Homework 1-6 Classifying Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes File
... 1. ___________ - This organism is made of many cells. Each cell has a nucleus, mitochondria and many chloroplasts. It can grow to over 100 ft tall and produces many woody cones for reproduction. 2. ___________- This organism is made of one cell. The cell contains many organelles such as lysosomes an ...
... 1. ___________ - This organism is made of many cells. Each cell has a nucleus, mitochondria and many chloroplasts. It can grow to over 100 ft tall and produces many woody cones for reproduction. 2. ___________- This organism is made of one cell. The cell contains many organelles such as lysosomes an ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Buffer – system of chemicals that takes up excess H ions or hydroxide ions ...
... Buffer – system of chemicals that takes up excess H ions or hydroxide ions ...
l2 biology: topics covered on the midterm exam and what to study
... Are a type of protein How do they function/are used in living organisms How do they work in a chemical reaction? Understand substrate, reactants, products. Effects of temperature, pH on enzyme action Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport: diffusion and osmosis: passive vs. active transport ...
... Are a type of protein How do they function/are used in living organisms How do they work in a chemical reaction? Understand substrate, reactants, products. Effects of temperature, pH on enzyme action Cell Membrane and Cellular Transport: diffusion and osmosis: passive vs. active transport ...
Name
... Name ________________________________________ Date ______________ Period __________ Reinforcement Worksheet – Cell Theory, Scientists, & Cell Types The invention of the microscope in the late 1500s revealed to early scientists a whole new world of tiny cells. Most cells are so small that they cannot ...
... Name ________________________________________ Date ______________ Period __________ Reinforcement Worksheet – Cell Theory, Scientists, & Cell Types The invention of the microscope in the late 1500s revealed to early scientists a whole new world of tiny cells. Most cells are so small that they cannot ...
Mitosis Lab Activity: 1. Diagram a cell in interphase, prophase
... 5. Calculate the time a cell spends in each phase. Consider that it takes, on average, 24 hours (or 1,440 minutes) for onion root tip cells to complete the cell cycle. You can calculate the amou ...
... 5. Calculate the time a cell spends in each phase. Consider that it takes, on average, 24 hours (or 1,440 minutes) for onion root tip cells to complete the cell cycle. You can calculate the amou ...
Understanding cell and tissue size and shape regulation in a stem
... computational morphodynamics approach Plant meristems are stem cell niches continuously providing new cells throughout the life of a growing plant. The maintenance of the shoot apical meristem is regulated by an interaction between hormones and a gene regulatory network. A negative feedback between ...
... computational morphodynamics approach Plant meristems are stem cell niches continuously providing new cells throughout the life of a growing plant. The maintenance of the shoot apical meristem is regulated by an interaction between hormones and a gene regulatory network. A negative feedback between ...
Biology Review
... 12. Identify these specialized cells from the descriptions of their functions (p.55). Cells that move bones Cells that cover the body and help keep moisture inside Cells that distribute oxygen and remove carbon dioxide Cells that transmit electrical signals from the brain ...
... 12. Identify these specialized cells from the descriptions of their functions (p.55). Cells that move bones Cells that cover the body and help keep moisture inside Cells that distribute oxygen and remove carbon dioxide Cells that transmit electrical signals from the brain ...
Week 18 - Crossroads Academy
... • Eukaryotic cells contain membrane bound nuclei such as a nucleus. • The cytoplasm is a souplike fluid containing water, dissolved substances and many small organelles • The Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of flattened sacs and tubes that form channels throughout the cytoplasm. Plays a majo ...
... • Eukaryotic cells contain membrane bound nuclei such as a nucleus. • The cytoplasm is a souplike fluid containing water, dissolved substances and many small organelles • The Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of flattened sacs and tubes that form channels throughout the cytoplasm. Plays a majo ...
biology exam review
... 19. Tendons connect ___________ to ____________. When muscle _____________ they pull the bone Muscles can only _________and therefore work in groups. (3.8) 20. Differentiate between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. (3.10) 21. Describe the functions of the following organ ...
... 19. Tendons connect ___________ to ____________. When muscle _____________ they pull the bone Muscles can only _________and therefore work in groups. (3.8) 20. Differentiate between the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. (3.10) 21. Describe the functions of the following organ ...
Monkemeier - Madison Public Schools
... structure and support. b. This is the area in the cytoplasm that contains the chromosome (DNA) c. This is the only membrane that the bacteria (prokaryote) is allowed to have. It lies just inside the cell wall. d. This is the fluid- like substance and area that is surrounded by the cell ...
... structure and support. b. This is the area in the cytoplasm that contains the chromosome (DNA) c. This is the only membrane that the bacteria (prokaryote) is allowed to have. It lies just inside the cell wall. d. This is the fluid- like substance and area that is surrounded by the cell ...
