Cell Analogy Rubric
... Using the diagrams from your notebook, you will create a ½ poster-sized drawing of an animal or plant cell and label its organelles (see details below). Next to each label (organelle) you will provide a picture and your analogy to the cell part. You must explain how your analogy relates to the organ ...
... Using the diagrams from your notebook, you will create a ½ poster-sized drawing of an animal or plant cell and label its organelles (see details below). Next to each label (organelle) you will provide a picture and your analogy to the cell part. You must explain how your analogy relates to the organ ...
Cell Theory Lab-honors-bio
... Cells are the basic unit of life because they are the simplest structure that displays all the characteristics of life. Five different scientists’ work led to a very important Cell Theory. You will examine various samples of cells that were important to the contribution of the Cell Theory. PURPOSE: ...
... Cells are the basic unit of life because they are the simplest structure that displays all the characteristics of life. Five different scientists’ work led to a very important Cell Theory. You will examine various samples of cells that were important to the contribution of the Cell Theory. PURPOSE: ...
Honors Biology Unit 2 Study Guide: Biochemistry
... 12. Describe the endosymbiosis theory. 13. List types of cells that would be expected to have cell walls and/or cell membranes 14. Describe what cell walls and cell membranes do 15. Diagram the structure of the cell wall and cell membrane 16. Explain and diagram the fluid mosaic model of membrane st ...
... 12. Describe the endosymbiosis theory. 13. List types of cells that would be expected to have cell walls and/or cell membranes 14. Describe what cell walls and cell membranes do 15. Diagram the structure of the cell wall and cell membrane 16. Explain and diagram the fluid mosaic model of membrane st ...
Life Science Semester Review Part 2 NAME
... 43. What does NOT occur in meiosis? a. Two nuclear divisions b. Formation of homologous chromosome pairs c. Two daughter cells at completion 44. Amy observes a unicellular organism under a microscope. Then she reexams the organism 30 minutes later and there are now two unicellular organisms on the ...
... 43. What does NOT occur in meiosis? a. Two nuclear divisions b. Formation of homologous chromosome pairs c. Two daughter cells at completion 44. Amy observes a unicellular organism under a microscope. Then she reexams the organism 30 minutes later and there are now two unicellular organisms on the ...
botany practice test i - sample questions-doc
... D. A plant attracts a pollinating insect by producing brightly colored flowers to increase the likelihood of successful a mating event leading to seed production. E. Sunlight energy is captured by a plant leaf through the process called photosynthesis. ...
... D. A plant attracts a pollinating insect by producing brightly colored flowers to increase the likelihood of successful a mating event leading to seed production. E. Sunlight energy is captured by a plant leaf through the process called photosynthesis. ...
Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function
... Note: In Eukaryotes, ORGANELLES float within cytoplasm and perform specific functions ...
... Note: In Eukaryotes, ORGANELLES float within cytoplasm and perform specific functions ...
Cytoskeleton
... Are fixed at one end and allowed to move freely at the other end – Movement is directional ...
... Are fixed at one end and allowed to move freely at the other end – Movement is directional ...
9-2 Mitosis and cytokinesis
... A. larger cells B. smaller cells C. cells with lower surface area to volume ratio ...
... A. larger cells B. smaller cells C. cells with lower surface area to volume ratio ...
organelle function ws. - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... surrounds the nucleus and controls what enters andleaves it. -a' 7. The €E $IP38.-arestructuresthatcontaindigestiveenzymes. o ffi 9. In addition to a cell membrane, plant cells also have a that serves to ...
... surrounds the nucleus and controls what enters andleaves it. -a' 7. The €E $IP38.-arestructuresthatcontaindigestiveenzymes. o ffi 9. In addition to a cell membrane, plant cells also have a that serves to ...
• SWBAT create and label cell diagrams in order to compare and
... and chloroplasts in your answer. ...
... and chloroplasts in your answer. ...
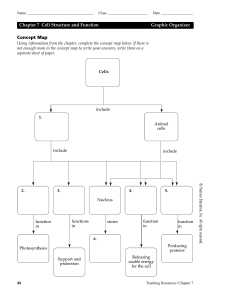
Concept Map Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Graphic
... Labeling Diagrams On the lines provided, label the structures found in an animal cell that correspond with the numbers in the diagram. Ribosome (attached) Nucleolus ...
... Labeling Diagrams On the lines provided, label the structures found in an animal cell that correspond with the numbers in the diagram. Ribosome (attached) Nucleolus ...
APB Unit 2 Outline - Westminster Public Schools Wiki
... What are various mechanisms by which substances cross membranes? ...
