Anton von Leeuwenhoek
... Nucleus-control center of the cell Chromosomes-provides direction for cell to follow Endoplasmic Reticulum-transportation network Mitchondrion-produces energy in the cell Vacuole-cell storage sac for food, waste and water ...
... Nucleus-control center of the cell Chromosomes-provides direction for cell to follow Endoplasmic Reticulum-transportation network Mitchondrion-produces energy in the cell Vacuole-cell storage sac for food, waste and water ...
1. Write scientific method down in order and describe each step
... •Smooth ER-- makes and modifies lipids • Mitochondria- Makes energy (ATP) for the cell by breaking down glucose •Vacuole- ...
... •Smooth ER-- makes and modifies lipids • Mitochondria- Makes energy (ATP) for the cell by breaking down glucose •Vacuole- ...
The Endomembrane System
... • Tags, sorts, & packages materials into transport vesicles – Golgi=“UPS headquarters” – Transport vesicles=“UPS trucks” • Delivering packages that have been tagged with their own barcode ...
... • Tags, sorts, & packages materials into transport vesicles – Golgi=“UPS headquarters” – Transport vesicles=“UPS trucks” • Delivering packages that have been tagged with their own barcode ...
Return to animal Cell
... semipermeable membrane. It is commonly used when describing the response of cells immersed in an external solution. Osmosis Demo Hypotonic Solution If water molecules continue to diffuse into the cell, it will cause the cell to swell, up to the point that cytolysis (rupture) may occur Isotonic solut ...
... semipermeable membrane. It is commonly used when describing the response of cells immersed in an external solution. Osmosis Demo Hypotonic Solution If water molecules continue to diffuse into the cell, it will cause the cell to swell, up to the point that cytolysis (rupture) may occur Isotonic solut ...
eukaryotic cell worksheet
... IB drawing rules. Your annotations of functions should not be included on the drawing but put underneath or on another piece of paper. The description of the organelle functions should be brief – not to exceed 10 words. 1. Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of an exocrine gland cell of t ...
... IB drawing rules. Your annotations of functions should not be included on the drawing but put underneath or on another piece of paper. The description of the organelle functions should be brief – not to exceed 10 words. 1. Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of an exocrine gland cell of t ...
Cells Test Tournament Review 1. What are 2 differences between
... Unwanted wastes and toxins might enter the cell; materials needed by the cell might diffuse out. Fluid = ability to change, move Pumps and channels Shrinking of a plant cell’s membrane Bursting of an animal cell’s membrane Interior Surfaces Help the body to recognize cells that are foreign ;Mosaic = ...
... Unwanted wastes and toxins might enter the cell; materials needed by the cell might diffuse out. Fluid = ability to change, move Pumps and channels Shrinking of a plant cell’s membrane Bursting of an animal cell’s membrane Interior Surfaces Help the body to recognize cells that are foreign ;Mosaic = ...
Transport in plants
... Plant cells need to be turgid (i.e rigid) to support plant tissues. Plant cells become turgid when water moves into the cell by osmosis, and the central vacuole swells and pushes against the cell wall. When plant cells are placed in concentrated sugar solutions they lose water by osmosis and they be ...
... Plant cells need to be turgid (i.e rigid) to support plant tissues. Plant cells become turgid when water moves into the cell by osmosis, and the central vacuole swells and pushes against the cell wall. When plant cells are placed in concentrated sugar solutions they lose water by osmosis and they be ...
Part a
... displace water molecules Osmolarity: The measure of total concentration of solute particles When solutions of different osmolarity are separated by a membrane, osmosis occurs until equilibrium is reached ...
... displace water molecules Osmolarity: The measure of total concentration of solute particles When solutions of different osmolarity are separated by a membrane, osmosis occurs until equilibrium is reached ...
Cells - Biology Junction
... 2. surrounds the outside of all cells 3. organisms made of more than one cell working together 5. cells like bacteria without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles 8. cell structures that perform specific functions for the cell 10. domain containing ancient bacterial forms 11. this determines the f ...
... 2. surrounds the outside of all cells 3. organisms made of more than one cell working together 5. cells like bacteria without a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles 8. cell structures that perform specific functions for the cell 10. domain containing ancient bacterial forms 11. this determines the f ...
Biology: Cell Unit Review
... Cells are basic unit of structure & function in organisms. All living organisms are composed of 1 or more cells. ...
... Cells are basic unit of structure & function in organisms. All living organisms are composed of 1 or more cells. ...
Structure and Function of Membranes
... Fluidity: • Phospholipid molecules move around constantly • Fluidity regulated by different kinds of fatty acid (FA) tails: • More unsaturated FA, membrane stays fluid at lower temp (winter) • More saturated FA, membrane is more stable at high temperatures (summer) • Cholesterol embedded in animal ...
... Fluidity: • Phospholipid molecules move around constantly • Fluidity regulated by different kinds of fatty acid (FA) tails: • More unsaturated FA, membrane stays fluid at lower temp (winter) • More saturated FA, membrane is more stable at high temperatures (summer) • Cholesterol embedded in animal ...
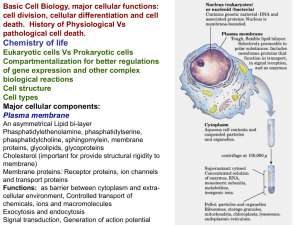
Basic Cell Biology
... if they have a lot of parasites robbing them of their nutrients. When the sugar in the ECF becomes too low, the cells do not have adequate energy. The puppy can become weak or develop seizures. Homeostasis is the maintenance of the ECF. Allows ...
