Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport
... Cell transport helps cells maintain homeostasis by keeping conditions within normal ranges inside all of an ...
... Cell transport helps cells maintain homeostasis by keeping conditions within normal ranges inside all of an ...
Cell Due2/25-26
... ____ 26. The primary function of the cell wall is to a. support and protect the cell. b. store DNA. c. direct the activities of the cell. d. help the cell move. ____ 27. Unlike the cell membrane, the cell wall is a. found in all organisms. b. composed of a lipid bilayer. c. selectively permeable. d. ...
... ____ 26. The primary function of the cell wall is to a. support and protect the cell. b. store DNA. c. direct the activities of the cell. d. help the cell move. ____ 27. Unlike the cell membrane, the cell wall is a. found in all organisms. b. composed of a lipid bilayer. c. selectively permeable. d. ...
The Physiology of Beta Cell Mass: Regulation of beta cell
... the exact mechanisms by which the lactogenic hormones drive beta cell expansion remain uncertain. Here we show that serotonin acts downstream of lactogen signaling to stimulate beta cell proliferation. Expression of serotonin synthetic enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase-1 (Tph1) and serotonin production ...
... the exact mechanisms by which the lactogenic hormones drive beta cell expansion remain uncertain. Here we show that serotonin acts downstream of lactogen signaling to stimulate beta cell proliferation. Expression of serotonin synthetic enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase-1 (Tph1) and serotonin production ...
Transport Unit Study Guide
... Be able to predict which type of molecules can diffuse through the plasma membrane and which kind need to use a transport protein Be able to explain the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis and give examples Be able to predict the eff ...
... Be able to predict which type of molecules can diffuse through the plasma membrane and which kind need to use a transport protein Be able to explain the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis and give examples Be able to predict the eff ...
Bio-Adembeads Antibodies Anti-Rabbit IgG
... Specific surface area: 10 m /g Iron oxide content: approx. 70% ...
... Specific surface area: 10 m /g Iron oxide content: approx. 70% ...
lesson-7-bio - WordPress.com
... 7. Microbodies- organelles same size of mitochondria containing oxidative enzymes. Types: ...
... 7. Microbodies- organelles same size of mitochondria containing oxidative enzymes. Types: ...
Cell City Analogy
... 11. Now that you made the comparison between the parts of a city and the organelles of a cell, draw out your city! a. On a SEPARATE sheet of paper, draw out your city with all of the places discussed above. b. Make sure to include all 11 buildings listed in the chart on the first page. Label each bu ...
... 11. Now that you made the comparison between the parts of a city and the organelles of a cell, draw out your city! a. On a SEPARATE sheet of paper, draw out your city with all of the places discussed above. b. Make sure to include all 11 buildings listed in the chart on the first page. Label each bu ...
Problem Set 3 Answer Key, Spring 2003 1) The following
... from part D. What is the cellular growth phenotype? Despite the constitutively active Ras without the farnesylation Ras cannot efficiently signal to Raf and activate the MAPK pathway. Raf is activated primarily by being brought to the membrane so if Ras is not at the membrane this will not occur. Th ...
... from part D. What is the cellular growth phenotype? Despite the constitutively active Ras without the farnesylation Ras cannot efficiently signal to Raf and activate the MAPK pathway. Raf is activated primarily by being brought to the membrane so if Ras is not at the membrane this will not occur. Th ...
CELLS
... • All living things are made of cells • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) • Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division) ...
... • All living things are made of cells • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) • Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division) ...
Cell Discovery 1st lenses used- 1500s (simple microscope) discovery of cells
... the inner membrane being highly folded. The mitochondria are often referred to as the "powerhouse" of the cell. The mitochondria release food energy from food molecules to be used by the cell. This process is called respiration. Some cells (muscle cells) require more energy than other cells and so w ...
... the inner membrane being highly folded. The mitochondria are often referred to as the "powerhouse" of the cell. The mitochondria release food energy from food molecules to be used by the cell. This process is called respiration. Some cells (muscle cells) require more energy than other cells and so w ...
Type 1 -IgE Mediated Response
... pain or burning along the vein back pain fever dyspnea ...
... pain or burning along the vein back pain fever dyspnea ...
cell structure and function chart
... nuclear envelope. Contains directions to make proteins and genetic information, DNA or RNA. (“Control Center of Cell”); inside is the nucleolus which makes ribosomes. ...
