Polygons Notes
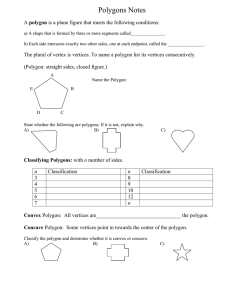
... A polygon is a plane figure that meets the following conditions: a) A shape that is formed by three or more segments called_______________. b) Each side intersects exactly two other sides, one at each endpoint, called the ________________. ...
... A polygon is a plane figure that meets the following conditions: a) A shape that is formed by three or more segments called_______________. b) Each side intersects exactly two other sides, one at each endpoint, called the ________________. ...
Lesson Plan Format
... All __________ are congruent in an equilateral polygon. All __________ are congruent in an equiangular polygon. A _______________ polygon is one that is both equilateral and equiangular. If a polygon is not regular, it is called irregular. A polygon is __________ if it has one or more interior angl ...
... All __________ are congruent in an equilateral polygon. All __________ are congruent in an equiangular polygon. A _______________ polygon is one that is both equilateral and equiangular. If a polygon is not regular, it is called irregular. A polygon is __________ if it has one or more interior angl ...
Lesson Plan Format
... All __________ are congruent in an equilateral polygon. All __________ are congruent in an equiangular polygon. A _______________ polygon is one that is both equilateral and equiangular. If a polygon is not regular, it is called irregular. A polygon is __________ if it has one or more interior angl ...
... All __________ are congruent in an equilateral polygon. All __________ are congruent in an equiangular polygon. A _______________ polygon is one that is both equilateral and equiangular. If a polygon is not regular, it is called irregular. A polygon is __________ if it has one or more interior angl ...
Part II
... Classify the angle as acute, right, obtuse, or straight. 1. The measure of the angle is 69°. ...
... Classify the angle as acute, right, obtuse, or straight. 1. The measure of the angle is 69°. ...
Lesson Plan Format
... All __________ are congruent in an equilateral polygon. All __________ are congruent in an equiangular polygon. A _______________ polygon is one that is both equilateral and equiangular. If a polygon is not regular, it is called irregular. A polygon is __________ if it has one or more interior angl ...
... All __________ are congruent in an equilateral polygon. All __________ are congruent in an equiangular polygon. A _______________ polygon is one that is both equilateral and equiangular. If a polygon is not regular, it is called irregular. A polygon is __________ if it has one or more interior angl ...
Lesson Plan Format
... All __________ are congruent in an equilateral polygon. All __________ are congruent in an equiangular polygon. A _______________ polygon is one that is both equilateral and equiangular. If a polygon is not regular, it is called irregular. A polygon is __________ if it has one or more interior angl ...
... All __________ are congruent in an equilateral polygon. All __________ are congruent in an equiangular polygon. A _______________ polygon is one that is both equilateral and equiangular. If a polygon is not regular, it is called irregular. A polygon is __________ if it has one or more interior angl ...
North Thurston Public Schools Geometry 3 rd Quarter Review Booklet
... Find the sum of: a. the interior angles of a 74-gon b. the exterior angles of a 74-gon ...
... Find the sum of: a. the interior angles of a 74-gon b. the exterior angles of a 74-gon ...
Pre-school Dictionary
... • A triangle is a plane shape with three straight sides and three angles • The angles inside a triangle always add up to 180 degrees • Triangles are classified according to their properties*. -Equilateral triangles have three equal sides and three 60 degree angles. They are regular -Isosceles triang ...
... • A triangle is a plane shape with three straight sides and three angles • The angles inside a triangle always add up to 180 degrees • Triangles are classified according to their properties*. -Equilateral triangles have three equal sides and three 60 degree angles. They are regular -Isosceles triang ...
Chapter 11 – Area of Polygons and Circles Section 11.1
... A heptagon has 4 interior angles that measure 160° each and 2 interior angles that are right angles. What is the measure of the other interior angle? ...
... A heptagon has 4 interior angles that measure 160° each and 2 interior angles that are right angles. What is the measure of the other interior angle? ...
tetrahedron - PlanetMath.org
... we may construct the perpendicular bisectors of the edges of the tetrahedron. These six planes will meet in the centre of the sphere which passes through the vertices of the tetrahedron. The six planes which connect an edge with the midpoint of the opposite edge (see what was said about edges coming ...
... we may construct the perpendicular bisectors of the edges of the tetrahedron. These six planes will meet in the centre of the sphere which passes through the vertices of the tetrahedron. The six planes which connect an edge with the midpoint of the opposite edge (see what was said about edges coming ...
Basic Tessellations
... There are eight tessellations that involve two or more types of regular polygons, with the same arrangement at each vertex. These are called Archimedean tessellations, by analogy with the Archimedean polyhedra, which will be discussed in Unit 12. The one shown here is (3, 6, 3, 6), which says that ...
... There are eight tessellations that involve two or more types of regular polygons, with the same arrangement at each vertex. These are called Archimedean tessellations, by analogy with the Archimedean polyhedra, which will be discussed in Unit 12. The one shown here is (3, 6, 3, 6), which says that ...
Geometry Fall 2011 Lesson 17 (S.A.S. Postulate)
... Definition: Two polygons are similar if their vertices can be paired so that 1) Corresponding angles are congruent 2) Corresponding sides are in proportion The symbol for similarity is ~. What is the ratio of the lengths of any two corresponding sides in the similar polygons at right? Definition: Th ...
... Definition: Two polygons are similar if their vertices can be paired so that 1) Corresponding angles are congruent 2) Corresponding sides are in proportion The symbol for similarity is ~. What is the ratio of the lengths of any two corresponding sides in the similar polygons at right? Definition: Th ...
Y4 New Curriculum Maths planning 5
... Use both types of set squares to draw shapes, using a ruler to join the angles you draw. Can you draw squares and rectangles? What other shapes are possible? Try to make both regular and irregular shapes. Label the shapes with their names and properties. Start with one right angle and see how many d ...
... Use both types of set squares to draw shapes, using a ruler to join the angles you draw. Can you draw squares and rectangles? What other shapes are possible? Try to make both regular and irregular shapes. Label the shapes with their names and properties. Start with one right angle and see how many d ...
Regular polytope
In mathematics, a regular polytope is a polytope whose symmetry is transitive on its flags, thus giving it the highest degree of symmetry. All its elements or j-faces (for all 0 ≤ j ≤ n, where n is the dimension of the polytope) — cells, faces and so on — are also transitive on the symmetries of the polytope, and are regular polytopes of dimension ≤ n. Regular polytopes are the generalized analog in any number of dimensions of regular polygons (for example, the square or the regular pentagon) and regular polyhedra (for example, the cube). The strong symmetry of the regular polytopes gives them an aesthetic quality that interests both non-mathematicians and mathematicians.Classically, a regular polytope in n dimensions may be defined as having regular facets [(n − 1)-faces] and regular vertex figures. These two conditions are sufficient to ensure that all faces are alike and all vertices are alike. Note, however, that this definition does not work for abstract polytopes.A regular polytope can be represented by a Schläfli symbol of the form {a, b, c, ...., y, z}, with regular facets as {a, b, c, ..., y}, and regular vertex figures as {b, c, ..., y, z}.