emboj2010191-sup
... (A) Neither PKA nor CK1 inhibitors abrogates malate’s protection. S2 cells pretreated with PKA (30 M H-89) (Zhao et al, 2007) or CK1 (8 M IC261) (Mennella et al, 2009) inhibitors were treated with 40 µM CHX ± 5 mM malate in standard Schneider’s medium. Cell density and viability were recorded by p ...
... (A) Neither PKA nor CK1 inhibitors abrogates malate’s protection. S2 cells pretreated with PKA (30 M H-89) (Zhao et al, 2007) or CK1 (8 M IC261) (Mennella et al, 2009) inhibitors were treated with 40 µM CHX ± 5 mM malate in standard Schneider’s medium. Cell density and viability were recorded by p ...
Name: :__________Period:____ Malaria 1. What is the name of the
... 4. List the symptoms of malaria. Fever, chills, convulsions (repeats in cycles). 5. What types of cells/organ does the protist infect in the person? Red blood cells and liver cells. 6. List some ways to control the spread of malaria. Control the mosquito population. Drain standing water, use bed net ...
... 4. List the symptoms of malaria. Fever, chills, convulsions (repeats in cycles). 5. What types of cells/organ does the protist infect in the person? Red blood cells and liver cells. 6. List some ways to control the spread of malaria. Control the mosquito population. Drain standing water, use bed net ...
Cell Organelles and Functions Powerpoint
... web of proteins in the cytoplasm. Acts as both a muscle and a skeleton. Keeps the cell’s membranes from collapsing. Also helps some cells move. Made of 3 types of protein. One protein is a hollow tube, the other two are long, stringy fibers ...
... web of proteins in the cytoplasm. Acts as both a muscle and a skeleton. Keeps the cell’s membranes from collapsing. Also helps some cells move. Made of 3 types of protein. One protein is a hollow tube, the other two are long, stringy fibers ...
Cell Cycle - Mr. Schukow's Science Site
... What might be the consequences of uncontrolled cell division in a multicellular organism? 2. What does it mean when we say that there are several “checkpoints” that occur during the cell cycle? 3. What are the “Questions” that a cell must “answer” during each of the following checkpoints: G1/S check ...
... What might be the consequences of uncontrolled cell division in a multicellular organism? 2. What does it mean when we say that there are several “checkpoints” that occur during the cell cycle? 3. What are the “Questions” that a cell must “answer” during each of the following checkpoints: G1/S check ...
Cells - Steven Lin`s Websites
... – Each cell has a job in an animal or plant’s body in order to keep it functioning properly. ...
... – Each cell has a job in an animal or plant’s body in order to keep it functioning properly. ...
Cell Membranes - WordPress.com
... Integral (or i________, or transmembrane) proteins span the whole width of the membrane. Peripheral (or e________) proteins are confined to the inner or outer surface of the membrane. Many proteins are glycoproteins – proteins with attached carbohydrate chains. Many integral proteins are carrier mol ...
... Integral (or i________, or transmembrane) proteins span the whole width of the membrane. Peripheral (or e________) proteins are confined to the inner or outer surface of the membrane. Many proteins are glycoproteins – proteins with attached carbohydrate chains. Many integral proteins are carrier mol ...
Name:
... 2. Click “Continue” again to observe “Osmosis and Diffusion”. Why does the balloon on the left get larger? 3. Click “Continue” to observe “Passive Transport”. NOTE: Osmosis and diffusion are forms of passive transport. This animation describes a special case of passive transport called facilitated d ...
... 2. Click “Continue” again to observe “Osmosis and Diffusion”. Why does the balloon on the left get larger? 3. Click “Continue” to observe “Passive Transport”. NOTE: Osmosis and diffusion are forms of passive transport. This animation describes a special case of passive transport called facilitated d ...
bk1B_ch09_sug ans_e
... The toxic substances absorbed by the plants may escape from the leaves and pollute the air. The plants containing the toxic substances may affect the environment if they are not properly disposed of. The clean-up process is slow because the plants take months to grow. (any 2) ...
... The toxic substances absorbed by the plants may escape from the leaves and pollute the air. The plants containing the toxic substances may affect the environment if they are not properly disposed of. The clean-up process is slow because the plants take months to grow. (any 2) ...
Parts of the Animal Cell
... DNA:DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA controls all of the cells activities. The DNA sends out messenger proteins that tell the cell what to do. Messenger proteins also report to the DNA about the cells activities. The cell would not know what to do without the DNA. Every cell within an organ ...
... DNA:DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA controls all of the cells activities. The DNA sends out messenger proteins that tell the cell what to do. Messenger proteins also report to the DNA about the cells activities. The cell would not know what to do without the DNA. Every cell within an organ ...
The Cell Cycle and Mitosis
... the cell places on its _____ and the more trouble the cell has moving enough _________and _________ across the cell membrane. ...
... the cell places on its _____ and the more trouble the cell has moving enough _________and _________ across the cell membrane. ...
