Cell Jeopardy Game
... following would you not find in a bacterial (prokaryotic) cell? -ribosomes -cell membrane -golgi bodies -DNA ...
... following would you not find in a bacterial (prokaryotic) cell? -ribosomes -cell membrane -golgi bodies -DNA ...
The Three Kingdoms of Life New Eukaryotic Phylogeny Alveolates
... Sporogony - 1 zygote gives rise to many sporozoites Gamogony - gamont gives rise to many gametes Merogony - process that increase the number of infective cells ...
... Sporogony - 1 zygote gives rise to many sporozoites Gamogony - gamont gives rise to many gametes Merogony - process that increase the number of infective cells ...
Cells labelling activity
... EAL Nexus – free downloadable teaching materials https://eal.britishcouncil.org/ This resource was originally developed by Z. Davies and has been adapted for EAL Nexus. ...
... EAL Nexus – free downloadable teaching materials https://eal.britishcouncil.org/ This resource was originally developed by Z. Davies and has been adapted for EAL Nexus. ...
Slide 1 - gwbiology
... The ECM may help coordinate the behavior of all the cells within that tissue. ◦ Direct connections (intercellular junctions) between cells also function in this coordination. ...
... The ECM may help coordinate the behavior of all the cells within that tissue. ◦ Direct connections (intercellular junctions) between cells also function in this coordination. ...
Optical methods for studying cell mechanics
... resolution. This technique can fast record actions potentials and also resolve the fast initiation and propagation of electromechanical signals within single neurons. Brightfield optical imaging approach has been applied to the mechanical wave visualization that associated with action potential in t ...
... resolution. This technique can fast record actions potentials and also resolve the fast initiation and propagation of electromechanical signals within single neurons. Brightfield optical imaging approach has been applied to the mechanical wave visualization that associated with action potential in t ...
Document
... 1. Inhale O2 into lungs 2. CO2 is a waste product of cellular Respiration (C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP ) 3. CO2 is removed from the cell through the cell membrane and into the capillary. 4. Blood travels throughout the body and the capillaries are picking up CO2 from the cell and carries it to ...
... 1. Inhale O2 into lungs 2. CO2 is a waste product of cellular Respiration (C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP ) 3. CO2 is removed from the cell through the cell membrane and into the capillary. 4. Blood travels throughout the body and the capillaries are picking up CO2 from the cell and carries it to ...
Cells Chapter 7-2 Cell Organelle Notes
... Organelles: “_______________________” • Specialized structures that ______________ specific ________ in the cell • Found only in __________________ cells • Many are membrane-____________ (a membrane surrounds the organelle) o ___________: watery matrix that organelles float in o ______________: ever ...
... Organelles: “_______________________” • Specialized structures that ______________ specific ________ in the cell • Found only in __________________ cells • Many are membrane-____________ (a membrane surrounds the organelle) o ___________: watery matrix that organelles float in o ______________: ever ...
The Cell City Culminating Task
... The Cell: Culminating Task Over the past few weeks, we have been learning about different cell organelles and the functions of these structures. The functions of these organelles can be compared to those of the various parts of a city. For example, the nucleus of the cell could be compared to the ci ...
... The Cell: Culminating Task Over the past few weeks, we have been learning about different cell organelles and the functions of these structures. The functions of these organelles can be compared to those of the various parts of a city. For example, the nucleus of the cell could be compared to the ci ...
Healing - Part 1 39KB
... represents a peak in the levels of particular cyclins, and then after that phase – the cyclins are degraded rapidly. Cyclins function by forming complexes with cyclin-dependent kinases. Thus the binding is necessary for important transitions between cell cycle phases. Checkpoints: This is a mechanis ...
... represents a peak in the levels of particular cyclins, and then after that phase – the cyclins are degraded rapidly. Cyclins function by forming complexes with cyclin-dependent kinases. Thus the binding is necessary for important transitions between cell cycle phases. Checkpoints: This is a mechanis ...
cells
... • Ability of an organism to maintain proper internal conditions despite changes in the environment. • They use energy • All organisms require energy for everyday life functions (staying organized, carrying on activities-finding/making food) • They reproduce • Making their own kind • Living things ne ...
... • Ability of an organism to maintain proper internal conditions despite changes in the environment. • They use energy • All organisms require energy for everyday life functions (staying organized, carrying on activities-finding/making food) • They reproduce • Making their own kind • Living things ne ...
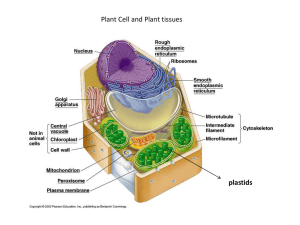
Plant Cells: Comparing Plant Cells with Animal Cells
... jelly-like fluid that the organelles float in? 3. What is the control center or brain of the animal cell called? ...
... jelly-like fluid that the organelles float in? 3. What is the control center or brain of the animal cell called? ...
Cells - El Camino College
... Nucleus: is the most distinct structure inside cell visible with light microscope. It has inside it DNA having all the information needed to form and run the cell. The segments of DNA are called Genes. Nuclear Envelope: is formed of 2 membranes with a gap between them. It has a large number of Nucle ...
