Furosemide Edema, initial dose: 20-40 mg/dose IV or IM
... Drug Usual Adult Dosage Furosemide Edema, initial dose: 20-40 mg/dose IV or IM every 2 hours as needed. Increase the dose by 20 mg every 2 hours until desired effects are seen. Edema, maintenance dosage: Give the effective dose once or twice daily. Up to 4 grams/day in patients with congestive heart ...
... Drug Usual Adult Dosage Furosemide Edema, initial dose: 20-40 mg/dose IV or IM every 2 hours as needed. Increase the dose by 20 mg every 2 hours until desired effects are seen. Edema, maintenance dosage: Give the effective dose once or twice daily. Up to 4 grams/day in patients with congestive heart ...
Table 2. Dosage regimens of injectable loop diuretics7
... Drug Usual Adult Dosage Furosemide Edema, initial dose: 20-40 mg/dose IV or IM every 2 hours as needed. Increase the dose by 20 mg every 2 hours until desired effects are seen. Edema, maintenance dosage: Give the effective dose once or twice daily. Up to 4 grams/day in patients with congestive heart ...
... Drug Usual Adult Dosage Furosemide Edema, initial dose: 20-40 mg/dose IV or IM every 2 hours as needed. Increase the dose by 20 mg every 2 hours until desired effects are seen. Edema, maintenance dosage: Give the effective dose once or twice daily. Up to 4 grams/day in patients with congestive heart ...
PDF
... the hypothalamic level, estrogen receptor depletion prevents the negative feed back of estrogen that activates pulsatile gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) secretion, which in turn results in increased pituitary gonadotropin hormones and ovarian follicular growth (2). In addition to its central a ...
... the hypothalamic level, estrogen receptor depletion prevents the negative feed back of estrogen that activates pulsatile gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) secretion, which in turn results in increased pituitary gonadotropin hormones and ovarian follicular growth (2). In addition to its central a ...
Chemistry 400 A
... 15. Which functional group was critical in making a birth control pill that could be taken orally? 16. What structural feature distinguishes estrogen from both progesterone and testosterone? 17. Depo-provera is a long lasting progesterone mimic. What functional group is present to achieve this effec ...
... 15. Which functional group was critical in making a birth control pill that could be taken orally? 16. What structural feature distinguishes estrogen from both progesterone and testosterone? 17. Depo-provera is a long lasting progesterone mimic. What functional group is present to achieve this effec ...
Bio 160 – Endocrine System
... time, duration of effects, type of signaling (electrical? Chemical?), type of effects on body, etc Where are endocrine tissues found in the body (provide specific examples)? Name the major endocrine glands in the body How are hormones usually classified, and give specific examples of each category H ...
... time, duration of effects, type of signaling (electrical? Chemical?), type of effects on body, etc Where are endocrine tissues found in the body (provide specific examples)? Name the major endocrine glands in the body How are hormones usually classified, and give specific examples of each category H ...
Endocrine Systems - Science Geek.net
... A. Prolactin 1. Produced in the anterior pituitary a. Initiates milk production in the mammary glands 2. Regulation by prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH) from hypothalamus a. High levels of estrogen during pregnancy stimulate release of PIH (1) PIH inhibits prolactin release b. Low levels of estroge ...
... A. Prolactin 1. Produced in the anterior pituitary a. Initiates milk production in the mammary glands 2. Regulation by prolactin-inhibiting hormone (PIH) from hypothalamus a. High levels of estrogen during pregnancy stimulate release of PIH (1) PIH inhibits prolactin release b. Low levels of estroge ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) – follicles in ovaries and sperm in testes • (women) Luteinizing hormone (LH) – ovulation of egg • (men) Interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) – testosterone production in testes ...
... • Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) – follicles in ovaries and sperm in testes • (women) Luteinizing hormone (LH) – ovulation of egg • (men) Interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) – testosterone production in testes ...
PowerPoint - Pitt Honors Human Physiology
... Affects water reabsorption in kidney at lower concentrations, hence the secondary name: antidiuretic hormone ...
