagnetism) is the strongest type: it is the only one that typically creates forces strong enough to be felt, and is responsible for the common phenomena of magnetism in magnets encountered in everyday life. Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields with three other types of magnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, but the forces are usually so weak that they can only be detected by sensitive instruments in a laboratory. An everyday example of ferromagnetism is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. The attraction between a magnet and ferromagnetic material is ""the quality of magnetism first apparent to the ancient world, and to us today"".Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are other materials that are noticeably attracted to them. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic. The common ones are iron, nickel, cobalt and most of their alloys, some compounds of rare earth metals, and a few naturally-occurring minerals such as lodestone.Ferromagnetism is very important in industry and modern technology, and is the basis for many electrical and electromechanical devices such as electromagnets, electric motors, generators, transformers, and magnetic storage such as tape recorders, and hard disks.