CELL MEMBRANE PLASMA MEMBRANE
... Plant cell placed in salt water? •Cytoplasm and membrane shrivel up •Cell wall remains in place •Plasmolysis ...
... Plant cell placed in salt water? •Cytoplasm and membrane shrivel up •Cell wall remains in place •Plasmolysis ...
Cell Parts and Functions: Fill in the Blanks
... 5. The structure that surrounds the cell and regulates what enters and leaves the cell is the ____________________________. 6. Nickname the “powerhouse of the cell,” the _____________________ are involved in energy production for the cell. 7. The ______________________ surrounds the nucleus and cont ...
... 5. The structure that surrounds the cell and regulates what enters and leaves the cell is the ____________________________. 6. Nickname the “powerhouse of the cell,” the _____________________ are involved in energy production for the cell. 7. The ______________________ surrounds the nucleus and cont ...
Identification of a novel autoantigen in aplastic anemia
... Shinji Nakao, Hiroyuki Takamatsu. Cellular Transplantation Biology, Kanazawa University Graduate School of Medical Science Although aplastic anemia (AA) is a T-cell mediated disease, recent studies have revealed the presence of antibodies (Abs) specific to proteins derived from hematopoietic progeni ...
... Shinji Nakao, Hiroyuki Takamatsu. Cellular Transplantation Biology, Kanazawa University Graduate School of Medical Science Although aplastic anemia (AA) is a T-cell mediated disease, recent studies have revealed the presence of antibodies (Abs) specific to proteins derived from hematopoietic progeni ...
Development and Genes
... What you need to know • How we go from one unspecialized cell to many specialized cells – Determination – Differentiation – Morphogenesis – Role of Mitosis and Gene Expression – *Take notes on all the examples you see of these in the film! ...
... What you need to know • How we go from one unspecialized cell to many specialized cells – Determination – Differentiation – Morphogenesis – Role of Mitosis and Gene Expression – *Take notes on all the examples you see of these in the film! ...
Bio summary
... been linked to and believed to be resisting cell death. Snail and Slug, of the snail family, trigger epithelial-mesenchymal transitions (EMTs) throughout the tumor progression, as well as the embryonic development. Studies of the family genes in all major vertebrate groups show that Snail is at the ...
... been linked to and believed to be resisting cell death. Snail and Slug, of the snail family, trigger epithelial-mesenchymal transitions (EMTs) throughout the tumor progression, as well as the embryonic development. Studies of the family genes in all major vertebrate groups show that Snail is at the ...
Why do Cells Divide?
... Need a proper SA:Vol ratio to support the needs of the cell You need the cell to remain small!! For example, if the cell size doubles it would need 8x more nutrients to survive and it would create 8x the waste to excrete!! The vol. increases faster than the surface area of the cell membrane! ...
... Need a proper SA:Vol ratio to support the needs of the cell You need the cell to remain small!! For example, if the cell size doubles it would need 8x more nutrients to survive and it would create 8x the waste to excrete!! The vol. increases faster than the surface area of the cell membrane! ...
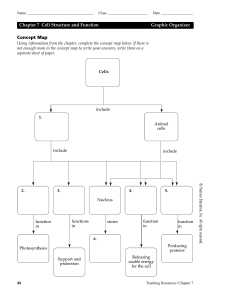
Concept Map Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Graphic
... Using information from the chapter, complete the concept map below. If there is not enough room in the concept map to write your answers, write them on a separate sheet of paper. ...
... Using information from the chapter, complete the concept map below. If there is not enough room in the concept map to write your answers, write them on a separate sheet of paper. ...
HW 11/3 Mitosis
... At the end of interphase, the cell has made duplicates of everything in preparation for dividing. As the cell begins to divide, it goes through a process called mitosis. In mitosis, the nucleus divides followed by the cytoplasm dividing, resulting in two cells. After the cytoplasm divides, cell divi ...
... At the end of interphase, the cell has made duplicates of everything in preparation for dividing. As the cell begins to divide, it goes through a process called mitosis. In mitosis, the nucleus divides followed by the cytoplasm dividing, resulting in two cells. After the cytoplasm divides, cell divi ...
Grade 8 Science Unit 4: “Cells, Tissues, Organs & Systems”
... •Tough, rigid structure that give plant cells their box-like shape •Made mostly of cellulose ...