... Affects water reabsorption in kidney at lower concentrations, hence the secondary name: antidiuretic hormone ...
Physio Lab 4 Endocrine in PhysioEx
... As a female ages, her female levels go down, and the male hormones appear to get higher, but they stay the same, get more hair. Male hormones lower with age too; their female hormone catch up, get more female characteristics. With age, she looks more dominate, he looks softer. Hormone replacement th ...
... As a female ages, her female levels go down, and the male hormones appear to get higher, but they stay the same, get more hair. Male hormones lower with age too; their female hormone catch up, get more female characteristics. With age, she looks more dominate, he looks softer. Hormone replacement th ...
Adrenal Glands
... (with blood pressure <180/110 mm Hg) can safely be given up to 0.036 mg epinephrine (two cartridges containing 1:100,000 epinephrine) at one appointment (the benefits of its use far outweighing any potential problems); intravascular injections are to be avoided. An additional concern with patients ...
... (with blood pressure <180/110 mm Hg) can safely be given up to 0.036 mg epinephrine (two cartridges containing 1:100,000 epinephrine) at one appointment (the benefits of its use far outweighing any potential problems); intravascular injections are to be avoided. An additional concern with patients ...
Endocrine System - Dr. Diamond`s Website
... – a specific protein within the nucleus – specific sites on the cell’s DNA ...
... – a specific protein within the nucleus – specific sites on the cell’s DNA ...
Emergency Contraception - Association of Reproductive Health
... To make an informed choice, women must know that ECPs—like all regular hormonal contraceptives such as the birth control pill, the implant Norplant, the vaginal ring NuvaRing, the Evra patch, and the injectables Lunelle and Depo-Provera,57 and even breastfeeding58,59,60,61— may prevent pregnancy by ...
... To make an informed choice, women must know that ECPs—like all regular hormonal contraceptives such as the birth control pill, the implant Norplant, the vaginal ring NuvaRing, the Evra patch, and the injectables Lunelle and Depo-Provera,57 and even breastfeeding58,59,60,61— may prevent pregnancy by ...
Follicle-stimulating Hormone (FSH) FSH is a hormone made by the
... FSH is a hormone made by the anterior pituitary gland. In women, during the first half of the menstrual cycle, FSH stimulates the growth and maturation of follicles in the ovaries and also, production of estradiol. In men, FSH stimulates production of sperm and promotes the production of androgen bi ...
... FSH is a hormone made by the anterior pituitary gland. In women, during the first half of the menstrual cycle, FSH stimulates the growth and maturation of follicles in the ovaries and also, production of estradiol. In men, FSH stimulates production of sperm and promotes the production of androgen bi ...
45_InstGuide_AR
... separate control mechanisms. Emphasize to your students that these important systems work together to regulate a number of physiological processes, that some molecules function both as hormones in the endocrine system and as chemical messengers in the nervous system, and that the hypothalamus and pi ...
... separate control mechanisms. Emphasize to your students that these important systems work together to regulate a number of physiological processes, that some molecules function both as hormones in the endocrine system and as chemical messengers in the nervous system, and that the hypothalamus and pi ...
Packaging the Pill
... participants could be dismissed as the result of a deliberate choice to become pregnant or the result of a woman's failure to follow instructions, the contraceptive could be deemed 100% successful. Researchers acknowledged that compliance was a problem, but considered it an issue primarily for inter ...
... participants could be dismissed as the result of a deliberate choice to become pregnant or the result of a woman's failure to follow instructions, the contraceptive could be deemed 100% successful. Researchers acknowledged that compliance was a problem, but considered it an issue primarily for inter ...
Emergency Contraception abstract
... Nearly 80% of pregnancies in adolescents are unintended12 and result from contraceptive failure or nonuse. The most commonly used method of contraception reported by teenagers who have had intercourse is the condom, followed by withdrawal and the oral contraceptive pill.9 Research has shown, however ...
... Nearly 80% of pregnancies in adolescents are unintended12 and result from contraceptive failure or nonuse. The most commonly used method of contraception reported by teenagers who have had intercourse is the condom, followed by withdrawal and the oral contraceptive pill.9 Research has shown, however ...
