* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2 and 3 Dimensional Figures
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Surface (topology) wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
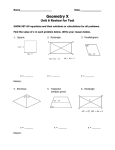
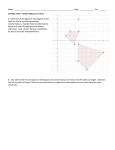
Standard 4.17a / Geometry Page 1 Two and Three Dimensional Figures Geometric figures are shapes that are either two- or three-dimensional. In math, we first work with shapes that have two dimensions. We can easily draw two-dimensional figures on a flat surface or plane. Two-Dimensional Figures Two-dimensional figures have only two dimensions: height and width. A polygon is a two-dimensional figure that has straight sides and is closed. Polygon is a word that comes from the Greek language and means “many” for “poly” and “angles” for “gon.” All of the plane figures, which will be described in this notepage are polygons. They include a triangle, a rectangle, a square, a rhombus, and a parallelogram. There are many more, and a lot of them have the ending, “gon,” in their name, like pentagon. Have you ever seen the building in Washington, D.C. called the Pentagon? It has five sides and five angles. A triangle is a polygon that has three sides and three angles. Both of these examples are triangles. Even though the length of their sides and the sizes of their angles are different, they both have three sides and three angles. 1 1 1 3 angles 2 sides 3 2 1 angles 3 2 3 2 A polygon with four sides is a quadrilateral. There are all kinds of quadrilaterals. One type of quadrilateral is a rectangle. A rectangle has four right angles. In this example, the small squares in the corners of the rectangle mean that the angles are right angles. right angles © 2007 Standard 4.17a / Geometry Page 2 Two and Three Dimensional Figures (continued) Another quadrilateral is a square. A square is a rectangle with four sides of equal length. If it is a rectangle, what kind of angles does a square have? Another quadrilateral is a rhombus. Like a square, a rhombus has sides of equal length, but there are no right angles. A rhombus looks like a square that leans. Is a rhombus a rectangle? The last kind of quadrilateral is a parallelogram. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two sets of parallel sides. The opposite sides of a parallelogram are of equal length, and the opposite angles of a parallelogram are the same size. A rectangle, a square, and a rhombus are all parallelograms. They are called parallelograms because the opposite sides are not just equal in length, but they are also parallel line segments. Parallel means that the points of the line segments are always the same distance apart. a 1 2 c d 4 3 Sides a and b are parallel line segments. Sides c and d are parallel line segments. Angles 1 and 3 are the same size. Angles 2 and 4 are the same size. b We can put the properties of these quadrilaterals in a table to help remember them. Name of figure quadrilateral rectangle square rhombus parallelogram Sides of equal length Parallel sides © 2007 Right angles Opposite angles equal Standard 4.17a / Geometry Page 3 Two and Three Dimensional Figures (continued) A circle is a closed curve with all of its points in one plane or flat surface. Each point on a circle is the same distance from the center of the circle. All points of the circle are equidistant from the center. center Three-dimensional figures It is important to identify and understand two-dimensional shapes in order to identify and understand space figures or three-dimensional figures. Plane figures exist only on a flat surface or plane. They have two dimensions of height and width. Three-dimensional figures exist in space. They take up a different type of space than plane or twodimensional figures. Three dimensional figures haves height, width and depth. depth height width A sphere is a three-dimensional figure. All of the points of a sphere are the same distance from its center. Any section cut across a sphere is a circle. A ball is a sphere. Earth and other planets are in the shape of a sphere. A cube is a three-dimensional solid figure. It has six congruent square faces and every edge has the same length. Congruent means that the six faces of the cube are exactly the same size and shape. A cube has 6 faces and 12 edges. edge face © 2007 Standard 4.17a / Geometry Page 4 Two and Three Dimensional Figures (continued) A rectangular prism is a three-dimensional solid figure. It has six rectangular faces and 12 edges. The edges of the rectangles do not have to be equal in length. The rectangles that are opposite or across from each other are congruent and parallel to each other. How many pairs of parallel, congruent faces can you find on this rectangle? A cylinder is a three-dimensional object. It is formed by two congruent, parallel circular bases joined by a curved surface. Think of the cardboard center of a paper towel roll or the Styrofoam “noodles” we use at the pool or beach to help us swim. Most cans are cylinder shaped. circular base A cone is a solid, pointed figure. It has a flat base that is usually a circle. This base is joined to a vertex by a curved surface. The easiest way to picture a cone is an ice cream cone or a party hat. vertex base A square pyramid is a solid figure that has a square base. This base is joined to a vertex by four triangular faces. Many people think of the pyramids in Egypt when describing what this figure looks like. vertex triangular face base © 2007