... •Tough, rigid structure that give plant cells their box-like shape •Made mostly of cellulose ...
HW 10/29 Mitosis
... At the end of interphase, the cell has made duplicates of everything in preparation for dividing. As the cell begins to divide, it goes through a process called mitosis. In mitosis, the nucleus divides followed by the cytoplasm dividing, resulting in two cells. After the cytoplasm divides, cell divi ...
... At the end of interphase, the cell has made duplicates of everything in preparation for dividing. As the cell begins to divide, it goes through a process called mitosis. In mitosis, the nucleus divides followed by the cytoplasm dividing, resulting in two cells. After the cytoplasm divides, cell divi ...
Chapter 3 Virtual Investigations Lab Virtual Tour of Animal Cell
... What do these do in the cell? ...
... What do these do in the cell? ...
cell structure
... • Delimiting plasma membrane to separate inside from outside • Metabolism to generate complex molecules from foodstuffs and energetic molecules from light (photosynthesis) or from respiration • Capacity for reproduction • genes --> transcription --> translation --> structure and regulation • (DNA) - ...
... • Delimiting plasma membrane to separate inside from outside • Metabolism to generate complex molecules from foodstuffs and energetic molecules from light (photosynthesis) or from respiration • Capacity for reproduction • genes --> transcription --> translation --> structure and regulation • (DNA) - ...
Osmosis
... (d) Explain why half a cucumber becomes soft if left lying on a kitchen shelf for a few days, but becomes turgid again if its cut end is placed in water. ___________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ...
... (d) Explain why half a cucumber becomes soft if left lying on a kitchen shelf for a few days, but becomes turgid again if its cut end is placed in water. ___________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ...
Cell Theory: 1. Every living thing is composed of one or more cells
... 1. Every living thing is composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the smallest/simplest unit of life. 3. Under current conditions, all cells come from preexisting cells. ...
... 1. Every living thing is composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the smallest/simplest unit of life. 3. Under current conditions, all cells come from preexisting cells. ...
Cell Division - St. Clairsville High School
... The length of the cell cycle varies from cell to cell. Most of the cell’s life is spent in interphase. Some cells, such as the human brain cells, never divide. ...
... The length of the cell cycle varies from cell to cell. Most of the cell’s life is spent in interphase. Some cells, such as the human brain cells, never divide. ...
Chapter 5: The Cell
... • “power plant” • Double membrane for extra surface area • Responsible for cellular respiration – Process by which energy is released using oxygen ...
... • “power plant” • Double membrane for extra surface area • Responsible for cellular respiration – Process by which energy is released using oxygen ...
semester 1 syllabus
... Biology I provides, through regular laboratory and field investigations, a study of the structures and functions of living organisms and their interactions with their environment. At a minimum, this study explores the functions and processes of cells and the roles and interdependencies of organisms ...
... Biology I provides, through regular laboratory and field investigations, a study of the structures and functions of living organisms and their interactions with their environment. At a minimum, this study explores the functions and processes of cells and the roles and interdependencies of organisms ...
Lesson Plan
... Q: Is the onion made of one cell or many cells? [Many] Q: What is the shape of these cells? Draw a cell on your worksheet — allow 3 mins. Q: Is there something surrounding the cell? What does it look like? [Cell wall] Q: Can you see a dark, round structure inside the cell? Do all the cells have the ...
... Q: Is the onion made of one cell or many cells? [Many] Q: What is the shape of these cells? Draw a cell on your worksheet — allow 3 mins. Q: Is there something surrounding the cell? What does it look like? [Cell wall] Q: Can you see a dark, round structure inside the cell? Do all the cells have the ...
Cell culture

Cell culture is the process by which cells are grown under controlled conditions, generally outside of their natural environment. In practice, the term ""cell culture"" now refers to the culturing of cells derived from multicellular eukaryotes, especially animal cells, in contrast with other types of culture that also grow cells, such as plant tissue culture, fungal culture, and microbiological culture (of microbes). The historical development and methods of cell culture are closely interrelated to those of tissue culture and organ culture. Viral culture is also related, with cells as hosts for the viruses. The laboratory technique of maintaining live cell lines (a population of cells descended from a single cell and containing the same genetic makeup) separated from their original tissue source became more robust in the middle 20th century.