... What are various mechanisms by which substances cross membranes? ...
organelles
... All organisms are made of CELLS • Cells make up our tissues that comprise our organs, that make our functioning ...
... All organisms are made of CELLS • Cells make up our tissues that comprise our organs, that make our functioning ...
Role of tumor suppressor WOX1 in breast cancer cell migration
... acts as a proapoptotic protein and tumor suppressor. Loss of heterozygosity and chromosomal rearrangement of the WOX1 gene is associated with ovarian, breast, hepatocellular, and prostate carcinomas. In addition, loss of WOX1 expression results in tumorigenesis. WOX1 is also associated with malignan ...
... acts as a proapoptotic protein and tumor suppressor. Loss of heterozygosity and chromosomal rearrangement of the WOX1 gene is associated with ovarian, breast, hepatocellular, and prostate carcinomas. In addition, loss of WOX1 expression results in tumorigenesis. WOX1 is also associated with malignan ...
Name that Organelle Review PPT
... nuclear envelope (membrane) with pores • Usually the largest organelle ...
... nuclear envelope (membrane) with pores • Usually the largest organelle ...
Mitochondrial Disease
... Mitochondrial Disease • Mitochondrial diseases result from failures of the mitochondria. Mitochondria are responsible for creating more than 90% of the energy needed by the body to sustain life and support growth. When they fail, less and less energy is generated within the cell. Cell injury and ev ...
... Mitochondrial Disease • Mitochondrial diseases result from failures of the mitochondria. Mitochondria are responsible for creating more than 90% of the energy needed by the body to sustain life and support growth. When they fail, less and less energy is generated within the cell. Cell injury and ev ...
The Cell - Shelly`s Science Spot
... • Identified in 1833 by Robert Brown • Found in both plant and animal cells • Large, oval shape • Centrally located in cell • Controls cell activities • It’s like the Mayor’s • Contains genetic Office in City Hall! information (DNA) ...
... • Identified in 1833 by Robert Brown • Found in both plant and animal cells • Large, oval shape • Centrally located in cell • Controls cell activities • It’s like the Mayor’s • Contains genetic Office in City Hall! information (DNA) ...
Biochemistry
... results in fragmentation of the cell membrane and nucleus (karyolysis). Eosinophilia is increased following death (“red is dead”). Functional changes include: reduced integrity of the cell membrane, the cytoskeleton, and the genetic apparatus along with reduced ATP and protein production. 2) To lear ...
... results in fragmentation of the cell membrane and nucleus (karyolysis). Eosinophilia is increased following death (“red is dead”). Functional changes include: reduced integrity of the cell membrane, the cytoskeleton, and the genetic apparatus along with reduced ATP and protein production. 2) To lear ...
A 12) In a hypotonic solution an animal cell will
... Plant Phys Chapter 1 and 10 Review Questions 1) In a hypotonic solution an animal cell will 2) Ions diffuse across membranes down their 3) What are the membrane structures that function in active transport? 4) The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule requires which of the fo ...
... Plant Phys Chapter 1 and 10 Review Questions 1) In a hypotonic solution an animal cell will 2) Ions diffuse across membranes down their 3) What are the membrane structures that function in active transport? 4) The bonding of two amino acid molecules to form a larger molecule requires which of the fo ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
... •2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. •Cells are the basic unit of life. ...
... •2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. •Cells are the basic unit of life. ...
Interesting facts: • Many cells in the body use exocytosis to release
... Many cells in the body use exocytosis to release enzymes or other proteins that act in other areas of the body like secretion of the hormones glucagon and insulin, or to release molecules that help cells communicate with one another more directly through the products that they secrete like neurotran ...
... Many cells in the body use exocytosis to release enzymes or other proteins that act in other areas of the body like secretion of the hormones glucagon and insulin, or to release molecules that help cells communicate with one another more directly through the products that they secrete like neurotran ...
combindedAronsMyxoNoSim
... • Cells Turning to follow tracks • Cells bending as the move along tracks ...
... • Cells Turning to follow tracks • Cells bending as the move along tracks ...
Course outline - E-Learning/An
... Course description: This course is concerned primarily with eukaryotic cells. Lectures are devoted to structural details and the molecular functions of the different parts of the cell. Lectures will introduce topics such as endocytosis, intramembrane transport, protein targeting, organelle biosynthe ...
... Course description: This course is concerned primarily with eukaryotic cells. Lectures are devoted to structural details and the molecular functions of the different parts of the cell. Lectures will introduce topics such as endocytosis, intramembrane transport, protein targeting, organelle biosynthe ...