Constitutes - Onto-Med
... Material Constitution • x materially constitutes y at t if and only if there are primary kinds F and G such that at t: ...
... Material Constitution • x materially constitutes y at t if and only if there are primary kinds F and G such that at t: ...
The Animal Cell
... stomach and small intestine which take in nutrients, breaks them down, and creates energy for the cell. The process of creating that energy is known as cellular respiration. The mitochondria is shaped perfectly to maximize its efforts. Mitochondria are very small organelles. You might find cells wit ...
... stomach and small intestine which take in nutrients, breaks them down, and creates energy for the cell. The process of creating that energy is known as cellular respiration. The mitochondria is shaped perfectly to maximize its efforts. Mitochondria are very small organelles. You might find cells wit ...
8D Unicellular Organisms
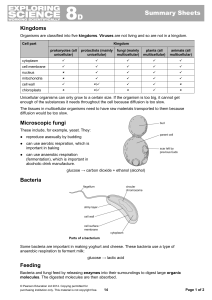
... Organisms are classified into five kingdoms. Viruses are not living and so are not in a kingdom. Cell part ...
... Organisms are classified into five kingdoms. Viruses are not living and so are not in a kingdom. Cell part ...
Presentation
... What are Cilia and Flagella and How are they used? .They are protein extensions of the cell membrane. They are used for movement of the cell. ...
... What are Cilia and Flagella and How are they used? .They are protein extensions of the cell membrane. They are used for movement of the cell. ...
Diapositiva 1 - r
... formulation of a phylogenetic hypothesis of “ageing”. In particular (Table I and fig. 5): a) apoptosis in yeast is triggered by starvation, damaged conditions of the cell, unsuccessful mating, etc., and in these cases it is favoured by kin selection because increases survival probability of kin cell ...
... formulation of a phylogenetic hypothesis of “ageing”. In particular (Table I and fig. 5): a) apoptosis in yeast is triggered by starvation, damaged conditions of the cell, unsuccessful mating, etc., and in these cases it is favoured by kin selection because increases survival probability of kin cell ...
Document
... Using the scenario below answer questions 1-9. Kari has been doing research on a new chemical to help tomato plants grow and produce bigger, healthier tomatoes. Kari hypothesized that the new chemical would increase plant growth producing larger tomatoes. She needed to set up an experiment to test t ...
... Using the scenario below answer questions 1-9. Kari has been doing research on a new chemical to help tomato plants grow and produce bigger, healthier tomatoes. Kari hypothesized that the new chemical would increase plant growth producing larger tomatoes. She needed to set up an experiment to test t ...
Transfer of Materials Across Membranes
... 1. Water, iodine, and glucose were small enough to pass through the dialysis membrane, but protein, starch, and lipid were too large to pass through. 2. Yes, iodine and water were going into the bag at the same time glucose was leaving. 3. It is semipermeable or selectively permeable and regulates w ...
... 1. Water, iodine, and glucose were small enough to pass through the dialysis membrane, but protein, starch, and lipid were too large to pass through. 2. Yes, iodine and water were going into the bag at the same time glucose was leaving. 3. It is semipermeable or selectively permeable and regulates w ...
The role of the replication licensing system in cell proliferation and
... sorts of chromosomal defects are commonly seen in cancer cells, though whether they are generated by replication defects such as these is currently unclear. This section will discuss how re-replication or endoreplication may play a role in this process. There are two general mechanisms by which cell ...
... sorts of chromosomal defects are commonly seen in cancer cells, though whether they are generated by replication defects such as these is currently unclear. This section will discuss how re-replication or endoreplication may play a role in this process. There are two general mechanisms by which cell ...
Cell Organelles File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... enclosed by cell membrane; Make up a little more than half of the cells volume; ...
... enclosed by cell membrane; Make up a little more than half of the cells volume; ...
File
... G. Cell membrane contains receptors that help transmit signals across membrane 1. Made of proteins 2. It detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response ...
... G. Cell membrane contains receptors that help transmit signals across membrane 1. Made of proteins 2. It detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response ...
The Cell & Organization of Life
... Scientist believe that mitochondria and chloroplast began as proK and were eaten by larger cells. Evidence that supports this theory: • They are about the same size as bacteria • They are surrounded by two membranes ...
... Scientist believe that mitochondria and chloroplast began as proK and were eaten by larger cells. Evidence that supports this theory: • They are about the same size as bacteria • They are surrounded by two membranes ...
Plasma Membrane
... Bound – attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), produce proteins for export, or for the plasma membrane ...
... Bound – attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), produce proteins for export, or for the plasma membrane ...
File
... concentrations to areas of LOW concentration with the HELP of a TRANSPORT protein. Like regular diffusion, this is a type of PASSIVE transport and does NOT require energy! • Animation: How Facilitated Diffusion Works ...
... concentrations to areas of LOW concentration with the HELP of a TRANSPORT protein. Like regular diffusion, this is a type of PASSIVE transport and does NOT require energy! • Animation: How Facilitated Diffusion Works ...
