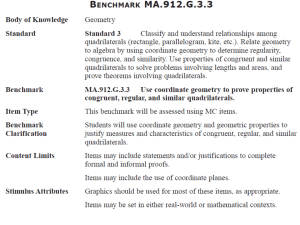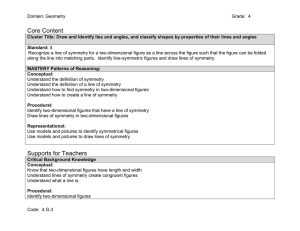
Domain: Geometry Grade: 4 Core Content Cluster Title: Draw and
... fold. Then ask students to identify if both parts match. Define where the line of symmetry is on the figure. Define what makes the figure symmetrical. Try the same thing with a two-dimensional figure that is not symmetrical. Assessment Tasks Used Skill-based Task: Identify symmetrical figures. Draw ...
... fold. Then ask students to identify if both parts match. Define where the line of symmetry is on the figure. Define what makes the figure symmetrical. Try the same thing with a two-dimensional figure that is not symmetrical. Assessment Tasks Used Skill-based Task: Identify symmetrical figures. Draw ...
2d shape 3d shape Angles - St Andrew`s CofE Primary School (Eccles)
... width or breadth and height), prism A prism has flat sides and has the same cross section along its length. The cross-section will always be a polygon. There are no curved faces in a prism. A prism is named after its base (triangular based prism) A cuboid/cube is also a prism. ...
... width or breadth and height), prism A prism has flat sides and has the same cross section along its length. The cross-section will always be a polygon. There are no curved faces in a prism. A prism is named after its base (triangular based prism) A cuboid/cube is also a prism. ...
Scale Factor
... Theorem 6.1 Perimeters of Similar Polygons If two polygons are similar, then the ratio of their perimeters is equal to the ratios of their corresponding sides (scale factor). ...
... Theorem 6.1 Perimeters of Similar Polygons If two polygons are similar, then the ratio of their perimeters is equal to the ratios of their corresponding sides (scale factor). ...
Lesson 4.2: Angles In a Polygon
... Area: The amount of surface the 2D shape covers. It’s measured in square units. Some of these units are: squared centimeters (cm2), squared meters (m2) and squared kilometers (km2). The general way to calculate the area of a rectangle is by multiplying base by height (altitude). However, to calculat ...
... Area: The amount of surface the 2D shape covers. It’s measured in square units. Some of these units are: squared centimeters (cm2), squared meters (m2) and squared kilometers (km2). The general way to calculate the area of a rectangle is by multiplying base by height (altitude). However, to calculat ...
Math 9 Study Guide Unit 7 Unit 7 - Similarity and Transformations
... If you are given a diagram with dimensions and the scale factor and asked to draw the scale diagram multiply each dimension by the scale factor to find out the dimensions of the scale (new) diagram. Scale factor can also be expressed as a ratio (ex. 1:150) Similar Polygons Polygons: have many sides ...
... If you are given a diagram with dimensions and the scale factor and asked to draw the scale diagram multiply each dimension by the scale factor to find out the dimensions of the scale (new) diagram. Scale factor can also be expressed as a ratio (ex. 1:150) Similar Polygons Polygons: have many sides ...
Quiz Review - Polygons and Polygon Angles
... Quiz Review Polygons and Polygon Angles Date: _____________ Period: ____ State if the shape is a polygon. If it is, decide whether it is concave or convex. ...
... Quiz Review Polygons and Polygon Angles Date: _____________ Period: ____ State if the shape is a polygon. If it is, decide whether it is concave or convex. ...
Keeping Track of your Learning
... Prove vertical angles are congruent. Prove when a transversal crosses parallel lines, alternate interior angles are congruent. Prove when a transversal crosses parallel lines, corresponding angles are congruent. Prove that points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are equidistant from the ...
... Prove vertical angles are congruent. Prove when a transversal crosses parallel lines, alternate interior angles are congruent. Prove when a transversal crosses parallel lines, corresponding angles are congruent. Prove that points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are equidistant from the ...
Interior and Exterior Angles in Polygons
... First, a polygon is a closed figure formed by joining line segments that meet only at their endpoints. The segments are called the sides of the polygon; each endpoint is called a vertex. ...
... First, a polygon is a closed figure formed by joining line segments that meet only at their endpoints. The segments are called the sides of the polygon; each endpoint is called a vertex. ...
Vocabulary - Hartland High School
... In geometry, two polygons that have the same shape and same size are called _____________. We learned that two polygons are CONGRUENT if and only if ___________________________ AND ___________________________ are equal. C ...
... In geometry, two polygons that have the same shape and same size are called _____________. We learned that two polygons are CONGRUENT if and only if ___________________________ AND ___________________________ are equal. C ...
Section 22.1
... 8. Show that if the defect of a regular pentagon is 90 then it can be used as a fundamental region to tile the hyperbolic plane. δ = 90 = ( 5 – 2) 180 – 5m A. which implies that m A = 90. thus each vertex of the pentagon is a right angle. This means that four of the pentagons will exactly fit at ...
... 8. Show that if the defect of a regular pentagon is 90 then it can be used as a fundamental region to tile the hyperbolic plane. δ = 90 = ( 5 – 2) 180 – 5m A. which implies that m A = 90. thus each vertex of the pentagon is a right angle. This means that four of the pentagons will exactly fit at ...
Angle Sum in a Triangle
... In this activity, we discover the sum of the 3 angles in a triangle 3 different ways: ...
... In this activity, we discover the sum of the 3 angles in a triangle 3 different ways: ...
1. The following figure is a box in which the top and bottom are
... 10. A student claims that if any two planes that do not intersect are parallel, then any two lines that do not intersect should also be parallel. How do you respond? No, it’s possible for two lines to be skew in three dimensions. In three dimensions, planes (2D objects) that do not intersect must be ...
... 10. A student claims that if any two planes that do not intersect are parallel, then any two lines that do not intersect should also be parallel. How do you respond? No, it’s possible for two lines to be skew in three dimensions. In three dimensions, planes (2D objects) that do not intersect must be ...
Geometry 6.3
... Similar Polygons Two or more polygons are similar, if corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding side lengths are proportional ...
... Similar Polygons Two or more polygons are similar, if corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding side lengths are proportional ...
Regular polytope
In mathematics, a regular polytope is a polytope whose symmetry is transitive on its flags, thus giving it the highest degree of symmetry. All its elements or j-faces (for all 0 ≤ j ≤ n, where n is the dimension of the polytope) — cells, faces and so on — are also transitive on the symmetries of the polytope, and are regular polytopes of dimension ≤ n. Regular polytopes are the generalized analog in any number of dimensions of regular polygons (for example, the square or the regular pentagon) and regular polyhedra (for example, the cube). The strong symmetry of the regular polytopes gives them an aesthetic quality that interests both non-mathematicians and mathematicians.Classically, a regular polytope in n dimensions may be defined as having regular facets [(n − 1)-faces] and regular vertex figures. These two conditions are sufficient to ensure that all faces are alike and all vertices are alike. Note, however, that this definition does not work for abstract polytopes.A regular polytope can be represented by a Schläfli symbol of the form {a, b, c, ...., y, z}, with regular facets as {a, b, c, ..., y}, and regular vertex figures as {b, c, ..., y, z}.