IGCSE BIOLOGY 2.1 Cellular organization State that living
... Animals must eat their food because they cannot photosynthesize. Animal cells may have several small vacuoles, or none at all. ...
... Animals must eat their food because they cannot photosynthesize. Animal cells may have several small vacuoles, or none at all. ...
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell
... proteins that have arrived from the endoplasmic reticulum. These proteins will either be stored inside the cell or be secreted to the outside of the cell. ...
... proteins that have arrived from the endoplasmic reticulum. These proteins will either be stored inside the cell or be secreted to the outside of the cell. ...
DO NOW - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... House genetic information Nucleolus: RNA synthesis Nuclear envelope Nuclear pores ...
... House genetic information Nucleolus: RNA synthesis Nuclear envelope Nuclear pores ...
1st Quarter Exam – Review Topics
... 1. A student noticed that when a dog is cut, the dog periodically licks its wounds. Usually after a few days, the wound begins to heal without ever showing signs of infection. The following steps outline the student's line of reasoning: a. I wonder why the dog's wound doesn't become infected. b. The ...
... 1. A student noticed that when a dog is cut, the dog periodically licks its wounds. Usually after a few days, the wound begins to heal without ever showing signs of infection. The following steps outline the student's line of reasoning: a. I wonder why the dog's wound doesn't become infected. b. The ...
Signal Receptors 4 types
... signaling pathways regulate the synthesis of enzymes or other proteins, usually by turning genes on or off in the nucleus ...
... signaling pathways regulate the synthesis of enzymes or other proteins, usually by turning genes on or off in the nucleus ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Orange Coast College
... Prepares proteins for export Makes lysosomes Packages material to add to plasma membrane ...
... Prepares proteins for export Makes lysosomes Packages material to add to plasma membrane ...
Viruses
... particles unlike any other organism. A virus consists of genetic material such as RNA or DNA wrapped in a protein coat. ...
... particles unlike any other organism. A virus consists of genetic material such as RNA or DNA wrapped in a protein coat. ...
Animal and plant cells have a nucleus, cytoplasm, and a cell
... The specimen appears to move in the opposite direction than it is actually moving. _____ Calculate total magnification using eyepiece magnification and objective lens magnification ...
... The specimen appears to move in the opposite direction than it is actually moving. _____ Calculate total magnification using eyepiece magnification and objective lens magnification ...
File - Ms. Morin`s Weebly 2
... help it survive. Your example CANNOT come from the textbook. Mountain pine beetle – releases pheromones to attract other beetles for mating, Salmon uses chemo-sensory to navigate back to their native ...
... help it survive. Your example CANNOT come from the textbook. Mountain pine beetle – releases pheromones to attract other beetles for mating, Salmon uses chemo-sensory to navigate back to their native ...
a. Cell membrane
... penetrate the hydrophobic core of the membrane. They can be easily removed without destroying the membrane structure. • Integral proteins : these are fully incorporated into the membrane and are in contact with both the inside and the outside of the cell. Some can act as channel ways for the transpo ...
... penetrate the hydrophobic core of the membrane. They can be easily removed without destroying the membrane structure. • Integral proteins : these are fully incorporated into the membrane and are in contact with both the inside and the outside of the cell. Some can act as channel ways for the transpo ...
Viruses - I Heart Science
... Active viruses – make the host cell create new viruses, which kills the host cell. Latent viruses – hide in the host cell without destroying it. ...
... Active viruses – make the host cell create new viruses, which kills the host cell. Latent viruses – hide in the host cell without destroying it. ...
Cells and Development - NIU Department of Biological Sciences
... After a few more divisions, cells on the outside of the morula flatten out, and the inside develops into a hollow ball, the blastocyst. On one side of the blastocyst a clump of cells, the inner cell mass, forms. The inner cell mass develops into the embryo and the amnion, the inner membrane. The oth ...
... After a few more divisions, cells on the outside of the morula flatten out, and the inside develops into a hollow ball, the blastocyst. On one side of the blastocyst a clump of cells, the inner cell mass, forms. The inner cell mass develops into the embryo and the amnion, the inner membrane. The oth ...
June 22, 2016 Yumanity Therapeutics and the New York Stem Cell
... announced a discovery collaboration with the New York Stem Cell Foundation (NYSCF) Research Institute, a non-profit organization dedicated to accelerating cures for major diseases through stem cell research. The immediate aim of the partnership is to generate induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) lin ...
... announced a discovery collaboration with the New York Stem Cell Foundation (NYSCF) Research Institute, a non-profit organization dedicated to accelerating cures for major diseases through stem cell research. The immediate aim of the partnership is to generate induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) lin ...
Cells
... D. A developing cell's function is determined by the number of organelles it contains. 5. What is the name of the process that appears in the diagram below? ...