A O
... policotrop affects the secretion of LH and FSH. LH and FSH through the systemic circulation to the gonads and connected to your receiver and stimulate the growth of follicles and product of secondary follicles. LH hormone and follicle-graph can also cause efflorescence. If you are not pregnant after ...
... policotrop affects the secretion of LH and FSH. LH and FSH through the systemic circulation to the gonads and connected to your receiver and stimulate the growth of follicles and product of secondary follicles. LH hormone and follicle-graph can also cause efflorescence. If you are not pregnant after ...
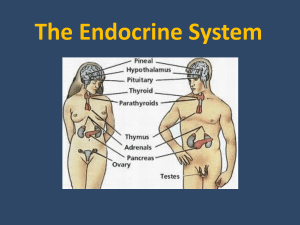
The Endocrine System
... •The endocrine system secretes hormones that stimulate growth and many kinds of reactions, such as activity levels and moods. •The major endocrine glands include the pituitary, the thyroid, the adrenals, the testes, and the ovaries. ...
... •The endocrine system secretes hormones that stimulate growth and many kinds of reactions, such as activity levels and moods. •The major endocrine glands include the pituitary, the thyroid, the adrenals, the testes, and the ovaries. ...
Lecture 15
... - messengers transported via blood/lymph structures that produce/release hormones cause short to long lasting changes in target cells with receptors for them ...
... - messengers transported via blood/lymph structures that produce/release hormones cause short to long lasting changes in target cells with receptors for them ...
Endocrine System
... • Hypothalamus-secretes many hormones that regulate the pituitary • Pituitary makes hormones that stimulate adrenals, thyroid, growth, and the production of ova and sperm • Thyroid-regulates metabolism • Parathroid-regulates calcium levels • Thymus-T-cell development • Adrenals-make adrenalin for fl ...
... • Hypothalamus-secretes many hormones that regulate the pituitary • Pituitary makes hormones that stimulate adrenals, thyroid, growth, and the production of ova and sperm • Thyroid-regulates metabolism • Parathroid-regulates calcium levels • Thymus-T-cell development • Adrenals-make adrenalin for fl ...
Summer Board review General Medicine Session 3
... for a palpable breast mass, which should be evaluated until diagnosis or resolution. ...
... for a palpable breast mass, which should be evaluated until diagnosis or resolution. ...
chapter 50 endocrine systems
... small number of physically connected tissues and organs Nearly all cells release chemical signals (hormones) Some hormone producing cells packaged in discrete glands- endocrine glands Hormones effects can occur in seconds or hours and may last a few minutes or several days ...
... small number of physically connected tissues and organs Nearly all cells release chemical signals (hormones) Some hormone producing cells packaged in discrete glands- endocrine glands Hormones effects can occur in seconds or hours and may last a few minutes or several days ...
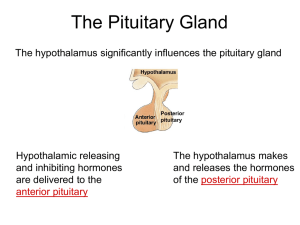
17. Pituitary and Adrenal Glands
... TSH – stimulates secretion of thyroid hormone and the growth of the thyroid gland. Important regulator of metabolic activity in the body. ...
... TSH – stimulates secretion of thyroid hormone and the growth of the thyroid gland. Important regulator of metabolic activity in the body. ...
Endocrine Problems after Childhood Cancer: Hypopituitarism
... Growth hormone affects the growth of body tissues and bone as well as fat, muscle, and sugar metabolism. For more information about growth hormone problems, see the related Health Link: Growth Hormone Deficiency. Gonadotropin (FSH, LH) deficiency: LH and FSH control the production of male and female ...
... Growth hormone affects the growth of body tissues and bone as well as fat, muscle, and sugar metabolism. For more information about growth hormone problems, see the related Health Link: Growth Hormone Deficiency. Gonadotropin (FSH, LH) deficiency: LH and FSH control the production of male and female ...