THE CELL
... Flattened, round sacs that look like a sack pancakes of ________________. Receives, modifies, and ships products by way of ___________ vesicles cytosol → cell membrane_ into the ____________________________ ...
... Flattened, round sacs that look like a sack pancakes of ________________. Receives, modifies, and ships products by way of ___________ vesicles cytosol → cell membrane_ into the ____________________________ ...
Cells Pretest - Warren County Schools
... Learning Target 2: I can describe the functions of the cell's organelles. 6. What structure allows only certain things to pass in and out of the cell? a. Cytoplasm b. Ribosomes c. Cell membrane d. Golgi body 7. What is made of folded membranes that move materials around inside the cell a. Nucleus b ...
... Learning Target 2: I can describe the functions of the cell's organelles. 6. What structure allows only certain things to pass in and out of the cell? a. Cytoplasm b. Ribosomes c. Cell membrane d. Golgi body 7. What is made of folded membranes that move materials around inside the cell a. Nucleus b ...
Get HW#__ Stamped Complete Do Now on p.
... the large paper for this. Your visual MUST include the following FOUR components: Title “A cell is like ______________” Your name Each picture/organelle labeled clearly A brief description of why its an analogy. ...
... the large paper for this. Your visual MUST include the following FOUR components: Title “A cell is like ______________” Your name Each picture/organelle labeled clearly A brief description of why its an analogy. ...
Parts of the Cell Plant and Animal
... • Since an animal cell does not have a cell wall, the cell membrane forms a barrier between the cytoplasm and the environment outside the cell; however, plants have a cell membrane as well. The cell membrane protects the cell and regulates what substances enter and leave the cell. ...
... • Since an animal cell does not have a cell wall, the cell membrane forms a barrier between the cytoplasm and the environment outside the cell; however, plants have a cell membrane as well. The cell membrane protects the cell and regulates what substances enter and leave the cell. ...
APB Unit 2 Outline - Westminster Public Schools Wiki
... What is the current model of the molecular architecture of membranes? ...
... What is the current model of the molecular architecture of membranes? ...
Transport worksheet
... 5. A red blood cell is placed in distilled water. Describe and explain the changes in the shape of the red blood cell. 6. If you took a fresh water amoeba (unicellular organism) and placed it in sea water, what changes would occur to the organism? 7. Two cells are attached by a common membrane. In c ...
... 5. A red blood cell is placed in distilled water. Describe and explain the changes in the shape of the red blood cell. 6. If you took a fresh water amoeba (unicellular organism) and placed it in sea water, what changes would occur to the organism? 7. Two cells are attached by a common membrane. In c ...
• Cells were discovered in 1665 by Robert Hooke • Early studies of
... All cells today represent a continuous line of descent from the first living cells ...
... All cells today represent a continuous line of descent from the first living cells ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some of the structures inside a cell that help it to live and perform its role in an organism? ________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
... Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.) 1. What are some of the structures inside a cell that help it to live and perform its role in an organism? ________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ...
Model - Sitka School District
... Plant and Animal Cells GLE SC2.1 Diversity of Life The student demonstrates an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles and diversity of living organisms by describing the basic structure and function of plant and animal cells. ...
... Plant and Animal Cells GLE SC2.1 Diversity of Life The student demonstrates an understanding of the structure, function, behavior, development, life cycles and diversity of living organisms by describing the basic structure and function of plant and animal cells. ...
Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of cellulose
... Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of chitin ...
... Protective layer external to the cell membrane, consists of chitin ...
Modelling of the behaviour of cell-wall interface
... The focus here is the mechanical description of the kinetic of adhesion of a single cell in terms of the failure and creation of connections during the rolling; the mechanical and physical interactions occurring at the cell-wall interface are modeled as stochastic phenomena. A 2D model is set up, wh ...
... The focus here is the mechanical description of the kinetic of adhesion of a single cell in terms of the failure and creation of connections during the rolling; the mechanical and physical interactions occurring at the cell-wall interface are modeled as stochastic phenomena. A 2D model is set up, wh ...
Show Microbiology
... – obtain and use energy – grow and develop – reproduce on their own – respond to their environment – adapt to their environment ...
... – obtain and use energy – grow and develop – reproduce on their own – respond to their environment – adapt to their environment ...
Mr - socesbio.c…
... Directions: You are Leonardo Da Vinci (not DiCaprio), in high school. You love art, but you are not so into Biology. In order to understand the cell, you will compare it to something you understand, and draw it, labeling all parts of your example, the organelle they represent and what their job/func ...
... Directions: You are Leonardo Da Vinci (not DiCaprio), in high school. You love art, but you are not so into Biology. In order to understand the cell, you will compare it to something you understand, and draw it, labeling all parts of your example, the organelle they represent and what their job/func ...
Aim: How do the organelles work together to maintain homeostasis?
... 1.The cell membrane forms a boundary that separates the cellular contents from the outside environment. 2. The cell membrane forms a barrier that keeps all substances that might harm the cell from entering the cell. 3. The cell membrane is capable of receiving and recognizing chemical signals. 4. Th ...
... 1.The cell membrane forms a boundary that separates the cellular contents from the outside environment. 2. The cell membrane forms a barrier that keeps all substances that might harm the cell from entering the cell. 3. The cell membrane is capable of receiving and recognizing chemical signals. 4. Th ...
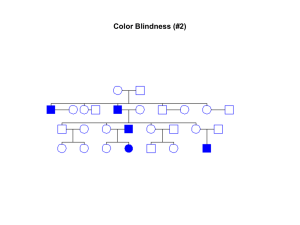
Extra Pedigree Problem - Winona State University
... kidney damage and loss of body water in urine painful erections in men (priapism) blood blockage in the spleen or liver (sequestration) eye damage low red blood cell counts (anemia) delayed growth ...
... kidney damage and loss of body water in urine painful erections in men (priapism) blood blockage in the spleen or liver (sequestration) eye damage low red blood cell counts (anemia) delayed growth ...
Different Types of Cells
... 5. How has the complexity of eukaryotes affected their ability to adapt and survive / thrive? ...
... 5. How has the complexity of eukaryotes affected their ability to adapt and survive / thrive? ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... 13. What is a centriole? In what type of cell (plant or animal) is it found? What does it do for the cell? ...
... 13. What is a centriole? In what type of cell (plant or animal) is it found? What does it do for the cell? ...
Reproduction
... 5) The manufactured protein enters the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). 6) A vesicle forms at the end of the ER, and carries the protein to the Golgi body. 7) The Golgi body repackages the protein for transport out of the cell. 8) A vesicle forms off the end of the Golgi body to carry the protein to the ...
... 5) The manufactured protein enters the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). 6) A vesicle forms at the end of the ER, and carries the protein to the Golgi body. 7) The Golgi body repackages the protein for transport out of the cell. 8) A vesicle forms off the end of the Golgi body to carry the protein to the ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.