... D. A developing cell's function is determined by the number of organelles it contains. 5. What is the name of the process that appears in the diagram below? ...
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
... animal and plant cells have cell membranes that enclose the cell. ► Both are filled with cytoplasm, a gel-like substance containing chemicals needed by the cell. ► Both have a nucleus where DNA is stored. ► Both have ribosomes, protein builders of cells. ► Both ...
... animal and plant cells have cell membranes that enclose the cell. ► Both are filled with cytoplasm, a gel-like substance containing chemicals needed by the cell. ► Both have a nucleus where DNA is stored. ► Both have ribosomes, protein builders of cells. ► Both ...
Global network analysis of drug tolerance, mode of
... • Affects VraSR, which controls gene expression is cell wall synthesis – Genes regulated this were RanaUp • SAR1461, SAR1964, SAR1030, SAR2442 ...
... • Affects VraSR, which controls gene expression is cell wall synthesis – Genes regulated this were RanaUp • SAR1461, SAR1964, SAR1030, SAR2442 ...
3-17_MICROBES_MAJOR_ GROUPS
... • Acellular – Viruses do not have cellular components, nor do they grow or metabolize organic materials. They generally consist of a piece of nucleic acid encased in protein which must use the cellular components of a living cell to reproduce. Prions (proteinaceous infectious particles) are infectio ...
... • Acellular – Viruses do not have cellular components, nor do they grow or metabolize organic materials. They generally consist of a piece of nucleic acid encased in protein which must use the cellular components of a living cell to reproduce. Prions (proteinaceous infectious particles) are infectio ...
Structures and Functions of Living Things
... 17. lysosomes – A small round cell structure that contains chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller ones. 18. bacteria – a cell that is usually smaller than a plant or animal cell and does not contain a nucleus. The only other organelles it shares with plants and animals are a cel ...
... 17. lysosomes – A small round cell structure that contains chemicals that break down large food particles into smaller ones. 18. bacteria – a cell that is usually smaller than a plant or animal cell and does not contain a nucleus. The only other organelles it shares with plants and animals are a cel ...
File
... how big they are compared to the other organelles and their function within a plant or animal cell. A few “off the top of my head” ideas: Your main character is adventuring inside a cell. Your main character is a doctor, trying to diagnose a patient with a cellular ...
... how big they are compared to the other organelles and their function within a plant or animal cell. A few “off the top of my head” ideas: Your main character is adventuring inside a cell. Your main character is a doctor, trying to diagnose a patient with a cellular ...
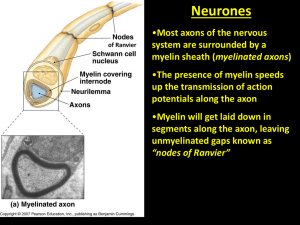
Myelin Sheaths Plant Hormone Intro
... • The part of a shoot sensitive to light is the tip. • The part of the shoot which responds to the stimulus is the part just below the tip. • These two parts of the shoot must be communicating with one another by means hormones. • Plant hormones are chemical that affect the activities of particular ...
... • The part of a shoot sensitive to light is the tip. • The part of the shoot which responds to the stimulus is the part just below the tip. • These two parts of the shoot must be communicating with one another by means hormones. • Plant hormones are chemical that affect the activities of particular ...
- mrsolson.com
... Golgi Apparatus(body) Phospholipid bilayer Active Transport(using ATP) Facilitated Diffusion Phagocytosis Turgor Pressure Objective Lens ...
... Golgi Apparatus(body) Phospholipid bilayer Active Transport(using ATP) Facilitated Diffusion Phagocytosis Turgor Pressure Objective Lens ...
Blood Cell ID - American Proficiency Institute
... appearance. This cell should not be mistaken for a hypersegmented neutrophil. Hypersegmentation should be considered when a cell has six or more nuclear lobes or when three or more five-lobed segmented neutrophils are counted per 100 leukocytes. Hypersegmented neutrophils are most commonly associate ...
... appearance. This cell should not be mistaken for a hypersegmented neutrophil. Hypersegmentation should be considered when a cell has six or more nuclear lobes or when three or more five-lobed segmented neutrophils are counted per 100 leukocytes. Hypersegmented neutrophils are most commonly associate ...
What is Life? - Home Page for Ross Koning
... Images lacking photo credits are mine and, as long as you are engaged in non-profit educational missions, you have my permission to use my images and slides in your teaching. However, please notice that some of the images in these slides have an associated URL photo credit to provide you with the lo ...
... Images lacking photo credits are mine and, as long as you are engaged in non-profit educational missions, you have my permission to use my images and slides in your teaching. However, please notice that some of the images in these slides have an associated URL photo credit to provide you with the lo ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.