Plant Structure and Function
... We shall begin the study of this unit by reviewing the structure of the different parts of a plant cell and how the structures of those parts are suited to the function they perform. As we have already learned, the cell is the basic unit of structure and function. A good understanding of cell struct ...
... We shall begin the study of this unit by reviewing the structure of the different parts of a plant cell and how the structures of those parts are suited to the function they perform. As we have already learned, the cell is the basic unit of structure and function. A good understanding of cell struct ...
Groupwork on Flow of Matter
... Checklist for Explanatory Model of the Flow of Matter from Food Cells to Our Cells Scientists use explanatory models in order to be able to connect a series of ideas to explain how a natural phenomenon might work. Their explanation includes the available evidence and existing scientific knowledge up ...
... Checklist for Explanatory Model of the Flow of Matter from Food Cells to Our Cells Scientists use explanatory models in order to be able to connect a series of ideas to explain how a natural phenomenon might work. Their explanation includes the available evidence and existing scientific knowledge up ...
backward design template - reflectivepractitionerwiki
... 3. Mini-Quiz- students will be given a quiz that will not count as a grade to assess their knowledge of cell organelles and kingdoms. Step 3: Plan Learning Experiences and Instruction Given the targeted understandings, other unit goals, and the assessment evidence identified, what knowledge and skil ...
... 3. Mini-Quiz- students will be given a quiz that will not count as a grade to assess their knowledge of cell organelles and kingdoms. Step 3: Plan Learning Experiences and Instruction Given the targeted understandings, other unit goals, and the assessment evidence identified, what knowledge and skil ...
Project
... cells. In this project students will compare and animal cell and plant cell contrast the organelles in both an animal cell Compare and contrast animal and plant and plant cell. Students will create a rap that cells shows their understanding of how the Explain the function of the various individual o ...
... cells. In this project students will compare and animal cell and plant cell contrast the organelles in both an animal cell Compare and contrast animal and plant and plant cell. Students will create a rap that cells shows their understanding of how the Explain the function of the various individual o ...
1 The Characteristics of Cells
... All living things are made of tiny structures called cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can perform all the functions needed for life. Most cells are so small you need a microscope to see them. More than 50 human cells can fit on the dot in this letter i. Some living things are made of only one ...
... All living things are made of tiny structures called cells. A cell is the smallest unit that can perform all the functions needed for life. Most cells are so small you need a microscope to see them. More than 50 human cells can fit on the dot in this letter i. Some living things are made of only one ...
Physiology 2008
... i. nerve cell endings are directly damaged ii. as a consequence of fluid accumulation (edema) from the vessels with increased permeability c. pain, limitation of movement due to the edema, and tissue destruction all contribute to disturbance of function E. Tissue Repair - the substitution of viable ...
... i. nerve cell endings are directly damaged ii. as a consequence of fluid accumulation (edema) from the vessels with increased permeability c. pain, limitation of movement due to the edema, and tissue destruction all contribute to disturbance of function E. Tissue Repair - the substitution of viable ...
Biol2174 Ionic composition of cells
... • Developed by Erwin Neher and Bert Sakman in the late 1970s and early 1980s. Revolutionised cell physiology. Neher and Sakman were awarded the Nobel prize for Medicine in 1991. • In their initial experiments they pressed a firepolished glass micropipette up against the membrane of an intact cell an ...
... • Developed by Erwin Neher and Bert Sakman in the late 1970s and early 1980s. Revolutionised cell physiology. Neher and Sakman were awarded the Nobel prize for Medicine in 1991. • In their initial experiments they pressed a firepolished glass micropipette up against the membrane of an intact cell an ...
Cell Cycle
... Cell Cycle Control How does cell “know” when to divide? Cell cycle controlled by many proteins (enzymes) at three main checkpoints: G1 checkpoint – decision made whether cell will divide (cell healthy and large enough). Some types of cell never pass this point (nerve, muscle) G2 checkpoint ...
... Cell Cycle Control How does cell “know” when to divide? Cell cycle controlled by many proteins (enzymes) at three main checkpoints: G1 checkpoint – decision made whether cell will divide (cell healthy and large enough). Some types of cell never pass this point (nerve, muscle) G2 checkpoint ...
Cells
... What happens if you pour dye on top of a layer of gelatin? At first, it is easy to see where the dye ends and the gelatin begins. But over time, the line between the two layers will blur, as shown in Figure 1. Why? Everything, including the gelatin and the dye, is made up of tiny moving particles. P ...
... What happens if you pour dye on top of a layer of gelatin? At first, it is easy to see where the dye ends and the gelatin begins. But over time, the line between the two layers will blur, as shown in Figure 1. Why? Everything, including the gelatin and the dye, is made up of tiny moving particles. P ...
Chromosomes and Cell Reproduction Human Reproduction
... Mitosis results in new cells with genetic material identical to that of the original cell. This process is the reason for human growth. Mitosis occurs in all cells of the body except the sex cells (egg and sperm cells). Sex cells undergo a different process called meiosis. Mitosis has 4 phases: ...