... nuclear envelope. Contains directions to make proteins and genetic information, DNA or RNA. (“Control Center of Cell”); inside is the nucleolus which makes ribosomes. ...
Collated questions suitable for AS91156
... Active transport and osmosis both occur across the cell membrane. Compare and contrast these two processes. Give examples of active transport and osmosis in living organisms to support your answer. ...
... Active transport and osmosis both occur across the cell membrane. Compare and contrast these two processes. Give examples of active transport and osmosis in living organisms to support your answer. ...
Name: How I`ll Show What I Know about Cells: Due Wednesday, Oct
... center of the poster, I will draw and label a plant or animal cell. I will use colorful pictures from the internet or magazines to illustrate the analogy for each part. I will explain the analogy in a brief sentence. For example, “The nucleus is like a brain because it controls all the cell’s proces ...
... center of the poster, I will draw and label a plant or animal cell. I will use colorful pictures from the internet or magazines to illustrate the analogy for each part. I will explain the analogy in a brief sentence. For example, “The nucleus is like a brain because it controls all the cell’s proces ...
Stem Cells
... The starfish contains stem cells that can divide, differentiate and produce new tissues to replace those that are lost. Humans and most other animals cannot do this, but scientists are studying how stem cells could be used to create new tissue and even new organs to treat disease, injury and conditi ...
... The starfish contains stem cells that can divide, differentiate and produce new tissues to replace those that are lost. Humans and most other animals cannot do this, but scientists are studying how stem cells could be used to create new tissue and even new organs to treat disease, injury and conditi ...
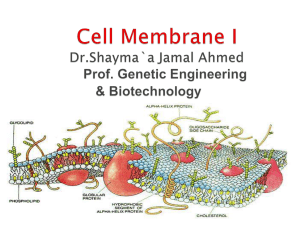
Plasma membrane Dr.Shayma`a Jamal Ahmed
... The plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipids. The membrane has many proteins embedded in it. The arrangement of protein & lipid molecules with in the membrane may suggest different models. The most accepted model is the Fluid-Mosaic model. ...
... The plasma membrane (cell membrane) is made of two layers of phospholipids. The membrane has many proteins embedded in it. The arrangement of protein & lipid molecules with in the membrane may suggest different models. The most accepted model is the Fluid-Mosaic model. ...
What is a cell?
... • A network of threadlike proteins that are joined together and help give the cell its shape and help it move. ...
... • A network of threadlike proteins that are joined together and help give the cell its shape and help it move. ...
bioreaction and bioreactor
... The cell wall protects the cell from external influences. The cell membrane provides for selective transport of materials into and out of the cell ...
... The cell wall protects the cell from external influences. The cell membrane provides for selective transport of materials into and out of the cell ...
cell division control
... when they become crowded forming a single layer of cells. It seems that when crowded, there is insufficient growth factor produced and nutrients for cell division to continue. Anchorage dependence- mammalian cells need to be attached to substratum like the inside of a culture jar or other tissue in ...
... when they become crowded forming a single layer of cells. It seems that when crowded, there is insufficient growth factor produced and nutrients for cell division to continue. Anchorage dependence- mammalian cells need to be attached to substratum like the inside of a culture jar or other tissue in ...
Keystone Study Points Answer Key
... The two strands of the double helix unzip, forming replication forks New bases are added, following the rules of base pairing (A with T and G with C) Semi-‐conservative: Each new DNA molecule ha ...
... The two strands of the double helix unzip, forming replication forks New bases are added, following the rules of base pairing (A with T and G with C) Semi-‐conservative: Each new DNA molecule ha ...
Autologous Tx
... break-through with discovery of HLA system – „modern era“ (second half of the 60thies ) allogeneic BMT of HLA-identical siblings ...
... break-through with discovery of HLA system – „modern era“ (second half of the 60thies ) allogeneic BMT of HLA-identical siblings ...
Question paper - Unit F211/01 - Cells, exchange and transport
... (a) Explain, using the term surface area to volume ratio, why large, active organisms need a specialised surface for gaseous exchange. ...
... (a) Explain, using the term surface area to volume ratio, why large, active organisms need a specialised surface for gaseous exchange. ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.