013368718X_CH10_143
... Mitosis is the process by which the nucleus of most eukaryotic cells divides. Mitosis has four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. 1. Label the four phases of mitosis in the diagram. 2. Label the spindles and centrioles in one of the phases. 3. Color each chromosome in prophase a d ...
... Mitosis is the process by which the nucleus of most eukaryotic cells divides. Mitosis has four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. 1. Label the four phases of mitosis in the diagram. 2. Label the spindles and centrioles in one of the phases. 3. Color each chromosome in prophase a d ...
Exam 1
... B. The techniques used to study organisms regardless of their size C. Both the size of the organism studied and the techniques employed in the study of organisms D. Neither the size of the organism studied nor the techniques employed in the study of organisms regardless of their size . Unlike other ...
... B. The techniques used to study organisms regardless of their size C. Both the size of the organism studied and the techniques employed in the study of organisms D. Neither the size of the organism studied nor the techniques employed in the study of organisms regardless of their size . Unlike other ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 3
... G. Cell membrane contains receptors that help transmit signals across membrane 1. Made of proteins 2. It detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response ...
... G. Cell membrane contains receptors that help transmit signals across membrane 1. Made of proteins 2. It detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response ...
Infectious Diseases and Single
... Bacteria Population Explosion Suppose a bacterium reproduces by binary fission every 20 minutes The new cells survive and reproduce at the same rate. After 16 hours two cells could become 8.5 billion Many bacterial diseases can be cured with antibiotics. Antibiotics are substances that slow or ...
... Bacteria Population Explosion Suppose a bacterium reproduces by binary fission every 20 minutes The new cells survive and reproduce at the same rate. After 16 hours two cells could become 8.5 billion Many bacterial diseases can be cured with antibiotics. Antibiotics are substances that slow or ...
high concentration to
... •Water rushes OUT of cell causing it to shrivel (water rushes to where there is more substances) •Can result in PLASMOLYSIS in plants which causes wilting ...
... •Water rushes OUT of cell causing it to shrivel (water rushes to where there is more substances) •Can result in PLASMOLYSIS in plants which causes wilting ...
Lecture notes for the aging lecture
... BY DAF16 AND ARE ASSOCIATED WITH INCREASED LIFE SPAN CLASS II GENES ARE REPRESSED BY DAF16 AND ARE ASSOCIATED ...
... BY DAF16 AND ARE ASSOCIATED WITH INCREASED LIFE SPAN CLASS II GENES ARE REPRESSED BY DAF16 AND ARE ASSOCIATED ...
4-2 Cell Organelles - TJ
... Multiple Choice Write the correct letter in the blank. 4. The cell membrane a. allows substances to pass into and out of the cell. b. prevents all substances from passing in and out of the cell. c. is composed mainly of a protein bilayer. d. is composed mainly of a lipid bilayer. 5. Substances produ ...
... Multiple Choice Write the correct letter in the blank. 4. The cell membrane a. allows substances to pass into and out of the cell. b. prevents all substances from passing in and out of the cell. c. is composed mainly of a protein bilayer. d. is composed mainly of a lipid bilayer. 5. Substances produ ...
Chapter 7 Review
... 3. the “brains” of the cell - site where DNA is located 4. a green organelle used by plants and algae for photosynthesis 6. a cell _____ is its boundary that controls what may enter or exit the cell 7. a spherical, colonial organism with cells that are genetically identical to each other 9. an organ ...
... 3. the “brains” of the cell - site where DNA is located 4. a green organelle used by plants and algae for photosynthesis 6. a cell _____ is its boundary that controls what may enter or exit the cell 7. a spherical, colonial organism with cells that are genetically identical to each other 9. an organ ...
What`s In Your Cells?
... made of cells. In even the tiniest unit of any living thing, there is a cell. Cells have special structures called organelles. The organelles help cells do the work of moving materials around, dividing to make more cells and making proteins for the body’s needs. Cells get energy through a process ca ...
... made of cells. In even the tiniest unit of any living thing, there is a cell. Cells have special structures called organelles. The organelles help cells do the work of moving materials around, dividing to make more cells and making proteins for the body’s needs. Cells get energy through a process ca ...
Systems Ch 2 BI
... Segments of DNA which contain instructions to make proteins are called genes. Genes control the activities of the cell and contain hereditary information which is passed on from one generation to the next. (Note: Human red blood cells do not contain nuclei.) ...
... Segments of DNA which contain instructions to make proteins are called genes. Genes control the activities of the cell and contain hereditary information which is passed on from one generation to the next. (Note: Human red blood cells do not contain nuclei.) ...
Cells and Cell Organelles ppt
... Stem Cells •Stem cells found in all multi-cellular organisms, they divide and differentiate into diverse specialized cell types and can self renew to produce more stem cells. •Humans stem cells: 2 types (1) embryonic ...
... Stem Cells •Stem cells found in all multi-cellular organisms, they divide and differentiate into diverse specialized cell types and can self renew to produce more stem cells. •Humans stem cells: 2 types (1) embryonic ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.