CHAPTER 6 Human Eye Notes FIB
... • Optical fibres: ____________ glass fibres that can transmit light from one place to another. o Total internal reflection – light entering one end of the fibre is reflected from side to side until it emerges from the other end. o Uses: used in ____________ to transmit images of the inside so ...
... • Optical fibres: ____________ glass fibres that can transmit light from one place to another. o Total internal reflection – light entering one end of the fibre is reflected from side to side until it emerges from the other end. o Uses: used in ____________ to transmit images of the inside so ...
February 6 pptx
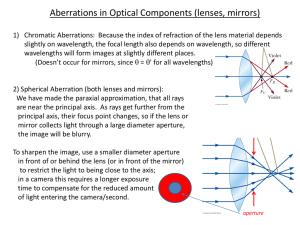
... 2) Spherical Aberration (both lenses and mirrors): We have made the paraxial approximation, that all rays are near the principal axis. As rays get further from the principal axis, their focus point changes, so if the lens or mirror collects light through a large diameter aperture, the image will be ...
... 2) Spherical Aberration (both lenses and mirrors): We have made the paraxial approximation, that all rays are near the principal axis. As rays get further from the principal axis, their focus point changes, so if the lens or mirror collects light through a large diameter aperture, the image will be ...
Ay 105 Lab Experiment #8: Infrared Array Camera
... the camera was new back in the mists of the early 1990’s, a coal-burning PC with a dedicated parallel input card converted the camera output into data files. Now, a “modern” VGA-USB converter and software are used to capture images. The downside of this is that captured images have (modest) addition ...
... the camera was new back in the mists of the early 1990’s, a coal-burning PC with a dedicated parallel input card converted the camera output into data files. Now, a “modern” VGA-USB converter and software are used to capture images. The downside of this is that captured images have (modest) addition ...
Refraction of Light
... result of an inability of the cornea and the lens to focus light on the retina. Instead, light is focused either in front of or behind the retina. ...
... result of an inability of the cornea and the lens to focus light on the retina. Instead, light is focused either in front of or behind the retina. ...
Physics 212 HW17 - University of St. Thomas
... which is typically 2.45 cm behind the lens. The eye’s lens is special in that it can change its focal length in order to focus images from very far and very close onto the retina, which stays 2.45 cm away. The average person with “20/20 vision” can focus on objects at infinity and objects no closer ...
... which is typically 2.45 cm behind the lens. The eye’s lens is special in that it can change its focal length in order to focus images from very far and very close onto the retina, which stays 2.45 cm away. The average person with “20/20 vision” can focus on objects at infinity and objects no closer ...
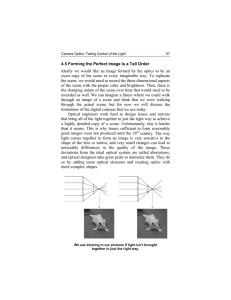
4.5 Forming the Perfect Image Is a Tall Order Ideally we would like
... than it seems. This is why lenses sufficient to form reasonably good images were not produced until the 16th century. The way light comes together to form an image is very sensitive to the shape of the lens or mirror, and very small changes can lead to noticeable differences in the quality of the im ...
... than it seems. This is why lenses sufficient to form reasonably good images were not produced until the 16th century. The way light comes together to form an image is very sensitive to the shape of the lens or mirror, and very small changes can lead to noticeable differences in the quality of the im ...
Focal Point and Focal Length Ray Diagram for lenses
... The near point is the closest distance for which the lens can accommodate to focus light on the retina. Typically at age 10, this is about 18 cm The average value is about 25 cm. It increases with age. • Up to 500 cm or greater at age 60 ...
... The near point is the closest distance for which the lens can accommodate to focus light on the retina. Typically at age 10, this is about 18 cm The average value is about 25 cm. It increases with age. • Up to 500 cm or greater at age 60 ...