... Nucleus: is the most distinct structure inside cell visible with light microscope. It has inside it DNA having all the information needed to form and run the cell. The segments of DNA are called Genes. Nuclear Envelope: is formed of 2 membranes with a gap between them. It has a large number of Nucle ...
Cell Structure and Function.
... Similarities between bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts Self-reproducing by binary fission Size of organism and genome ...
... Similarities between bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts Self-reproducing by binary fission Size of organism and genome ...
What in the CELL?
... • Using the Plant and Animal Cell Foldable (provided by Mrs. Regelski) – List all the differences between plants and animals. ...
... • Using the Plant and Animal Cell Foldable (provided by Mrs. Regelski) – List all the differences between plants and animals. ...
Diapositiva 1
... Primary wall composition and architecture Primary walls isolated form higher plant tissues and cells are composed predominantly of polysaccharides together with lesser amounts of structural glycoproteins (hydroxyproline-rich extensins), phenolic esters (ferulic and coumaric acids), ionically and co ...
... Primary wall composition and architecture Primary walls isolated form higher plant tissues and cells are composed predominantly of polysaccharides together with lesser amounts of structural glycoproteins (hydroxyproline-rich extensins), phenolic esters (ferulic and coumaric acids), ionically and co ...
Hoerner EDAY 2
... important part of learning is reviewing to make sure that you still remember things. Below I have placed a series of review questions regarding our Life Science unit. Please read through these pages ...
... important part of learning is reviewing to make sure that you still remember things. Below I have placed a series of review questions regarding our Life Science unit. Please read through these pages ...
Lab Biology Fall Semester Final Exam Study Guide
... Period: The flow of energy through the biosphere: All energy comes from the ___________________. Producers capture that energy and put it through the process of _________________________. Next, consumers and producers use that energy through the process of ___________________. ...
... Period: The flow of energy through the biosphere: All energy comes from the ___________________. Producers capture that energy and put it through the process of _________________________. Next, consumers and producers use that energy through the process of ___________________. ...
Cells and Cell Processes
... Have many membrane-bound organelles* Do not have membrane-bound organelles* Size: larger Size: very small Includes plants, animals, fungus, protists Only includes bacteria *Membrane-bound organelles refer to membrane-bound structures within the cell that carry out a particular function such as mitoc ...
... Have many membrane-bound organelles* Do not have membrane-bound organelles* Size: larger Size: very small Includes plants, animals, fungus, protists Only includes bacteria *Membrane-bound organelles refer to membrane-bound structures within the cell that carry out a particular function such as mitoc ...
Goal 2 - PBworks
... into cells. A hormone (red) encounters a receptor (blue) in the membrane of a cell. A G protein (green) becomes activated and makes contact with the receptor to which the hormone is attached. The G protein passes the hormone's message to the cell by switching on a cell enzyme (purple) that triggers ...
... into cells. A hormone (red) encounters a receptor (blue) in the membrane of a cell. A G protein (green) becomes activated and makes contact with the receptor to which the hormone is attached. The G protein passes the hormone's message to the cell by switching on a cell enzyme (purple) that triggers ...
Name___________________ Date Section 1 2 3 4 (circle one
... Looking Inside Cells Bulleted Notes Read Cells and Heredity section 1.2 online (pp. 16 - 24) then complete the following bulleted notes. The red headings have been done for you. Please fill out the blue sub-headings and bullet notes for ...
... Looking Inside Cells Bulleted Notes Read Cells and Heredity section 1.2 online (pp. 16 - 24) then complete the following bulleted notes. The red headings have been done for you. Please fill out the blue sub-headings and bullet notes for ...
developed
... – They will accumulate on one side of the zygote cell. This accumulation determines the poles of the cell and what each end will start development of in the organism. – They are referred to as “maternal” because they are produced in the female egg cell. ...
... – They will accumulate on one side of the zygote cell. This accumulation determines the poles of the cell and what each end will start development of in the organism. – They are referred to as “maternal” because they are produced in the female egg cell. ...
ch08_Cell-Cell Communication
... of cell adhesion proteins found in plasma membranes that bind only to other cadherins of the same type, causing cells of the same tissue type to bind together. ...
... of cell adhesion proteins found in plasma membranes that bind only to other cadherins of the same type, causing cells of the same tissue type to bind together. ...
Chapter 2-1 Vocabulary - Class Notes
... Nucleus –An organelle that directs and controls the activities of the cell. [Homeowner of the house] - (Both plant and animal cells) Nuclear Membrane – A membrane surrounding the nucleus that protects it, and regulates The materials that go into and out of the nucleus. [Clothes and skin of the Homeo ...
... Nucleus –An organelle that directs and controls the activities of the cell. [Homeowner of the house] - (Both plant and animal cells) Nuclear Membrane – A membrane surrounding the nucleus that protects it, and regulates The materials that go into and out of the nucleus. [Clothes and skin of the Homeo ...
LAB ASSIGNMENT 1
... NAME: _____________________________ LAB ASSIGNMENT 1 Due at the start of Lab on July 8 ...
... NAME: _____________________________ LAB ASSIGNMENT 1 Due at the start of Lab on July 8 ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.