In a 1-celled organism
... – Membranes provide surface area for chemical rxns. – Various polypeptides are combined here to make 1 large protein molecule. – These are stored in vesicles and are released when needed. ...
... – Membranes provide surface area for chemical rxns. – Various polypeptides are combined here to make 1 large protein molecule. – These are stored in vesicles and are released when needed. ...
Cell Biology
... Protein gradient (higher conc inside ring) makes spin. Not all pK’s have flagella Photosynthetic cyanobacterium Plasma membrane o Regulates uptake and release (pump) through channels/pores o Interfaces with environment Eukaryotes- compartmentalisation o Animal cell o Plant cell Adjacent walls, cel ...
... Protein gradient (higher conc inside ring) makes spin. Not all pK’s have flagella Photosynthetic cyanobacterium Plasma membrane o Regulates uptake and release (pump) through channels/pores o Interfaces with environment Eukaryotes- compartmentalisation o Animal cell o Plant cell Adjacent walls, cel ...
Cell communication Premedical Biology
... of double layer of phospholipids and incorporated proteins • controls traffic into and out of the cell • is selectively permeable, it allows sufficient ...
... of double layer of phospholipids and incorporated proteins • controls traffic into and out of the cell • is selectively permeable, it allows sufficient ...
Made of cisternae membrane sacs Sac of digestive enzymes that
... that surrounds ALL cells and controls which molecules enter or leave ...
... that surrounds ALL cells and controls which molecules enter or leave ...
Hypertonic solution
... hypertonic solution- a solution that contains more solutes, or dissolved substances, than there are inside cellsthe cells will shrink, or crenate as water moves outside the cell (this is because water is in higher concentration inside the cell than outside, so it follows its concentration gradient a ...
... hypertonic solution- a solution that contains more solutes, or dissolved substances, than there are inside cellsthe cells will shrink, or crenate as water moves outside the cell (this is because water is in higher concentration inside the cell than outside, so it follows its concentration gradient a ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Contain dozens of specialized structures called organelles. Includes protists, fungi, plants and animals. ...
... Contain dozens of specialized structures called organelles. Includes protists, fungi, plants and animals. ...
Document
... Usually attached to the outer surface These are different in each individual Cell recognition - “ID cards”, enable the body to ...
... Usually attached to the outer surface These are different in each individual Cell recognition - “ID cards”, enable the body to ...
Cells 1
... The growth of cells outside the body in an artificial medium is referred to as … In vivo ...
... The growth of cells outside the body in an artificial medium is referred to as … In vivo ...
Cell Structure Worksheet /25
... 5. Cells of the pancreas will incorporate radioactively labeled amino acids into a protein. This “tagging” of newly synthesized proteins allow researchers to track the location of these proteins in a cell. In this case, we are tracking an enzyme that is eventually secreted by pancreatic cells. Which ...
... 5. Cells of the pancreas will incorporate radioactively labeled amino acids into a protein. This “tagging” of newly synthesized proteins allow researchers to track the location of these proteins in a cell. In this case, we are tracking an enzyme that is eventually secreted by pancreatic cells. Which ...
Cells: Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
... Pathogenic – feed on living things The kind that make you sick! Decomposers – feed on dead things ...
... Pathogenic – feed on living things The kind that make you sick! Decomposers – feed on dead things ...
Organelles PPT
... As cell size increases, it’s ability to exchange materials with its environment becomes limited by the amount of membrane area that is available for exchange. ...
... As cell size increases, it’s ability to exchange materials with its environment becomes limited by the amount of membrane area that is available for exchange. ...
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
... – Pathogenic – feed on living things ! • The kind that make you sick!! ...
... – Pathogenic – feed on living things ! • The kind that make you sick!! ...
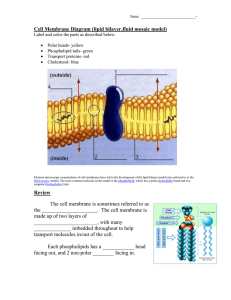
Cell Membrane Diagram (lipid bilayer,fluid mosaic model)
... fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
... fluid-mosaic model). The most common molecule in the model is the phospholipid, which has a polar (hydrophilic) head and two nonpolar (hydrophobic) tails. ...
animal cells
... wall, chloroplast, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum (use sheet that we filled out together) Water travels across a cell membrane during the process of osmosis Know how plant cells and animal cells are different In diffusion particles move to areas of lower concentrat ...
... wall, chloroplast, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum (use sheet that we filled out together) Water travels across a cell membrane during the process of osmosis Know how plant cells and animal cells are different In diffusion particles move to areas of lower concentrat ...
SBI 3C- The Cell: Part Two -use this note as a guide to fill in board
... Vacuoles: a large membrane-bound sac that takes up a large amount of space in most Plant Cells, LARGE vacuoles are only found in plant cells Structure: -a large membrane-bound sac filled with a watery solution -watery solution contains dissolved sugars, minerals, proteins Function: A.The vacuole ser ...
... Vacuoles: a large membrane-bound sac that takes up a large amount of space in most Plant Cells, LARGE vacuoles are only found in plant cells Structure: -a large membrane-bound sac filled with a watery solution -watery solution contains dissolved sugars, minerals, proteins Function: A.The vacuole ser ...
Organic Molecules - Riverdale Middle School
... • Contain the instructions that cells need to carry out all the functions of life • Red meat, shellfish, mushrooms, and peas • Examples: – DNA – genetic material that carries information about an organism; directs cell functions; found in the cell’s nucleus – RNA – makes proteins ...
... • Contain the instructions that cells need to carry out all the functions of life • Red meat, shellfish, mushrooms, and peas • Examples: – DNA – genetic material that carries information about an organism; directs cell functions; found in the cell’s nucleus – RNA – makes proteins ...
OLD BIO Cell
... B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving. D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids and proteins Cel ...
... B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving. D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids and proteins Cel ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.