OCR Document - mackenziekim
... Draw ray diagrams to scale for each object position of the investigation: 3f; 2f; 1.5f; O.5f. Using a ray box, determine the focal length of the lens. Verify the focal length using another method. Place the candle at these locations: i) 3x the focal length in front of the lens ii) 2x the focal lengt ...
... Draw ray diagrams to scale for each object position of the investigation: 3f; 2f; 1.5f; O.5f. Using a ray box, determine the focal length of the lens. Verify the focal length using another method. Place the candle at these locations: i) 3x the focal length in front of the lens ii) 2x the focal lengt ...
PPT
... Tilt-shift lenses • Tilting the lens with respect to the image plane allows to choose an arbitrary plane of focus ...
... Tilt-shift lenses • Tilting the lens with respect to the image plane allows to choose an arbitrary plane of focus ...
LENSES and MIRRORS
... parallel to the optical axis pass through a convex lens, they are bent toward the center of the lens. Examples: Magnifying glass and corrective lenses for farsightedness. A concave lens is thinner in the center than on its edges. When light rays traveling parallel to the optical axis pass through a ...
... parallel to the optical axis pass through a convex lens, they are bent toward the center of the lens. Examples: Magnifying glass and corrective lenses for farsightedness. A concave lens is thinner in the center than on its edges. When light rays traveling parallel to the optical axis pass through a ...
OPTICAL BENCH SET using METER STICK
... Place the object maker on the meter stick using the required distance. Place the light source at the end of the bench, the object marker about 10 cm from the light source, and the lens exactly 50 cm from the object marker (p). Move the screen on the bench until a sharp image is formed on the screen. ...
... Place the object maker on the meter stick using the required distance. Place the light source at the end of the bench, the object marker about 10 cm from the light source, and the lens exactly 50 cm from the object marker (p). Move the screen on the bench until a sharp image is formed on the screen. ...
Refraction, Lenses, Aberrations
... A lens is a piece of glass (plastic) with two refracting surfaces, which are either curved (e.g., a segment of a sphere) or plain. Lenses are used to form images by refraction in optical instruments (microscopes, telescopes, cameras, etc.) ...
... A lens is a piece of glass (plastic) with two refracting surfaces, which are either curved (e.g., a segment of a sphere) or plain. Lenses are used to form images by refraction in optical instruments (microscopes, telescopes, cameras, etc.) ...
CP Physics - Ms. Lisa Cole-
... 2. The area of the eye on which light is focused is called the ____________________ 3. As a ray of light passes from air into the lens, the speed of light ____________. 4. A diverging lens ____________________________ 5. A magnifying glass is usually a ____________________________. 6. If a person’s ...
... 2. The area of the eye on which light is focused is called the ____________________ 3. As a ray of light passes from air into the lens, the speed of light ____________. 4. A diverging lens ____________________________ 5. A magnifying glass is usually a ____________________________. 6. If a person’s ...
Parts of the Microscope and Their Function
... Keeps the slide in place on the stage. Stage clips Location where the slide is placed. Contains an opening that lets light pass through. Stage Controls the amount of light that enters the stage. Diaphragm Provides light for viewing the specimen. Light This is the bottom of the microscope and it supp ...
... Keeps the slide in place on the stage. Stage clips Location where the slide is placed. Contains an opening that lets light pass through. Stage Controls the amount of light that enters the stage. Diaphragm Provides light for viewing the specimen. Light This is the bottom of the microscope and it supp ...
Geometrical Optics
... Aberrations are imperfections in the optical image formed by a spherical lens (or optical mirror). There are five main aberrations: 1. Chromatic aberration. The refractive index of glass varies with wavelength. This results in different focal lengths and image magnifications for different colours. ...
... Aberrations are imperfections in the optical image formed by a spherical lens (or optical mirror). There are five main aberrations: 1. Chromatic aberration. The refractive index of glass varies with wavelength. This results in different focal lengths and image magnifications for different colours. ...
