Deterministic Global Parameter Estimation for a Budding
... Students: Nick Allen* Emery Conrad+ Ranjit Randhawa* Marc Vass* Jason Zwolak* ...
... Students: Nick Allen* Emery Conrad+ Ranjit Randhawa* Marc Vass* Jason Zwolak* ...
What type of cells did you observe?
... AIM: How can we describe the structure and function of cell organelles? DN: What are organelles? Name at least two organelles and describe the function of each one. HW: Read pages 173-183, page 183 #1-6 ...
... AIM: How can we describe the structure and function of cell organelles? DN: What are organelles? Name at least two organelles and describe the function of each one. HW: Read pages 173-183, page 183 #1-6 ...
Biology LP 10.17-10.28
... Using a biology book as a reference, carefully draw, label, and describe the parts of a prokaryotic & a eukaryotic cell. Using the book, read about prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Write a paragraph that describes the main characteristics of each as well as their primary differences. Share findings with ...
... Using a biology book as a reference, carefully draw, label, and describe the parts of a prokaryotic & a eukaryotic cell. Using the book, read about prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Write a paragraph that describes the main characteristics of each as well as their primary differences. Share findings with ...
Modeling Meiosis - Highline Public Schools
... 12. Telophase 2 and Cytokinesis: Each of the two cells pinches in the middle and then divides in half. Move and then cut the yarn to show these cells being divided in half. Draw the chromosomes the 3rd-level bubbles of the diagram below. How many cells are formed? ___________________________________ ...
... 12. Telophase 2 and Cytokinesis: Each of the two cells pinches in the middle and then divides in half. Move and then cut the yarn to show these cells being divided in half. Draw the chromosomes the 3rd-level bubbles of the diagram below. How many cells are formed? ___________________________________ ...
Cell Analogy Analogy to a School
... the cell's hereditary material, or DNA, and it coordinates the cell's activities Analogy: Office controls what goes on through the entire school Found in both plant and animal cells ...
... the cell's hereditary material, or DNA, and it coordinates the cell's activities Analogy: Office controls what goes on through the entire school Found in both plant and animal cells ...
Click here for Section 5.1 Study Guide
... 7. During which stage of the cell cycle is DNA copied? During S-Phase (referred to also as Synthesis) 8. Which stages of the cell cycle generally require about the same amount of time in all human cells? M-phase (mitosis and cytokinesis), S-Phase when DNA is synthesized, and Gap 2. Gap 1 is the high ...
... 7. During which stage of the cell cycle is DNA copied? During S-Phase (referred to also as Synthesis) 8. Which stages of the cell cycle generally require about the same amount of time in all human cells? M-phase (mitosis and cytokinesis), S-Phase when DNA is synthesized, and Gap 2. Gap 1 is the high ...
Cell Junctions II
... Size of gap junction channel can be determined with fluorescent molecules of different sizes ...
... Size of gap junction channel can be determined with fluorescent molecules of different sizes ...
Chapter 1
... Chromosomes-contains genetic info. pass from one generation to the next. ChromatIN- material IN chromosomes DNA-(DNA and protein found in chromatin) RNA and ribosomes- found in nucleolus ...
... Chromosomes-contains genetic info. pass from one generation to the next. ChromatIN- material IN chromosomes DNA-(DNA and protein found in chromatin) RNA and ribosomes- found in nucleolus ...
surface area ÷ volume
... • Which has a larger surface are to volume ratio – a tennis ball or a soccer ball? Explain your answer. • What limits the maximum size of a cell? Some single celled organisms have been found to consist of cells over 4 mm long. Speculate – what sorts of adaptations should biologists look for to expla ...
... • Which has a larger surface are to volume ratio – a tennis ball or a soccer ball? Explain your answer. • What limits the maximum size of a cell? Some single celled organisms have been found to consist of cells over 4 mm long. Speculate – what sorts of adaptations should biologists look for to expla ...
5 E`s Lesson Components
... Engagement: The activities in this section capture the student’s attention, stimulate their thinking and help them access prior knowledge. Review plant cell parts and functions: Bring in a jello snack. Use a clear pyrex dish (cell wall). Line the dish with slices of banana (cell membrane). Fill with ...
... Engagement: The activities in this section capture the student’s attention, stimulate their thinking and help them access prior knowledge. Review plant cell parts and functions: Bring in a jello snack. Use a clear pyrex dish (cell wall). Line the dish with slices of banana (cell membrane). Fill with ...
Chap 4 sec 2 Fact Review Sheet
... The presence of a cell wall distinguishes the plant cell from the animal cell. Cell Membrane: 10. All cells have a cell membrane made up of proteins and lipids. 11. The cell membrane is a protective barrier that encloses a cell. 12. The cell membrane is the outmost structure of cells that lack a cel ...
... The presence of a cell wall distinguishes the plant cell from the animal cell. Cell Membrane: 10. All cells have a cell membrane made up of proteins and lipids. 11. The cell membrane is a protective barrier that encloses a cell. 12. The cell membrane is the outmost structure of cells that lack a cel ...
Cell Structures Microviewer Activity
... Draw the onion cell and be sure to label the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, and cell wall. ...
... Draw the onion cell and be sure to label the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, and cell wall. ...
Course outline cell biology 2016 2017 (2) modified (1)
... Course description: This course is concerned primarily with eukaryotic cells. Lectures are devoted to structural details and the molecular functions of the different parts of the cell. Lectures will introduce topics such as endocytosis, intramembrane transport, protein targeting, organelle biosynthe ...
... Course description: This course is concerned primarily with eukaryotic cells. Lectures are devoted to structural details and the molecular functions of the different parts of the cell. Lectures will introduce topics such as endocytosis, intramembrane transport, protein targeting, organelle biosynthe ...
PROKARYOTIC CELLS - Life is a journey: Mr. T finding his way
... 3. The cell elongates, causing the two chromosomes to separate 4. The plasma membrane then grows inward and splits the cell into two daughter cells 5. These 2 cells than both grow to the size of the parent cell ...(Show a video) ...
... 3. The cell elongates, causing the two chromosomes to separate 4. The plasma membrane then grows inward and splits the cell into two daughter cells 5. These 2 cells than both grow to the size of the parent cell ...(Show a video) ...
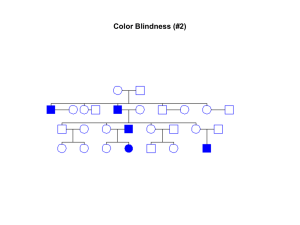
Extra Pedigree Problem - Winona State University
... Sickle Cell Anemia Affects the B-chain of Hemoglobin. It is a genetically inherited disease, and is seen commonly in Africa. Sickle Cell Disease is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. Normal red blood cells are round like doughnuts, and they move through small blood tubes in the body to ...
... Sickle Cell Anemia Affects the B-chain of Hemoglobin. It is a genetically inherited disease, and is seen commonly in Africa. Sickle Cell Disease is a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. Normal red blood cells are round like doughnuts, and they move through small blood tubes in the body to ...
Biology End-of-Course Test Study Guide
... Cellular Organelles structure and function (nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts and ribosomes) Microscope technique (total magnification) Cellular organization (cellstissuesorgansorgan systems) Plant cells vs. Animal cells Homeostasis (temperature, pH, water ...
... Cellular Organelles structure and function (nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts and ribosomes) Microscope technique (total magnification) Cellular organization (cellstissuesorgansorgan systems) Plant cells vs. Animal cells Homeostasis (temperature, pH, water ...