Membrane WS
... The above four containers represent solutions with different concentrations of solutes. Answer the following questions using what you know about osmosis and diffusion. 1. Which container has the greatest concentration of solutes? 2. Which container has the least concentration of solutes? 3. The mov ...
... The above four containers represent solutions with different concentrations of solutes. Answer the following questions using what you know about osmosis and diffusion. 1. Which container has the greatest concentration of solutes? 2. Which container has the least concentration of solutes? 3. The mov ...
Cell Organelles Powerpoint 1
... 4) The best reason to explain why cells are so small is... a) being small allows them to maximize their chemical reactions b) being small makes it easier to move materials in and out of the cell c) being small makes it harder for a cell to loose the organelles inside it d) being small gives the cel ...
... 4) The best reason to explain why cells are so small is... a) being small allows them to maximize their chemical reactions b) being small makes it easier to move materials in and out of the cell c) being small makes it harder for a cell to loose the organelles inside it d) being small gives the cel ...
IB Biology Summer Assignment WHS
... Transport across membranes Some molecules cross membranes without using any energy and other molecules need cell energy to cross. ...
... Transport across membranes Some molecules cross membranes without using any energy and other molecules need cell energy to cross. ...
Warm Up (5 minutes)
... (solvent) and substances that are dissolved in water (solutes) In other words, they are located in solutions There are 3 types of solutions in which cells can ...
... (solvent) and substances that are dissolved in water (solutes) In other words, they are located in solutions There are 3 types of solutions in which cells can ...
Diffusion Worksheet
... Define dialysis: __________________________________________________________________ Define osmosis: __________________________________________________________________ Define facilitated diffusion: ________________________________________________________ Define filtration: ___________________________ ...
... Define dialysis: __________________________________________________________________ Define osmosis: __________________________________________________________________ Define facilitated diffusion: ________________________________________________________ Define filtration: ___________________________ ...
Stages of the cell cycle
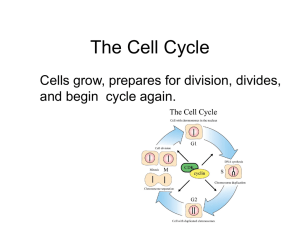
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
... The Cell Cycle Cells grow, prepares for division, divides, and begin cycle again. ...
CH05_Lecture
... to stimulus (chemical or electrical) – 3 conditions determine direction • Relative concentration on either side of membrane • Voltage differences across membrane • Gated channels – channel open or closed ...
... to stimulus (chemical or electrical) – 3 conditions determine direction • Relative concentration on either side of membrane • Voltage differences across membrane • Gated channels – channel open or closed ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... 2. What is the function of the nucleus of every cell? 3. What does every cell within the human body have the same of? 4. Why is a liver cell different from a muscle cell? Click on “Mitochondria.” 5. What ...
... 2. What is the function of the nucleus of every cell? 3. What does every cell within the human body have the same of? 4. Why is a liver cell different from a muscle cell? Click on “Mitochondria.” 5. What ...
The Cell Cycle - KathleenMihokWilmU
... - largest portion of cell’s life - cells that don’t divide (nerve cells) stay in G1 phase their whole life S Phase (synthesis phase) - DNA copied - at end, each chromosome consists of 2 chromatids ...
... - largest portion of cell’s life - cells that don’t divide (nerve cells) stay in G1 phase their whole life S Phase (synthesis phase) - DNA copied - at end, each chromosome consists of 2 chromatids ...
Cell Surfaces and Junctions
... functions, they must work together. • For example, macrophages use actin filaments to move and extend pseudopodia, capturing their prey, bacteria. • Food vacuoles are digested by lysosomes, a product of the endomembrane system of ER and Golgi. ...
... functions, they must work together. • For example, macrophages use actin filaments to move and extend pseudopodia, capturing their prey, bacteria. • Food vacuoles are digested by lysosomes, a product of the endomembrane system of ER and Golgi. ...
Although they are both eukaryotic cells, there are unique
... and light energy to make glucose and oxygen. This is a major difference between plants and animals; plants (autotrophs) are able to make their own food, like sugars, while animals (heterotrophs) must ingest their food. Like mitochondria, chloroplasts have outer and inner membranes, but within the sp ...
... and light energy to make glucose and oxygen. This is a major difference between plants and animals; plants (autotrophs) are able to make their own food, like sugars, while animals (heterotrophs) must ingest their food. Like mitochondria, chloroplasts have outer and inner membranes, but within the sp ...
The Cell in Action
... materials between a Cell Membrane cell and its environment takes “The Gate Keeper” place at the cell’s membrane. • The cell membrane is semipermeable which means that only certain substances can pass through. • To understand how materials move into and out of the cell, you need to know about diffusi ...
... materials between a Cell Membrane cell and its environment takes “The Gate Keeper” place at the cell’s membrane. • The cell membrane is semipermeable which means that only certain substances can pass through. • To understand how materials move into and out of the cell, you need to know about diffusi ...
Cell Structure and Function Guided Notes
... b. Cells are the basic unit of _____________________________________________________ in an organism (basic unit of life). c. Cells come from the reproduction of ___________________________________________________ (cell division). 7. Cells, the basic units of organisms, can __________________________ ...
