Animal and Plant Cells
... The Cell Each cell must accomplish certain tasks to stay alive: • Breathe • Nourish itself • Repair itself • Reproduce • Eliminate waste The cell has internal structures called ORGANELLES which accomplish these tasks. ...
... The Cell Each cell must accomplish certain tasks to stay alive: • Breathe • Nourish itself • Repair itself • Reproduce • Eliminate waste The cell has internal structures called ORGANELLES which accomplish these tasks. ...
Apple Osmosis Lab - A Taste of Chemistry
... Water passes through aquaporins in cell membranes from an area of high water concentration (low solute concentration) to an area of low water concentration (high solute concentration). This process is called osmosis. It requires no cellular energy to be used, and occurs due to the random, continuous ...
... Water passes through aquaporins in cell membranes from an area of high water concentration (low solute concentration) to an area of low water concentration (high solute concentration). This process is called osmosis. It requires no cellular energy to be used, and occurs due to the random, continuous ...
CELL ANALOGY PICTURE BOOK
... Cell(plasma)membrane Cell(plasma) membrane Cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton ...
... Cell(plasma)membrane Cell(plasma) membrane Cytoskeleton Cytoskeleton ...
GCMS lesson plan September 5
... brings the stories they developed to life. Today is the final day for the students to draw and color their cell city. The student’s projects will be submitted Wednesday. Teacher Input: TTW monitor the students as they develop their projects using PowerPoint. TTW assist the students as needed. Closur ...
... brings the stories they developed to life. Today is the final day for the students to draw and color their cell city. The student’s projects will be submitted Wednesday. Teacher Input: TTW monitor the students as they develop their projects using PowerPoint. TTW assist the students as needed. Closur ...
G protein
... Testosterone, like other hormones, travels through the blood and enters cells throughout the body. In the cytosol, they bind and activate receptor proteins. These activated proteins enter the nucleus and turn on genes that control male sex ...
... Testosterone, like other hormones, travels through the blood and enters cells throughout the body. In the cytosol, they bind and activate receptor proteins. These activated proteins enter the nucleus and turn on genes that control male sex ...
Introduction to Cells
... The cell is the smallest unit that retains the properties of life. Under current conditions, all cells come from pre-existing cells. All cells DO have an outer membrane (called the plasma membrane), but this observation is not considered part of the cell theory. ...
... The cell is the smallest unit that retains the properties of life. Under current conditions, all cells come from pre-existing cells. All cells DO have an outer membrane (called the plasma membrane), but this observation is not considered part of the cell theory. ...
1. The transport method of neurotransmitters between nerve cells is
... 11. What is the primary factor that determines if endocytosis or exocytosis would be needed to move a substance across the cell membrane as opposed to diffusion or osmosis? a. the chemical properties of the molecules being moved b. the size of the molecules being moved c. the differences in concentr ...
... 11. What is the primary factor that determines if endocytosis or exocytosis would be needed to move a substance across the cell membrane as opposed to diffusion or osmosis? a. the chemical properties of the molecules being moved b. the size of the molecules being moved c. the differences in concentr ...
Notes for Organelles and Function
... If a cell needs a lot of energy…it will have more mitochondria ...
... If a cell needs a lot of energy…it will have more mitochondria ...
Keystone Quia Quiz—Cell Physiology Unit Question Source and
... In a cell, which of the following organelles most likely contains digestive enzymes? A. centriole B. chloroplast C. lysosome ** D. ribosome North Carolina—2008 (2) Standard BIO.A.1.2.1 Some organelles have their own DNA that is distinct from the cell’s nuclear DNA. This is true of which organelle? A ...
... In a cell, which of the following organelles most likely contains digestive enzymes? A. centriole B. chloroplast C. lysosome ** D. ribosome North Carolina—2008 (2) Standard BIO.A.1.2.1 Some organelles have their own DNA that is distinct from the cell’s nuclear DNA. This is true of which organelle? A ...
me239 mechanics of the cell 1.2 introduction to the cell 1.2
... intermediate filaments, microtubules can also bear compression. in addition, they form a highway for intracellular transport. ...
... intermediate filaments, microtubules can also bear compression. in addition, they form a highway for intracellular transport. ...
bk1B_ch09_sug ans_e
... dissolve in the moist surface of the mesophyll cells. They then diffuse to the neighbouring cells. 1m Gases diffuse from the leaves to the environment in the reverse way. In woody stems, gas exchange takes place through the lenticels. ...