... if they have a lot of parasites robbing them of their nutrients. When the sugar in the ECF becomes too low, the cells do not have adequate energy. The puppy can become weak or develop seizures. Homeostasis is the maintenance of the ECF. Allows ...
7-3 Cell Transport - MrKanesSciencePage
... No energy required Carrier proteins transport molecules across the membrane (from high to low concentrations) Molecules may be too big or cells may need to get the molecules quickly ...
... No energy required Carrier proteins transport molecules across the membrane (from high to low concentrations) Molecules may be too big or cells may need to get the molecules quickly ...
Looking Inside Cells
... • Nucleus • Acts as the “brain” of the cell • The cell’s control center, directs cell’s activities • Nuclear envelope • Nucleus is surrounded by this membrane • Materials pass in and out of the nucleus through pores in this structure • Chromatin • Contains instructions that direct the functions of a ...
... • Nucleus • Acts as the “brain” of the cell • The cell’s control center, directs cell’s activities • Nuclear envelope • Nucleus is surrounded by this membrane • Materials pass in and out of the nucleus through pores in this structure • Chromatin • Contains instructions that direct the functions of a ...
Study Topics in AP Biology Listed by Big Idea (Pat Mote)
... 10. Hydrolysis vs. dehydration synthesis 11. Energy capturing: NADP, NAD, Oxygen 12. Light reactions of photosynthesis vs. Calvin Cycle 13. Cell respiration: ATP production, electron pathways 14. Chemiosmosis 15. Use of carbon in ecosystems 16. Use of nitrogen in ecosystems 17. Properties of water 1 ...
... 10. Hydrolysis vs. dehydration synthesis 11. Energy capturing: NADP, NAD, Oxygen 12. Light reactions of photosynthesis vs. Calvin Cycle 13. Cell respiration: ATP production, electron pathways 14. Chemiosmosis 15. Use of carbon in ecosystems 16. Use of nitrogen in ecosystems 17. Properties of water 1 ...
File
... from passive? Complete the chart. 2. What part of the cell is used to bring in particles? 3. How does a cell (including white blood cells) take in LARGE particles? 4. How does a cell take in small or liquid particles? ...
... from passive? Complete the chart. 2. What part of the cell is used to bring in particles? 3. How does a cell (including white blood cells) take in LARGE particles? 4. How does a cell take in small or liquid particles? ...
Practice Quiz
... golgi apparatus 2. The organelle functions to package and deliver proteins: lysosome endoplasmic reticulum mitochondrion golgi apparatus 3. Cell organelles are located within the ____ of the cell. nucleus cytoplasm cell membrane lysosomes 4. The endoplasmic reticulum functions to: transport material ...
... golgi apparatus 2. The organelle functions to package and deliver proteins: lysosome endoplasmic reticulum mitochondrion golgi apparatus 3. Cell organelles are located within the ____ of the cell. nucleus cytoplasm cell membrane lysosomes 4. The endoplasmic reticulum functions to: transport material ...
Cells Vocabulary - jeffyoshimura.com
... A specialized structure in the nucleus, formed from various chromosomes and active in the synthesis of ribosomes. The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane. A microbody containing enzymes that transfer hydrogen from vari ...
... A specialized structure in the nucleus, formed from various chromosomes and active in the synthesis of ribosomes. The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. The diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane. A microbody containing enzymes that transfer hydrogen from vari ...
2 ONION SKIN (200x) 3 GREEN LEAF (300x) 4 CHEEK CELLS (900x)
... Lying in the cytoplasm is a darker round body called the nucleus. C points to a nucleus. How many nuclei does each cell of the onion skin have? The membrane (D) in the fresh onion skin is hard to see because it lies flat against the inner surface of the wall. Most cells have these three parts: a mem ...
... Lying in the cytoplasm is a darker round body called the nucleus. C points to a nucleus. How many nuclei does each cell of the onion skin have? The membrane (D) in the fresh onion skin is hard to see because it lies flat against the inner surface of the wall. Most cells have these three parts: a mem ...
Slide 1
... Double membrane-bound structures, power plants of eukaryotic cells Site for citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation and fatty acid metabolism in energy generating biochemical pathway Outer mitochondrial membrane Inter-membrane space Inner mitochondrial membrane (contains components of electr ...
... Double membrane-bound structures, power plants of eukaryotic cells Site for citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation and fatty acid metabolism in energy generating biochemical pathway Outer mitochondrial membrane Inter-membrane space Inner mitochondrial membrane (contains components of electr ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ AP Biology: Unit 5, DBA #1 Review Ms
... ________________________E. Structures made of microtubules that are used for movement… they are short and numerous on the outside of the cell. ________________________F. Structures made of microtubules that are used for movement… they are long and there are usually 1-3 of them on the outside of a ce ...
... ________________________E. Structures made of microtubules that are used for movement… they are short and numerous on the outside of the cell. ________________________F. Structures made of microtubules that are used for movement… they are long and there are usually 1-3 of them on the outside of a ce ...
I can now explain how the different specialized organelles
... I can now explain how the different specialized organelles processes and needs inside a cell. The evidence that I uploaded is my poster I drew of a cell showing all the different organelles and where they are located inside the cell. What I can explain now is different because in the past I knew org ...
... I can now explain how the different specialized organelles processes and needs inside a cell. The evidence that I uploaded is my poster I drew of a cell showing all the different organelles and where they are located inside the cell. What I can explain now is different because in the past I knew org ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.