Cell Test: Study Guide - Peoria Public Schools
... know and explain the Cell Theory name and describe the two types of cells 2. What are the building blocks of organisms? describe the relationship between atoms and molecules identify types of molecules are needed for life processes 3. What are the different parts that make up a cell? know ...
... know and explain the Cell Theory name and describe the two types of cells 2. What are the building blocks of organisms? describe the relationship between atoms and molecules identify types of molecules are needed for life processes 3. What are the different parts that make up a cell? know ...
The Function of Organelles
... mitochondria is stored in ATP Most of cell’s ATP made here Animal cells can’t make own food so we need these to break down sugar for energy ...
... mitochondria is stored in ATP Most of cell’s ATP made here Animal cells can’t make own food so we need these to break down sugar for energy ...
File
... of phospholipids • contains enzymes that catalyze oxidation reactions producing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as a by-product • additional enzymes break down the H2O2 which is toxic to the cell ...
... of phospholipids • contains enzymes that catalyze oxidation reactions producing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as a by-product • additional enzymes break down the H2O2 which is toxic to the cell ...
Cell Parts Notes
... • Prokaryote = 1 celled organisms that lack a nucleus or other structures bound by a membrane. • They have been on Earth the Longest. ...
... • Prokaryote = 1 celled organisms that lack a nucleus or other structures bound by a membrane. • They have been on Earth the Longest. ...
Cells “The Building Blocks of Life”
... living organisms. • Living matter enclosed by a barrier that separates it from the exterior environment. • What is a theory? – A set of statements or principles devised to explain a group of facts or phenomena – Based on limited information or knowledge – Verified or falsified through experimentatio ...
... living organisms. • Living matter enclosed by a barrier that separates it from the exterior environment. • What is a theory? – A set of statements or principles devised to explain a group of facts or phenomena – Based on limited information or knowledge – Verified or falsified through experimentatio ...
Cells and Cell Organelles assignment
... Cells and Cell Organelles The following questions should be answered in complete sentences that make sense. Your answer should also include definitions of any other biological terms you use in your answer. Provide enough of a description in your answer so as to explain the basics of the concept to s ...
... Cells and Cell Organelles The following questions should be answered in complete sentences that make sense. Your answer should also include definitions of any other biological terms you use in your answer. Provide enough of a description in your answer so as to explain the basics of the concept to s ...
Cell Transport PP
... 1. How do transport proteins that are pumps differ from those that are channels? ...
... 1. How do transport proteins that are pumps differ from those that are channels? ...
Unit: Cell Theory and Structure (Ch. 7 “I can…” state discuss
... Unit: Cell Theory and Structure (Ch. 7) ...
... Unit: Cell Theory and Structure (Ch. 7) ...
Cell Organelle Notes
... Remember that the plasma membrane helps maintain homeostasis within an organism All cells have a cell membrane Cell Wall Rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of PLANTS, Provides ______________________ The cell wall allows the cell to become quite turgid without bursting PLAN ...
... Remember that the plasma membrane helps maintain homeostasis within an organism All cells have a cell membrane Cell Wall Rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of PLANTS, Provides ______________________ The cell wall allows the cell to become quite turgid without bursting PLAN ...
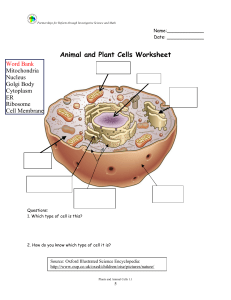
Name Date The Structure and Function of Cells Cell Part Structure
... Place where proteins are primarily of RNA; may be made attached to endoplasmic reticulum or floating free in cytoplasm; produced in nucleolus Rod shaped organelle; located in the cytoplasm; has a smooth outer membrane and a greatly folded inner membrane ...
... Place where proteins are primarily of RNA; may be made attached to endoplasmic reticulum or floating free in cytoplasm; produced in nucleolus Rod shaped organelle; located in the cytoplasm; has a smooth outer membrane and a greatly folded inner membrane ...
Biology Unit Study Check List Cell: • Organelles • Limit of size
... Parts of the microscope Magnification Field of View Calculating high power field diameter Actual Size Biological Diagrams (see webpage) ...
... Parts of the microscope Magnification Field of View Calculating high power field diameter Actual Size Biological Diagrams (see webpage) ...
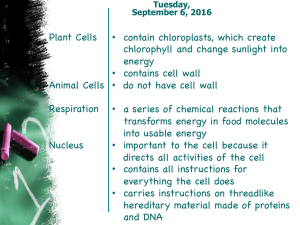
Plant Cells Animal Cells Respiration Nucleus • contain chloroplasts
... chlorophyll and change sunlight into energy ...
... chlorophyll and change sunlight into energy ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.