Lenses (docx)
... c. Set up an experiment to verify your predictions. Note that you will most likely have to tilt the mirror from the optical axis in order to be able to ‘catch’ the image without blocking rays with your screen. Ignore that effect in parts (a) and (b). Present your measured data and show that your pre ...
... c. Set up an experiment to verify your predictions. Note that you will most likely have to tilt the mirror from the optical axis in order to be able to ‘catch’ the image without blocking rays with your screen. Ignore that effect in parts (a) and (b). Present your measured data and show that your pre ...
Lab 11: Lenses and Optics
... If you (or your cat) wear glasses or contact lenses, you are already familiar with the science of optics. Whether you realize it or not, you understand the idea of a focal point. You are very aware when an image is out of focus (no glasses) or in focus (put your glasses back on). You even know the d ...
... If you (or your cat) wear glasses or contact lenses, you are already familiar with the science of optics. Whether you realize it or not, you understand the idea of a focal point. You are very aware when an image is out of focus (no glasses) or in focus (put your glasses back on). You even know the d ...
Lens Design OPTI 517 Syllabus
... According to the Arizona Code of Academic Integrity (http://dos.web.arizona.edu/uapolicies/cai2.html), “Integrity is expected of every student in all academic work. The guiding principle of academic integrity is that a student’s submitted work must be the student’s own.” Unless otherwise noted by th ...
... According to the Arizona Code of Academic Integrity (http://dos.web.arizona.edu/uapolicies/cai2.html), “Integrity is expected of every student in all academic work. The guiding principle of academic integrity is that a student’s submitted work must be the student’s own.” Unless otherwise noted by th ...
Optics 101 for non-optical engineers
... improves the color saturation of reds, oranges, and earth-tone colors such as rust, brown and amber. The range of colors improved by the enhancing filter makes it popular for use on autumn foliage and brownish-red scenic compositions, such as those found at the Grand Canyon. It is also the filter of ...
... improves the color saturation of reds, oranges, and earth-tone colors such as rust, brown and amber. The range of colors improved by the enhancing filter makes it popular for use on autumn foliage and brownish-red scenic compositions, such as those found at the Grand Canyon. It is also the filter of ...
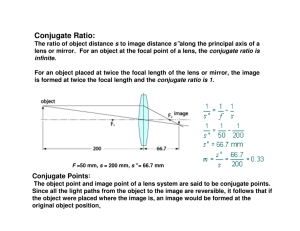
Conjugate Ratio:
... The object point and image point of a lens system are said to be conjugate points. Since all the light paths from the object to the image are reversible, it follows that if the object were placed where the image is, an image would be formed at the original object position. ...
... The object point and image point of a lens system are said to be conjugate points. Since all the light paths from the object to the image are reversible, it follows that if the object were placed where the image is, an image would be formed at the original object position. ...
outline21379
... To improve lens centration and stability (for example, post-PK & post-RK cases) ...
... To improve lens centration and stability (for example, post-PK & post-RK cases) ...
Lenses: Bending Light
... at one point called the focal point.The distance between the focal point and the centre of the lens is called the focal length. Images are formed by placing objects at different distances from the convex lens. The theory behind this is quite complex, since convex lenses can produce both larger and s ...
... at one point called the focal point.The distance between the focal point and the centre of the lens is called the focal length. Images are formed by placing objects at different distances from the convex lens. The theory behind this is quite complex, since convex lenses can produce both larger and s ...
Lecture 31 - Purdue Physics
... determines how much light will reach the image plane. • Pupils are typically circular: the area varies as the square of the diameter, 9. • The image area varies as the square of the lateral dimension, : ~ • Light intensity at the image plane varies as 9/ • (9/ ) is called the relative aperture ...
... determines how much light will reach the image plane. • Pupils are typically circular: the area varies as the square of the diameter, 9. • The image area varies as the square of the lateral dimension, : ~ • Light intensity at the image plane varies as 9/ • (9/ ) is called the relative aperture ...
lecture8 - Tamara L Berg
... When you turn the lens of a camera to focus it -- you're moving it closer or farther away from the film surface. As you move the lens, you can line up the focused real image of an object so it falls directly on the film surface. ...
... When you turn the lens of a camera to focus it -- you're moving it closer or farther away from the film surface. As you move the lens, you can line up the focused real image of an object so it falls directly on the film surface. ...
Factors controlling heat exchange between the human body and its
... The finite resolution of the eye is that even a well-functioning eye can not differentiate between images formed on the retina from objects at different depths. The distance Δ at which the images of the point are clear is called the depth of focus. Then the diaphragm is used, the improvement in visi ...
... The finite resolution of the eye is that even a well-functioning eye can not differentiate between images formed on the retina from objects at different depths. The distance Δ at which the images of the point are clear is called the depth of focus. Then the diaphragm is used, the improvement in visi ...
9-26 Geometrical Optics
... Fermat’s principle can be used to derive the shape of a boundary that images light from one side of the boundary to another. This shape is a cartesian oval and is used for aspheric lenses Spherical lenses can well approximate the ideal shape of an aspherical lens for paraxial beams and are usually m ...
