... specifically bind the Fe portion of IgE antibody with high affinity. After active or passive sensitization with IgE, exposure to specific antigen triggers both cell types to undergo a series of biochemical and morphological alterations that eventually results in the release of prefonned (granule ass ...
Anti-Myosin 1C antibody ab154498 Product datasheet 1 Abreviews 3 Images
... Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and Spanish Extensive multi-media technical resources to help you We invest ...
... Replacement or refund for products not performing as stated on the datasheet Valid for 12 months from date of delivery Response to your inquiry within 24 hours We provide support in Chinese, English, French, German, Japanese and Spanish Extensive multi-media technical resources to help you We invest ...
Cell Structure & Function
... • All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. ...
... • All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. ...
Cell Structure & Function
... • All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. ...
... • All living things are made up of cells. • Cells are the smallest working units of all living things. • All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division. ...
Name
... 14. What do you call the interaction where there is a struggle between organisms to survive as they attempt to use the same limited resource? Competition ...
... 14. What do you call the interaction where there is a struggle between organisms to survive as they attempt to use the same limited resource? Competition ...
Honors Biology - UNIT 6
... Plant and algae cell walls are composed mostly of the polysaccharide cellulose. Many plants have two cell walls for added strength such as woody plants. The first cell wall is thin and flexible called the primary cell wall it is mostly cellulose mixed with a substance called lignin for added support ...
... Plant and algae cell walls are composed mostly of the polysaccharide cellulose. Many plants have two cell walls for added strength such as woody plants. The first cell wall is thin and flexible called the primary cell wall it is mostly cellulose mixed with a substance called lignin for added support ...
brief overview of the 5 kingdoms
... Sensitivity - response to a stimulus (e.g. light or chemicals such as food) Growth – increase in cellular mass and/or increase in number of cells Reproduction – formation of another organism. Since viruses cannot reproduce on their own without being inside a host cell, they are not regarded as ...
... Sensitivity - response to a stimulus (e.g. light or chemicals such as food) Growth – increase in cellular mass and/or increase in number of cells Reproduction – formation of another organism. Since viruses cannot reproduce on their own without being inside a host cell, they are not regarded as ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
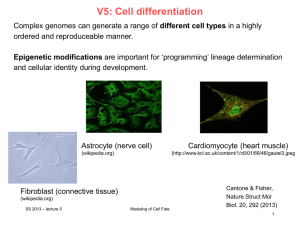
... Adult cells in cell culture have a much reduced ability of self regeneration and a reduced ability for differentiation compared to embryonic stem cells. For example, neural stem cells can differentiate to all cell types of neural tissue (neorons, glia), but likely not into liver or muscle cells. ...
... Adult cells in cell culture have a much reduced ability of self regeneration and a reduced ability for differentiation compared to embryonic stem cells. For example, neural stem cells can differentiate to all cell types of neural tissue (neorons, glia), but likely not into liver or muscle cells. ...
Unit1CellsVocabulary
... 7. Cytoplasm: fluid inside a cell, is where everything is in the cell, like a factory floor 8. Organelles: structures in cells that perform specific functions 9. DNA: short for deoxyribonucleic acid. Contains instructions for all cell processes 10. Nucleus: organelle in eukaryotic cells that contain ...
... 7. Cytoplasm: fluid inside a cell, is where everything is in the cell, like a factory floor 8. Organelles: structures in cells that perform specific functions 9. DNA: short for deoxyribonucleic acid. Contains instructions for all cell processes 10. Nucleus: organelle in eukaryotic cells that contain ...
03 Movement in and out of cells
... Movement in and out of cells Cells need to take in oxygen and nutrients for respiration. They also need to remove waste products such as CO2. The cell membrane controls movement of materials. Generally, this is determined by the size of the molecule. Smaller molecules move through more easily and qu ...
... Movement in and out of cells Cells need to take in oxygen and nutrients for respiration. They also need to remove waste products such as CO2. The cell membrane controls movement of materials. Generally, this is determined by the size of the molecule. Smaller molecules move through more easily and qu ...
Chapter 3 - Martini
... • Organisms depend upon the activity of cells to exist • Subcellular structures are responsible for specific cellular biochemical functions according to the “complimentarity of structure & function” ...
... • Organisms depend upon the activity of cells to exist • Subcellular structures are responsible for specific cellular biochemical functions according to the “complimentarity of structure & function” ...
Cell
... Plant Cuticle • Cuticle (表皮) • A waxy covering that protects exposed surfaces and limits water loss ...
... Plant Cuticle • Cuticle (表皮) • A waxy covering that protects exposed surfaces and limits water loss ...