... dissolve in the moist surface of the mesophyll cells. They then diffuse to the neighbouring cells. 1m Gases diffuse from the leaves to the environment in the reverse way. In woody stems, gas exchange takes place through the lenticels. ...
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
... • The smooth endoplasmic reticulum has functions in several metabolic processes, including synthesis of lipids, metabolism of carbohydrates and calcium concentration, and attachment of receptors on cell membrane proteins. It is connected to the nuclear envelope. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is foun ...
... • The smooth endoplasmic reticulum has functions in several metabolic processes, including synthesis of lipids, metabolism of carbohydrates and calcium concentration, and attachment of receptors on cell membrane proteins. It is connected to the nuclear envelope. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is foun ...
Unit 2
... The hydrophobic core of the membrane impedes the transport of ions and polar molecules which are hydrophilic. Hydrophobic molecules can dissolve in the membrane and cross it with ease. Hydrophobic substances pass through membranes rapidly because of their solubility in the lipid bilayer. Larger pola ...
... The hydrophobic core of the membrane impedes the transport of ions and polar molecules which are hydrophilic. Hydrophobic molecules can dissolve in the membrane and cross it with ease. Hydrophobic substances pass through membranes rapidly because of their solubility in the lipid bilayer. Larger pola ...
Ch. 8 Cells & Their Environment
... 3. What is diffusion? Why is diffusion an example of passive transport? - The movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, down the concentration gradient. ...
... 3. What is diffusion? Why is diffusion an example of passive transport? - The movement of substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration, down the concentration gradient. ...
Relation types used in CL
... “mature natural killer cell” has_low_plasma_membrane_amount “neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (CD56)” ...
... “mature natural killer cell” has_low_plasma_membrane_amount “neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (CD56)” ...
Plant vs Animal Cell Activity
... Target Concept: Identify differences between plant and animal cells, learn function and structure of cell organelles (cell wall, cell membrane, vacuole, chloroplasts, flagella, cilia) Standards Addressed: Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of ce ...
... Target Concept: Identify differences between plant and animal cells, learn function and structure of cell organelles (cell wall, cell membrane, vacuole, chloroplasts, flagella, cilia) Standards Addressed: Standard B-2: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the structure and function of ce ...
-Always keep cell specimens hydrated with water when making slides
... Make a chart of all cell structures which can be observed in eukaryotic cells and the primary function of each. ** List those which CAN be viewed with the light microscope first, followed by those which require an electron microscope. Designate . ** Use an asterisk to identify any structures which a ...
... Make a chart of all cell structures which can be observed in eukaryotic cells and the primary function of each. ** List those which CAN be viewed with the light microscope first, followed by those which require an electron microscope. Designate . ** Use an asterisk to identify any structures which a ...
The Cell Organelle Worksheet
... __enters__ and leaves the cell. Phospholipids or PROTEINS scattered across the surface of the membrane act as the doorways into and out of the cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a series of double membranes that _transport substances__ back and forth between the cell membrane and the _Golgi Body__, ...
... __enters__ and leaves the cell. Phospholipids or PROTEINS scattered across the surface of the membrane act as the doorways into and out of the cell. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a series of double membranes that _transport substances__ back and forth between the cell membrane and the _Golgi Body__, ...
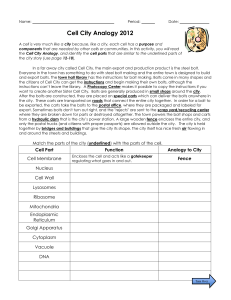
Cell City Analogy - Rochester Community Schools
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
Cell Organelles
... All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing cell. ...
... All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing cell. ...
Active Transport
... energy, but.... • As living beings, we NEED energy to sustain life processes. We eat food containing nutrients for energy, glucose being one of them. – Recall: glucose cannot be sustained inside body as it is soluble, so it must be converted into glycogen to get energy “stores” – This conversion MAK ...
... energy, but.... • As living beings, we NEED energy to sustain life processes. We eat food containing nutrients for energy, glucose being one of them. – Recall: glucose cannot be sustained inside body as it is soluble, so it must be converted into glycogen to get energy “stores” – This conversion MAK ...
Cell Growth & Division Notes
... life is spent in interphase Longest phase – (90% of cell’s growth) ...
... life is spent in interphase Longest phase – (90% of cell’s growth) ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.