... Mitosis results in new cells with genetic material identical to that of the original cell. This process is the reason for human growth. Mitosis occurs in all cells of the body except the sex cells (egg and sperm cells). Sex cells undergo a different process called meiosis. Mitosis has 4 phases: ...
here - The University of Sydney
... Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a highly conserved biological process required for the removal of unwanted, damaged or infected cells. The central regulators of apoptotic programmed cell death belong to the BCL‐2 family of proteins. A delicate interplay ...
... Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is a highly conserved biological process required for the removal of unwanted, damaged or infected cells. The central regulators of apoptotic programmed cell death belong to the BCL‐2 family of proteins. A delicate interplay ...
File - Mrs. Glazebrook
... Other Membrane Components There are other parts to the membrane, including cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates ...
... Other Membrane Components There are other parts to the membrane, including cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates ...
What is a stem cell?
... neoplasm: abnormal growth of cells benign: non-cancerous malignant: cancerous Cancer: cellular growth disorder that results from the mutation of genes that regulate the cell cycle Cancer cells lack differentiation have abnormal nuclei form tumors undergo metastasis & angiogenesis ...
... neoplasm: abnormal growth of cells benign: non-cancerous malignant: cancerous Cancer: cellular growth disorder that results from the mutation of genes that regulate the cell cycle Cancer cells lack differentiation have abnormal nuclei form tumors undergo metastasis & angiogenesis ...
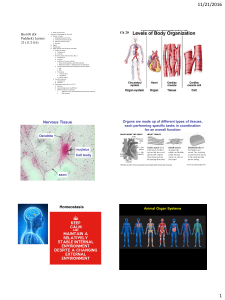
Nervous Tissue Homeostasis
... distinguishing the nervous system into a central & peripheral system. Note which part of the system is involved in each step: sensory input, integration, motor output. ...
... distinguishing the nervous system into a central & peripheral system. Note which part of the system is involved in each step: sensory input, integration, motor output. ...
Cell Growth and Mitosis Notes:
... What are the main events of the cell cycle? Cell Cycle The ______________ is the series of events that cells go through as they _______ and __________. _______________ is the period of growth that occurs between cell divisions. During the cell cycle: • a cell _____________ • prepares for ___________ ...
... What are the main events of the cell cycle? Cell Cycle The ______________ is the series of events that cells go through as they _______ and __________. _______________ is the period of growth that occurs between cell divisions. During the cell cycle: • a cell _____________ • prepares for ___________ ...
23-1 Specialized Tissues in Plants
... D) ___________________ Tissue 1) Cells that lie between ______________ and vascular tissues make up the ground __________________. 2) The three kinds of ground tissue are: (i) _________________________ (ii) _________________________ (iii)_________________________ (b) Parenchyma cells have __________ ...
... D) ___________________ Tissue 1) Cells that lie between ______________ and vascular tissues make up the ground __________________. 2) The three kinds of ground tissue are: (i) _________________________ (ii) _________________________ (iii)_________________________ (b) Parenchyma cells have __________ ...
Familial Connection with Mast Cell.EDS.Dysautonomia
... Fellinger et al. Allergol Immunopathol. 2014 ...
... Fellinger et al. Allergol Immunopathol. 2014 ...
Bacterial growth
... a-Substances required for growth that the cell cannot produce using the basic requirements already listed ( Ex. : vitamins, amino acids, carbohydrates, blood factors ) b- Organisms may be described as being fastidious Two types organisms based on source of nutrients : 1-Autotrophs - utilize inorgani ...
... a-Substances required for growth that the cell cannot produce using the basic requirements already listed ( Ex. : vitamins, amino acids, carbohydrates, blood factors ) b- Organisms may be described as being fastidious Two types organisms based on source of nutrients : 1-Autotrophs - utilize inorgani ...
Unit 4 Notes
... • Cyclin increase in concentration in G2 and bind with a specific Cdk to form MPF • MPF signals the start of Mitosis • At end of mitosis, enzymes break down cyclin…so no MPF…and no more dividing (Cdk concentration remains the same) ...
... • Cyclin increase in concentration in G2 and bind with a specific Cdk to form MPF • MPF signals the start of Mitosis • At end of mitosis, enzymes break down cyclin…so no MPF…and no more dividing (Cdk concentration remains the same) ...
The Prokaryotes Simplest organisms All unicellular
... 4. Feeding B. Flagella - Solid, unsheathed, protein - Filament, hook, basal body C. Axial Filaments D. Fimbriae and Pili ...
... 4. Feeding B. Flagella - Solid, unsheathed, protein - Filament, hook, basal body C. Axial Filaments D. Fimbriae and Pili ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... Nucleus Ribosome Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Vesicles Export How is the nucleus involved in protein synthesis? It contains the directions for making protiens What organelle is considered a “factory”, because it takes in raw materials and converts them to cell products that can be ...
... Nucleus Ribosome Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Vesicles Export How is the nucleus involved in protein synthesis? It contains the directions for making protiens What organelle is considered a “factory”, because it takes in raw materials and converts them to cell products that can be ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.