Animal Cells - WordPress.com
... • A cell membrane keeps all the parts of the cell inside. • It controls what enters and exits the cell such as water, nutrients and waste and thereby protects and supports the cell. • It is the outermost layer in the animal cell. ...
... • A cell membrane keeps all the parts of the cell inside. • It controls what enters and exits the cell such as water, nutrients and waste and thereby protects and supports the cell. • It is the outermost layer in the animal cell. ...
K - FJchimie11
... around to create equilibrium. It is a passive movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration. However, there are some key differences between the two. Osmosis involves only water. Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of high co ...
... around to create equilibrium. It is a passive movement of molecules from high concentration to low concentration. However, there are some key differences between the two. Osmosis involves only water. Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of high co ...
Cell Travel Brochure 2
... Due Date October 21, 2016 (This Friday) Learning Goal: Compare plant and animal cells. Objective You will produce a travel brochure that describes a plant or animal cell as if it were a large amusement park or attraction. Examples could be (but not limited to) a: Luxury hotel, Ski resort, Amusement ...
... Due Date October 21, 2016 (This Friday) Learning Goal: Compare plant and animal cells. Objective You will produce a travel brochure that describes a plant or animal cell as if it were a large amusement park or attraction. Examples could be (but not limited to) a: Luxury hotel, Ski resort, Amusement ...
Life Science
... Epithelial cells are used for protection and forming the lining of many body surfaces. They can be removed easily and are replaced quickly. ...
... Epithelial cells are used for protection and forming the lining of many body surfaces. They can be removed easily and are replaced quickly. ...
Top of Form Chapter 1: Bacteria Compared with Other
... DNA; this is surrounded by cytoplasm, within which proteins are synthesized and energy is generated. Viruses have an inner core of genetic material (either DNA or RNA) but no cytoplasm, and so they depend on host cells to provide the machinery for protein synthesis and energy generation. ...
... DNA; this is surrounded by cytoplasm, within which proteins are synthesized and energy is generated. Viruses have an inner core of genetic material (either DNA or RNA) but no cytoplasm, and so they depend on host cells to provide the machinery for protein synthesis and energy generation. ...
Organelle Web
... on “Cell membrane.” What type of molecule makes up the double layer in the cell membrane? Describe the function of a. If all cells in your body have the the cell membrane. same genetic material, how do we have a wide variety of cells (nerve The cell membrane is made of two cells, liver cells, skin c ...
... on “Cell membrane.” What type of molecule makes up the double layer in the cell membrane? Describe the function of a. If all cells in your body have the the cell membrane. same genetic material, how do we have a wide variety of cells (nerve The cell membrane is made of two cells, liver cells, skin c ...
Muscle Cells
... keep the body healthy. Some white blood cells gobble up invader cells and harmful substances. Other white blood cells produce weapons, called antibodies, to fight invaders. Platelets are the blood's repairmen. Groups of them stick together to form a plug whenever a blood vessel breaks. ...
... keep the body healthy. Some white blood cells gobble up invader cells and harmful substances. Other white blood cells produce weapons, called antibodies, to fight invaders. Platelets are the blood's repairmen. Groups of them stick together to form a plug whenever a blood vessel breaks. ...
Cell Structure
... • The cell is the fundamental unit of life. All organisms, whatever their type or size, are composed of cells. The modern theory of cellular organisation states:– All living things are composed of cells and cell products. – New cells are formed only by the division of pre-existing cells – The cell c ...
... • The cell is the fundamental unit of life. All organisms, whatever their type or size, are composed of cells. The modern theory of cellular organisation states:– All living things are composed of cells and cell products. – New cells are formed only by the division of pre-existing cells – The cell c ...
Cell Processes - De Soto Area School District
... passing through it The amount of raw materials needed by a large cell couldn’t enter fast enough The wastes produced couldn’t leave fast enough ...
... passing through it The amount of raw materials needed by a large cell couldn’t enter fast enough The wastes produced couldn’t leave fast enough ...
Cells
... 1. Which of the following is the only cell organelle that is capable of converting light energy into chemical energy? A. mitochondrion B. vacuole C. chloroplast D. endoplasmic reticulum 2. Some prokaryotes and eukaryotes have whip-like projections that help propel the cell through liquid. What is th ...
... 1. Which of the following is the only cell organelle that is capable of converting light energy into chemical energy? A. mitochondrion B. vacuole C. chloroplast D. endoplasmic reticulum 2. Some prokaryotes and eukaryotes have whip-like projections that help propel the cell through liquid. What is th ...
Oregonism
... where μ represents the specific growth rate. During exponential growth the specific growth rate reaches its maximum and remains constant at μ = μmax. ...
... where μ represents the specific growth rate. During exponential growth the specific growth rate reaches its maximum and remains constant at μ = μmax. ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.