Read more... Using the Document Camera
... modes - light off, light on and light on with guide positioning marks. If there is sufficient lighting at the front of the teaching space where the document camera is positioned on the lectern, it may not be necessary to use the camera’s light at all. Experiment. 6. Adjust the orientation of the cam ...
... modes - light off, light on and light on with guide positioning marks. If there is sufficient lighting at the front of the teaching space where the document camera is positioned on the lectern, it may not be necessary to use the camera’s light at all. Experiment. 6. Adjust the orientation of the cam ...
Mirrors and Images
... These three rays follow the rules for how light rays are bent by the lens: 1. A light ray passing through the center of the lens is not deflected at all (A). 2. A light ray parallel to the axis passes through the far focal point (B). 3. A light ray passing through the near focal point emerges para ...
... These three rays follow the rules for how light rays are bent by the lens: 1. A light ray passing through the center of the lens is not deflected at all (A). 2. A light ray parallel to the axis passes through the far focal point (B). 3. A light ray passing through the near focal point emerges para ...
Real-Time Image Processing Requirements
... To see a signal which is 10-4 of the sky brightness the sky must be measured with enough photons such that the shot noise is suppressed to this level or better. Since shot noise goes like the square root of the signal, at least 108 photons must be read by the cameras. Modern CMOS cameras of the size ...
... To see a signal which is 10-4 of the sky brightness the sky must be measured with enough photons such that the shot noise is suppressed to this level or better. Since shot noise goes like the square root of the signal, at least 108 photons must be read by the cameras. Modern CMOS cameras of the size ...
UV Lenses - Machine Vision Systems
... *Compact in design and ideal for integration into machine vision systems. *Focus and iris locking screws against vibration and shock. *Extended wavelength range (280nm to 365nm) by introduction of fluorite. High resolution ...
... *Compact in design and ideal for integration into machine vision systems. *Focus and iris locking screws against vibration and shock. *Extended wavelength range (280nm to 365nm) by introduction of fluorite. High resolution ...
PolarView™ ND filter
... High performance digital cameras are normally designed to be sensitive in low light conditions, increasing the risk of over exposure in bright ambient light. To ensure optimal image exposure over a wide range of lighting conditions, the well-equipped photographer often carries a number of ND filters ...
... High performance digital cameras are normally designed to be sensitive in low light conditions, increasing the risk of over exposure in bright ambient light. To ensure optimal image exposure over a wide range of lighting conditions, the well-equipped photographer often carries a number of ND filters ...
File
... tube and in 1608 took his invention to the Dutch government. It was kept a secret as it was thought to be an advantage for warfare. Hans told the Italian astronomer and physicist Galileo Galilei. Galileo than made the then made a telescope that could magnify 30 times and was the first person in hi ...
... tube and in 1608 took his invention to the Dutch government. It was kept a secret as it was thought to be an advantage for warfare. Hans told the Italian astronomer and physicist Galileo Galilei. Galileo than made the then made a telescope that could magnify 30 times and was the first person in hi ...
Microscopy - u.arizona.edu
... moves object – goal is to place object in focal plane of objective lens B. Do NOT use Coarse Focus Adjustment when using longer (40X, 100X) objectives; coarsely focus first at low mag then use fine with high mags d. Base and Arm A. Always transport a microscope with one hand on each the arm and base ...
... moves object – goal is to place object in focal plane of objective lens B. Do NOT use Coarse Focus Adjustment when using longer (40X, 100X) objectives; coarsely focus first at low mag then use fine with high mags d. Base and Arm A. Always transport a microscope with one hand on each the arm and base ...
Camera

A camera is an optical instrument for recording images, which may be stored locally, transmitted to another location, or both. The images may be individual still photographs or sequences of images constituting videos or movies. The word camera comes from camera obscura, which means ""dark chamber"" and is the Latin name of the original device for projecting an image of external reality onto a flat surface. The modern photographic camera evolved from the camera obscura. The functioning of the camera is very similar to the functioning of the human eye.