Determining the proportional distribution of propagons between
... micromanipulation to fresh solid YPD media containing 5mM GdnHCl. Incubate both mother and daughter cells at 30o C for 48h to allow them grow into small colonies. As these colonies are grown in the presence of 3mM GdnHCl, propagon replication remains inhibited within the cells of the colony, so that ...
... micromanipulation to fresh solid YPD media containing 5mM GdnHCl. Incubate both mother and daughter cells at 30o C for 48h to allow them grow into small colonies. As these colonies are grown in the presence of 3mM GdnHCl, propagon replication remains inhibited within the cells of the colony, so that ...
Basic Bio 3
... Respiration This is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between an organism and its environment. Selective Permeability This is an ability of a plasma membrane to allow some substances to cross across the membrane more easily than others. System This is a group of interdependent organs with si ...
... Respiration This is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between an organism and its environment. Selective Permeability This is an ability of a plasma membrane to allow some substances to cross across the membrane more easily than others. System This is a group of interdependent organs with si ...
The Cell School to Home LESSON 2 1.
... Directions: Use your textbook to answer each question or respond to each statement. ...
... Directions: Use your textbook to answer each question or respond to each statement. ...
Life Science 2014 Trimester Exam- Study Guide Be able understand
... Understand the difference between eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells Know the difference between plant and animal cells Know the organization of an organism from cells to organisms Know the structure and function of parts of the microscope Know what microscope we use in class Understand the diff ...
... Understand the difference between eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells Know the difference between plant and animal cells Know the organization of an organism from cells to organisms Know the structure and function of parts of the microscope Know what microscope we use in class Understand the diff ...
Cell Unit Project (Chapters 1-2)
... Directions: Be sure to add colored pictures (provide websites) and be creative. All foldables must be colored. Characteristics of all Living Things 1. List the characteristics of all living things (4) 2. List the needs of all living things (3) 3. What are the components of the Cell Theory? Contribut ...
... Directions: Be sure to add colored pictures (provide websites) and be creative. All foldables must be colored. Characteristics of all Living Things 1. List the characteristics of all living things (4) 2. List the needs of all living things (3) 3. What are the components of the Cell Theory? Contribut ...
3 The cell as the basic unit of life
... Several organs and tissues working for the same ultimate functions form a system. (b) organ level (c) The skin cells degenerate continuously and those dead cells are pushed towards the skin surface where they are rubbed off or detach automatically. His skin still functions well because many skin cel ...
... Several organs and tissues working for the same ultimate functions form a system. (b) organ level (c) The skin cells degenerate continuously and those dead cells are pushed towards the skin surface where they are rubbed off or detach automatically. His skin still functions well because many skin cel ...
Answers to Cells and Membrane Transport Quiz Review 1. Cells are
... Answers to Cells and Membrane Transport Quiz Review 1. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. ALL living things are made of cells. ALL cells arise from exiting cells. 2. Increases at a slower rate. 3. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus and eukaryotic cells do. 4. Cell ...
... Answers to Cells and Membrane Transport Quiz Review 1. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. ALL living things are made of cells. ALL cells arise from exiting cells. 2. Increases at a slower rate. 3. Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus and eukaryotic cells do. 4. Cell ...
Cheek Cells Lab - Rimac-Science-Web
... • To examine prepared slides of bacteria • To identify differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. ...
... • To examine prepared slides of bacteria • To identify differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. ...
Diversity of Cell Structure and Function
... 1. Complete the table to list three structures in the plant cell which are not found in animal cells and explain why each of these structures is useful for plant cells, but not for animal cells. ...
... 1. Complete the table to list three structures in the plant cell which are not found in animal cells and explain why each of these structures is useful for plant cells, but not for animal cells. ...
Reinforcement
... double-layer of phospholipids that forms a boundary between a cell and its surrounding environment membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes ...
... double-layer of phospholipids that forms a boundary between a cell and its surrounding environment membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes ...
Cett5 frLluZ * c4tv1
... Name the light related chemical reaction that occurs in the chloroplasts. ...
... Name the light related chemical reaction that occurs in the chloroplasts. ...
Scientists Notes - Woodland Hills School District
... *Contributed to the Cell Theory The Cell Theory: All living things are made of one or more ...
... *Contributed to the Cell Theory The Cell Theory: All living things are made of one or more ...
Scientists – Microscopes
... Looked at cork under microscope (also spiders, insects, flowers, etc.) Observed that cork was made of empty little boxes he named cells 3. Robert Brown When: 1800’s Discovery: nucleus Observation: observed objects in the center of cells 4. Matthias Schleiden* When: 1830’s Observations: Used micr ...
... Looked at cork under microscope (also spiders, insects, flowers, etc.) Observed that cork was made of empty little boxes he named cells 3. Robert Brown When: 1800’s Discovery: nucleus Observation: observed objects in the center of cells 4. Matthias Schleiden* When: 1830’s Observations: Used micr ...
Guided Notes sheet
... Cells are the basic ______________ of structure and function in living organisms ...
... Cells are the basic ______________ of structure and function in living organisms ...
The Cell Theory
... unit of structure and function in living things • All cells come from pre-existing cells ...
... unit of structure and function in living things • All cells come from pre-existing cells ...
Cells
... Cells Cell Theory: 1. Every organism is composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the smallest unit that has the properties of life. 3. The continuity of life arises directly from the growth and division of single cells. ...
... Cells Cell Theory: 1. Every organism is composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the smallest unit that has the properties of life. 3. The continuity of life arises directly from the growth and division of single cells. ...
The Parts of A Cell - Lemoore Elementary School
... • Some cells, like plants and fungi have a rigid cell wall. • Cell walls provide shape, support, and protection for the cell. • Animal cells DO NOT have cell walls. ...
... • Some cells, like plants and fungi have a rigid cell wall. • Cell walls provide shape, support, and protection for the cell. • Animal cells DO NOT have cell walls. ...
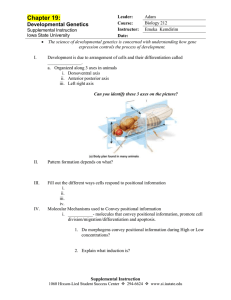
Chap 19 - Iowa State University
... In normal oocte development products of the _______ gene is accumulated at the anterior end and they later act as _________ causing development of anterior end of the embryo. ...
... In normal oocte development products of the _______ gene is accumulated at the anterior end and they later act as _________ causing development of anterior end of the embryo. ...
Chapter 1 (C) Review
... _____ 7. Which of the following best describes an organ? a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. T ...
... _____ 7. Which of the following best describes an organ? a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. T ...
Oct. 5, 2015 Cells - AP Biology Study Guide
... 5. Describe the nucleus of eukaryotes with respect to structure and function. 6. Describe the organelles associated with the endomembrane system, and tell the general function of each. 7. Contrast the structure and function of mitochondria and chloroplasts. 8. List several surface structures of cell ...
... 5. Describe the nucleus of eukaryotes with respect to structure and function. 6. Describe the organelles associated with the endomembrane system, and tell the general function of each. 7. Contrast the structure and function of mitochondria and chloroplasts. 8. List several surface structures of cell ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.