Similar Figures #2
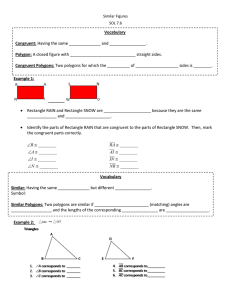
... Polygon: A closed figure with _____________________________ straight sides. Congruent Polygons: Two polygons for which the __________ of ___________________ sides is ________. Example 1: ...
... Polygon: A closed figure with _____________________________ straight sides. Congruent Polygons: Two polygons for which the __________ of ___________________ sides is ________. Example 1: ...
MA.8.G.2.3 Demonstrate that the sum of the angles in a triangle is
... You know that the 4 angles of a quadrilateral add up to 360o You know that angle R = 90 o You know that angle Q and angle T are congruent based on the curve and tick mark. Let’s call them x. So, set up an equation: ...
... You know that the 4 angles of a quadrilateral add up to 360o You know that angle R = 90 o You know that angle Q and angle T are congruent based on the curve and tick mark. Let’s call them x. So, set up an equation: ...
smaller angle?
... 5) Given the regular hexagon, describe a rigid motion or sequence of rigid motions that would map ∆AOB onto ∆DOC. ...
... 5) Given the regular hexagon, describe a rigid motion or sequence of rigid motions that would map ∆AOB onto ∆DOC. ...
2 and 3 Dimensional Figures
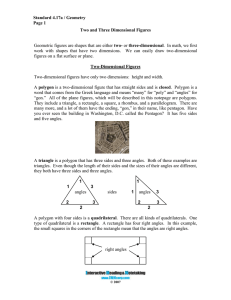
... Geometric figures are shapes that are either two- or three-dimensional. In math, we first work with shapes that have two dimensions. We can easily draw two-dimensional figures on a flat surface or plane. Two-Dimensional Figures Two-dimensional figures have only two dimensions: height and width. A po ...
... Geometric figures are shapes that are either two- or three-dimensional. In math, we first work with shapes that have two dimensions. We can easily draw two-dimensional figures on a flat surface or plane. Two-Dimensional Figures Two-dimensional figures have only two dimensions: height and width. A po ...
Slides (Powerpoint) - Personal Web Pages
... • Since loops are non-planar and star shaped a split plane is used • Split Plane= a Plane orthogonal to the average plane that contains the split line. • Split plane helps determine the non-overlapping of loops. • If split plane isn’t able to make two non-overlapping loops then the vertex and it’s a ...
... • Since loops are non-planar and star shaped a split plane is used • Split Plane= a Plane orthogonal to the average plane that contains the split line. • Split plane helps determine the non-overlapping of loops. • If split plane isn’t able to make two non-overlapping loops then the vertex and it’s a ...
Angles and Area of Polygons
... (a) Take a copy of the polygons in circles. For each polygon use a straightedge to draw lines from the center to each vertex. These lines will look like spokes of a wheel. (b) Note that each polygon has been divided up into triangles. Look at the inscribed square. Inscribed means it is drawn inside ...
... (a) Take a copy of the polygons in circles. For each polygon use a straightedge to draw lines from the center to each vertex. These lines will look like spokes of a wheel. (b) Note that each polygon has been divided up into triangles. Look at the inscribed square. Inscribed means it is drawn inside ...
Regular stellated Polyhedra or Kepler
... Icosahedron which give very nice Polyhedra, among them the so called regular stellated Polyhedra or Kepler-Poinsot Polyhedra, and the third stellation of the Icosahedron. A face of a convex polyhedron is the figure that we can see in a polyhedron which is contained in a plane. In the case of the Dod ...
... Icosahedron which give very nice Polyhedra, among them the so called regular stellated Polyhedra or Kepler-Poinsot Polyhedra, and the third stellation of the Icosahedron. A face of a convex polyhedron is the figure that we can see in a polyhedron which is contained in a plane. In the case of the Dod ...
8.2.1 - 8.2.2
... It is important to note that if the answer is not a whole number, then either an error was made or there is no polygon with interior angles that sum to the given measure. Since the answer is the number of sides, the answer must be a whole number. Polygons cannot have “7.2” sides! ...
... It is important to note that if the answer is not a whole number, then either an error was made or there is no polygon with interior angles that sum to the given measure. Since the answer is the number of sides, the answer must be a whole number. Polygons cannot have “7.2” sides! ...
POLYGONS 8.1.1 – 8.1.5 Example 1
... if the answer is not a whole number, an error was made or there is no polygon with its interior angles summing to the measure given. Since the answer is the number of sides, the answer can only be a whole number. Polygons cannot have “7.2” sides! ...
... if the answer is not a whole number, an error was made or there is no polygon with its interior angles summing to the measure given. Since the answer is the number of sides, the answer can only be a whole number. Polygons cannot have “7.2” sides! ...
Study Guide Quiz #5
... 33. The measure of each interior angle of a regular polygon is 120°. How many sides does the polygon have? ...
... 33. The measure of each interior angle of a regular polygon is 120°. How many sides does the polygon have? ...
Chapter 8 Notes - Kenston Local Schools
... A polygon is a closed figure made up of straight line segments connected end-to-end. These segments may not cross (intersect) at any other points. A regular polygon is equilateral and equiangular (all sides have the same length the interior angles have equal measure). The example is a regular hexago ...
... A polygon is a closed figure made up of straight line segments connected end-to-end. These segments may not cross (intersect) at any other points. A regular polygon is equilateral and equiangular (all sides have the same length the interior angles have equal measure). The example is a regular hexago ...
File - F.O.M. Math 11
... 6) In each figure shown in the textbook, the congruent sides form a regular polygon. Determine the values of a, b, c, and d. a) ...
... 6) In each figure shown in the textbook, the congruent sides form a regular polygon. Determine the values of a, b, c, and d. a) ...
Regular polytope
In mathematics, a regular polytope is a polytope whose symmetry is transitive on its flags, thus giving it the highest degree of symmetry. All its elements or j-faces (for all 0 ≤ j ≤ n, where n is the dimension of the polytope) — cells, faces and so on — are also transitive on the symmetries of the polytope, and are regular polytopes of dimension ≤ n. Regular polytopes are the generalized analog in any number of dimensions of regular polygons (for example, the square or the regular pentagon) and regular polyhedra (for example, the cube). The strong symmetry of the regular polytopes gives them an aesthetic quality that interests both non-mathematicians and mathematicians.Classically, a regular polytope in n dimensions may be defined as having regular facets [(n − 1)-faces] and regular vertex figures. These two conditions are sufficient to ensure that all faces are alike and all vertices are alike. Note, however, that this definition does not work for abstract polytopes.A regular polytope can be represented by a Schläfli symbol of the form {a, b, c, ...., y, z}, with regular facets as {a, b, c, ..., y}, and regular vertex figures as {b, c, ..., y, z}.