Diabetes in Native Americans: The interaction between diet and genes
... vesicles fuse to form first flat sacks of Golgi apparatus ...
... vesicles fuse to form first flat sacks of Golgi apparatus ...
fluid mosaic model - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... 1. They are long and extremely thin protein fibres that occur in bundles made of 2 proteins called Actin and Myosin. 2. Organelles move around the cytoplasm on these. ...
... 1. They are long and extremely thin protein fibres that occur in bundles made of 2 proteins called Actin and Myosin. 2. Organelles move around the cytoplasm on these. ...
A Probable Growth Cycle in Bacillus megaterium
... points seen in stained specimens correspond in some way with these granules. ...
... points seen in stained specimens correspond in some way with these granules. ...
CELL ORGANELLES REVIEW
... 2. Cells that have internal membranes surrounding specialised organelles are: A. eukaryotic B. prokaryotic C. unicellular 3. The controlling organelle within a cell is the: A. nucleolus B. gene C. nucleus 4. The jellylike fluid that contains nutrients in a cell is the: A. cytoplasm B. vacuole C. nuc ...
... 2. Cells that have internal membranes surrounding specialised organelles are: A. eukaryotic B. prokaryotic C. unicellular 3. The controlling organelle within a cell is the: A. nucleolus B. gene C. nucleus 4. The jellylike fluid that contains nutrients in a cell is the: A. cytoplasm B. vacuole C. nuc ...
NAME OF ORGANELLE
... nucleolus ribosome rough endoplasmic reticulum smooth endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus vacuole lysosome Mitochondria ...
... nucleolus ribosome rough endoplasmic reticulum smooth endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus vacuole lysosome Mitochondria ...
Jan 14
... • Meristems: plants have perpetually embryonic regions, and can form new ones • No germ line! Cells at apical meristem become flowers: allows Lamarckian evolution! • Different parts of the same 2000 year old tree have different DNA & form different gametes ...
... • Meristems: plants have perpetually embryonic regions, and can form new ones • No germ line! Cells at apical meristem become flowers: allows Lamarckian evolution! • Different parts of the same 2000 year old tree have different DNA & form different gametes ...
Culturing Viruses in the Laboratory
... Culturing Viruses in the Laboratory • Culturing Viruses in Cell (Tissue) Culture – Consists of cells isolated from an organism and grown on a medium or in a broth – Two types of cell cultures • Diploid cell cultures • Continuous cell cultures ...
... Culturing Viruses in the Laboratory • Culturing Viruses in Cell (Tissue) Culture – Consists of cells isolated from an organism and grown on a medium or in a broth – Two types of cell cultures • Diploid cell cultures • Continuous cell cultures ...
cell wall
... Osmosis- movement of WATER molecules from an area where there are many to an area where there are few ...
... Osmosis- movement of WATER molecules from an area where there are many to an area where there are few ...
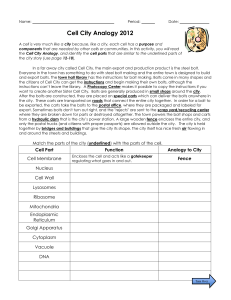
Cell City Analogy - Rochester Community Schools
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
Doellman, Cell Structure and Function Unit Exam
... 32. You have just discovered a mutant plant that no one else has ever seen before. This plant is very unusual because its cells do not contain a cell wall. Predict how the lack of cell wall will impact the plant’s survival on Earth. (Hint: What will it look like? What accommodations will it have to ...
... 32. You have just discovered a mutant plant that no one else has ever seen before. This plant is very unusual because its cells do not contain a cell wall. Predict how the lack of cell wall will impact the plant’s survival on Earth. (Hint: What will it look like? What accommodations will it have to ...
Unit 2 Lesson 3
... • Cellular respiration is the process by which cells get energy by breaking down food. • Mitochondrion is an organelle where cellular respiration occurs. • Mitochondria have their own DNA and two membranes. ...
... • Cellular respiration is the process by which cells get energy by breaking down food. • Mitochondrion is an organelle where cellular respiration occurs. • Mitochondria have their own DNA and two membranes. ...
Cell structure and function
... replisome as replication occurs • MreB – an actin homolog plays role in determination of cell shape ...
... replisome as replication occurs • MreB – an actin homolog plays role in determination of cell shape ...
Chapter 3 Study Guide
... 8) What organelle stores the cell’s genetic (DNA & RNA) information? 9) How would you best describe the rough ER? 10) What organelle is responsible for energy? 11) What organelle contains enzymes to break down old cell parts? 12) The process of photosynthesis happens in what organelle? 13) What orga ...
... 8) What organelle stores the cell’s genetic (DNA & RNA) information? 9) How would you best describe the rough ER? 10) What organelle is responsible for energy? 11) What organelle contains enzymes to break down old cell parts? 12) The process of photosynthesis happens in what organelle? 13) What orga ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.