* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
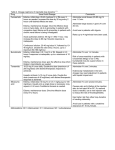
Download Table 2. Dosage regimens of injectable loop diuretics7
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Dextropropoxyphene wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Dydrogesterone wikipedia , lookup
Table 2. Dosage regimens of injectable loop diuretics7-12 Drug Usual Adult Dosage Furosemide Edema, initial dose: 20-40 mg/dose IV or IM every 2 hours as needed. Increase the dose by 20 mg every 2 hours until desired effects are seen. Edema, maintenance dosage: Give the effective dose once or twice daily. Up to 4 grams/day in patients with congestive heart failure and 6 grams/day in patients with chronic renal failure is being investigated. Comments Administer small doses (20-80 mg) IV over 1-2 min. Administer large doses (1 gram) IV over 30 min. Avoid use in patients with oliguria. Rates up to 4 mg/minute have been used. Acute pulmonary edema: 40 mg IV. After 1 hour, may increase the dose to 80 mg if diuretic response is inadequate. Bumetanide Torsemide Ethacrynic acid Continuous infusion: 20-40 mg bolus IV, followed by 1040 mg/hour. Double the rate every 2 hours, up to a maximum 80-160 mg/hour. Edema, initial dose: 0.5-1 mg IV or IM. Repeat in 2-3 hours if response is inadequate, up to a maximum of 10 mg/day. Edema, maintenance dose: give the effective dose (from titration) intermittently as needed. 10-20 mg IV once daily. Double the dose (maximum of 200 mg/dose) until desired therapeutic response is achieved. Hepatic cirrhosis: 5-10 mg IV once daily. Double the dose (maximum of 40 mg/dose) until desired therapeutic response is achieved. Edema, initial dose: 50 mg IV or 0.5-1 mg/kg (up to 100 mg/dose). Usually only a single dose is necessary; may repeat in 2-4 hours if additional diuresis is needed. Edema, maintenance dose: Give the effective dose every 8-12 hours. Administer IV over 1-2 minutes. Risk of cross-reactivity in patients with furosemide allergy is low (1:40); bumetanide may be a good choice in these patients. Administer IV over 2 minutes. Extensively metabolized in the liver; dosage may need adjustment in patients with hepatic impairment. Administer IV over several minutes. Causes pain and irritation at the injection site; do not inject IM or SC. If a second dose is needed, use a new injection site to reduce the risk of thrombophlebitis. Has higher risk than other loop diuretics of causing ototoxicity. Avoid use in patients with a creatinine clearance of< 10 mL/minute. Abbreviations: IM = intramuscular; IV = intravenous; SC = subcutaneous