... Fermat’s principle can be used to derive the shape of a boundary that images light from one side of the boundary to another. This shape is a cartesian oval and is used for aspheric lenses Spherical lenses can well approximate the ideal shape of an aspherical lens for paraxial beams and are usually m ...
Chapter 25
... Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave nature of light must be used ...
... Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave nature of light must be used ...
Assessing age-related changes in the biomechanical properties of
... Developed a co-focused ultrasound and OCE system to study the biomechanical property of the rabbit lens; 2) The parameters of maximal displacement, natural frequency can be used for assessment; 3) Stiffness of the rabbit crystalline lens increases with age; 4) Prospective future work would be to co ...
... Developed a co-focused ultrasound and OCE system to study the biomechanical property of the rabbit lens; 2) The parameters of maximal displacement, natural frequency can be used for assessment; 3) Stiffness of the rabbit crystalline lens increases with age; 4) Prospective future work would be to co ...
Thin Lenses
... Focal length for a lens in air is related to the curvature of its front and back surfaces (R1 and R2) and to the index of refraction, n, of the lens material. Sign convention of lens radii R1 and R2 The signs of the lens radii indicate whether the corresponding surfaces are convex (R > 0, bulging ou ...
... Focal length for a lens in air is related to the curvature of its front and back surfaces (R1 and R2) and to the index of refraction, n, of the lens material. Sign convention of lens radii R1 and R2 The signs of the lens radii indicate whether the corresponding surfaces are convex (R > 0, bulging ou ...
4.6 Lenses
... • is a straight line that passes through the centre of the lens, that intersects it at 90 (called a normal) • when rays that are parallel to the PA pass through a converging lens, the ...
... • is a straight line that passes through the centre of the lens, that intersects it at 90 (called a normal) • when rays that are parallel to the PA pass through a converging lens, the ...
Problem Sheet
... at distances varying from the near point (about 25 cm) to infinity. Estimate the range of lens powers which can be achieved by the lens and cornea in combination. A short-sighted optics lecturer can only focus on objects up to 50 cm away. What type and power of contact lens does he need to correct ...
... at distances varying from the near point (about 25 cm) to infinity. Estimate the range of lens powers which can be achieved by the lens and cornea in combination. A short-sighted optics lecturer can only focus on objects up to 50 cm away. What type and power of contact lens does he need to correct ...
Problem Sheet
... focal length) and the lens itself (with variable focal length), which can be approximated as a thin lens at a distance of 17 mm from the retina. The eye is capable of focusing on objects at ...
... focal length) and the lens itself (with variable focal length), which can be approximated as a thin lens at a distance of 17 mm from the retina. The eye is capable of focusing on objects at ...
Active Aperture Control and Sensor Modulation for Flexible Imaging
... density filter in front of the camera to capture high dynamic range image. These two methods must be implemented on a panning camera in order to image every scene point with different exposures. [12] discussed three possible designs to achieve “adaptive” HDR using an SLM, where the SLM is placed adj ...
... density filter in front of the camera to capture high dynamic range image. These two methods must be implemented on a panning camera in order to image every scene point with different exposures. [12] discussed three possible designs to achieve “adaptive” HDR using an SLM, where the SLM is placed adj ...
Imaging
... · Ray 1 is the ray which travels parallel to the axis and after going through the lens it passes through the focal point. · Ray 2 passes through the center of the lens. · Ray 3 goes through the focal point and then travels parallel to the axis after passing through the lens. Thus any point on the ob ...
... · Ray 1 is the ray which travels parallel to the axis and after going through the lens it passes through the focal point. · Ray 2 passes through the center of the lens. · Ray 3 goes through the focal point and then travels parallel to the axis after passing through the lens. Thus any point on the ob ...
Thin Lenses
... image of a given object when geometric characteristics of the optical device are known. ...
... image of a given object when geometric characteristics of the optical device are known. ...
Chapter 25
... Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave nature of light must be used ...
... Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave nature of light must be used ...
Here
... – In considering thin lens combinations, apply the this lens equation to each lens so that the image of one lens is the object of the next lens in the system. Ray 2 leaves the object and is parallel to the optical axis. Ray 3 goes through an object focus and strikes the lens. – In geometric construc ...
... – In considering thin lens combinations, apply the this lens equation to each lens so that the image of one lens is the object of the next lens in the system. Ray 2 leaves the object and is parallel to the optical axis. Ray 3 goes through an object focus and strikes the lens. – In geometric construc ...
Ray Tracing
... double, or any number of thin lenses, one can follow this simple procedure to achieve a satisfactory solution. Basically all of these problems are about locating the final image given an object and a (set of) lens (lenses). A single thin convex lens is always a good start. Suppose the lens has a foc ...
... double, or any number of thin lenses, one can follow this simple procedure to achieve a satisfactory solution. Basically all of these problems are about locating the final image given an object and a (set of) lens (lenses). A single thin convex lens is always a good start. Suppose the lens has a foc ...
Camera

A camera is an optical instrument for recording images, which may be stored locally, transmitted to another location, or both. The images may be individual still photographs or sequences of images constituting videos or movies. The word camera comes from camera obscura, which means ""dark chamber"" and is the Latin name of the original device for projecting an image of external reality onto a flat surface. The modern photographic camera evolved from the camera obscura. The functioning of the camera is very similar to the functioning of the human eye.