... b. Cells are the basic unit of _____________________________________________________ in an organism (basic unit of life). c. Cells come from the reproduction of ___________________________________________________ (cell division). 7. Cells, the basic units of organisms, can __________________________ ...
cell unit targets - www .alexandria .k12 .mn .us
... Cell Biology is an exploding field with many job opportunities. Cell Biologists battle cancer, create Clones of animals and plants, maintain frozen embryos of endangered species, teach bacteria to make medicines for human use, and many other exciting things. If you are interested in cells or any top ...
... Cell Biology is an exploding field with many job opportunities. Cell Biologists battle cancer, create Clones of animals and plants, maintain frozen embryos of endangered species, teach bacteria to make medicines for human use, and many other exciting things. If you are interested in cells or any top ...
Cells
... The cell wall is found surrounding plant cells only This surrounds the cell membrane of a plant cell and gives the cell protection and ...
... The cell wall is found surrounding plant cells only This surrounds the cell membrane of a plant cell and gives the cell protection and ...
Document
... The cell membrane has a two-layered structure mainly made of protein, lipid and carbohydrate molecules Protein molecules are embedded in the lipid bilayer Carbohydrate molecules may branch out from the external surface of the membrane ...
... The cell membrane has a two-layered structure mainly made of protein, lipid and carbohydrate molecules Protein molecules are embedded in the lipid bilayer Carbohydrate molecules may branch out from the external surface of the membrane ...
Chapter 12
... The aim is to produce two identical daughter cells each containing exact replicas of the mother cell’s chromosomes (this means the entire genome = all genes need to be duplicated exactly). Thus, all the DNA must be copied so there are two complete sets, one set for each daughter cell. The outline o ...
... The aim is to produce two identical daughter cells each containing exact replicas of the mother cell’s chromosomes (this means the entire genome = all genes need to be duplicated exactly). Thus, all the DNA must be copied so there are two complete sets, one set for each daughter cell. The outline o ...
(1.2) Cell Division (p22-27)
... Cell Division • Cells must divide to survive. • There is a limit to how large a cell can grow. • If the amount of material in a cell is too large the cell dies. ...
... Cell Division • Cells must divide to survive. • There is a limit to how large a cell can grow. • If the amount of material in a cell is too large the cell dies. ...
Transport through the cell membrane
... sodium through the cell membrane. This is called co-transport. The carrier in this instance has as an attachment site for both the sodium ion and the substance. Once they both are attached, the energy gradient of the sodium ion causes both the sodium ion and the other substance to be transported tog ...
... sodium through the cell membrane. This is called co-transport. The carrier in this instance has as an attachment site for both the sodium ion and the substance. Once they both are attached, the energy gradient of the sodium ion causes both the sodium ion and the other substance to be transported tog ...
Slide 1
... Microtubules are conveyer belts inside the cells. They move vesicles, granules, organelles like mitochondria, and chromosomes via special attachment proteins. They also serve a cytoskeletal role. Structurally, they are polymers of tubulin which is a globular protein.. The tubulin molecules are the b ...
... Microtubules are conveyer belts inside the cells. They move vesicles, granules, organelles like mitochondria, and chromosomes via special attachment proteins. They also serve a cytoskeletal role. Structurally, they are polymers of tubulin which is a globular protein.. The tubulin molecules are the b ...
Animal and Plant Cells
... The Cell Each cell must accomplish certain tasks to stay alive: • Breathe • Nourish itself • Repair itself • Reproduce • Eliminate waste The cell has internal structures called ORGANELLES which accomplish these tasks. ...
... The Cell Each cell must accomplish certain tasks to stay alive: • Breathe • Nourish itself • Repair itself • Reproduce • Eliminate waste The cell has internal structures called ORGANELLES which accomplish these tasks. ...
GCMS lesson plan September 5
... brings the stories they developed to life. Today is the final day for the students to draw and color their cell city. The student’s projects will be submitted Wednesday. Teacher Input: TTW monitor the students as they develop their projects using PowerPoint. TTW assist the students as needed. Closur ...
... brings the stories they developed to life. Today is the final day for the students to draw and color their cell city. The student’s projects will be submitted Wednesday. Teacher Input: TTW monitor the students as they develop their projects using PowerPoint. TTW assist the students as needed. Closur ...
Cytosol

The cytosol or intracellular fluid (ICF) or cytoplasmic matrix is the liquid found inside cells. It is separated into compartments by membranes. For example, the mitochondrial matrix separates the mitochondrion into many compartments.In the eukaryotic cell, the cytosol is within the cell membrane and is part of the cytoplasm, which also comprises the mitochondria, plastids, and other organelles (but not their internal fluids and structures); the cell nucleus is separate. In prokaryotes, most of the chemical reactions of metabolism take place in the cytosol, while a few take place in membranes or in the periplasmic space. In eukaryotes, while many metabolic pathways still occur in the cytosol, others are contained within organelles.The cytosol is a complex mixture of substances dissolved in water. Although water forms the large majority of the cytosol, its structure and properties within cells is not well understood. The concentrations of ions such as sodium and potassium are different in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid; these differences in ion levels are important in processes such as osmoregulation, cell signaling, and the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as endocrine, nerve and muscle cells. The cytosol also contains large amounts of macromolecules, which can alter how molecules behave, through macromolecular crowding.Although it was once thought to be a simple solution of molecules, the cytosol has multiple levels of organization. These include concentration gradients of small molecules such as calcium, large complexes of enzymes that act together to carry out metabolic pathways, and protein complexes such as proteasomes and carboxysomes that enclose and separate parts of the cytosol.