in-vivo-staining - kehsscience.org
... Permeabilization involves treatment of cells with (usually) a mild detergent. This detergent treatment will dissolve the cell membranes, and allow larger dye molecules access to the cell's interior. Fixation–which may itself consist of several steps–aims to preserve the shape of the cells or tissue ...
... Permeabilization involves treatment of cells with (usually) a mild detergent. This detergent treatment will dissolve the cell membranes, and allow larger dye molecules access to the cell's interior. Fixation–which may itself consist of several steps–aims to preserve the shape of the cells or tissue ...
PowerPoint file
... • Smear air-dry heat-fix • Basic dyes: cationic chromophore • Acidic dyes: anionic chromophore negative staining (good for capsules) • Three types of staining techniques: Simple, differential, and special ...
... • Smear air-dry heat-fix • Basic dyes: cationic chromophore • Acidic dyes: anionic chromophore negative staining (good for capsules) • Three types of staining techniques: Simple, differential, and special ...
LAB 3 - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... envelope (rather than the basic gram- related properties). ...
... envelope (rather than the basic gram- related properties). ...
www.abnova.com Live-Dead Cell Staining Kit (Cat # KA0901 V.01
... Distinguishing between live and dead cells is very important for investigation of growth control and cell death. The Live-Dead Cell Staining Kit provides the ready-to-use reagents for convenient discrimination between live and dead cells. The kit utilizes Live-DyeTM, a cell-permeable green fluoresce ...
... Distinguishing between live and dead cells is very important for investigation of growth control and cell death. The Live-Dead Cell Staining Kit provides the ready-to-use reagents for convenient discrimination between live and dead cells. The kit utilizes Live-DyeTM, a cell-permeable green fluoresce ...
Observation of bacteria using staining procedures Simple staining Gram staining
... – Spread the organisms over the slide – The smear is allowed to dry – Slide is passed through flame several times to heat-kill and fix organisms • A bacterial stain is stained with crystal violet (fuchsin, methylene blue) 1 min • Stain is briefly washed off slide with water Allow the slide to airdry ...
... – Spread the organisms over the slide – The smear is allowed to dry – Slide is passed through flame several times to heat-kill and fix organisms • A bacterial stain is stained with crystal violet (fuchsin, methylene blue) 1 min • Stain is briefly washed off slide with water Allow the slide to airdry ...
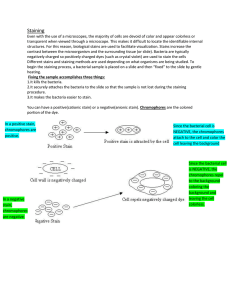
Simple staining
... Simple staining involves the use of only 1 dye and is used primarily as a means to study the morphology and structure of organisms. Differential staining uses more than 2 dyes and is also used to differentiate the organisms into one of two groups. Simple staining – there are two methods: positive st ...
... Simple staining involves the use of only 1 dye and is used primarily as a means to study the morphology and structure of organisms. Differential staining uses more than 2 dyes and is also used to differentiate the organisms into one of two groups. Simple staining – there are two methods: positive st ...
Chapter 3 Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope
... what is seen in the case of dark-field. • Simple staining – a basic dye is used to stain the cell to determine the shape and arrangement of the cells. • Gram staining is a differential staining. It places bacteria into 2 groups. ...
... what is seen in the case of dark-field. • Simple staining – a basic dye is used to stain the cell to determine the shape and arrangement of the cells. • Gram staining is a differential staining. It places bacteria into 2 groups. ...
Acid
... • Bacterial cell resistant to colorisation with some staining (Gram) • Their cell wall is relatively not permeable, containig lipids, fatty acids...(ex. Mycobacterium tbc, Corynebacteria...) • If stained (with strong basic stains (basic fuchsin in 5% fenole – they resist to decolorisation with stron ...
... • Bacterial cell resistant to colorisation with some staining (Gram) • Their cell wall is relatively not permeable, containig lipids, fatty acids...(ex. Mycobacterium tbc, Corynebacteria...) • If stained (with strong basic stains (basic fuchsin in 5% fenole – they resist to decolorisation with stron ...
topic-3.doc
... Spore stain: used to stain endospores of Clostridium and Bacillus o endospores do not readily take up dye, but once it penetrates the stain is not easily decolorized o heat smear over steam, rinse with water o counterstain with safranin o Endospores - Green; Vegetative cells - Red Flagellar stain: f ...
... Spore stain: used to stain endospores of Clostridium and Bacillus o endospores do not readily take up dye, but once it penetrates the stain is not easily decolorized o heat smear over steam, rinse with water o counterstain with safranin o Endospores - Green; Vegetative cells - Red Flagellar stain: f ...
Gram Stain
... Staining Even with the use of a microscopes, the majority of cells are devoid of color and appear colorless or transparent when viewed through a microscope. This makes it difficult to locate the identifiable internal structures. For this reason, biological stains are used to facilitate visualization ...
... Staining Even with the use of a microscopes, the majority of cells are devoid of color and appear colorless or transparent when viewed through a microscope. This makes it difficult to locate the identifiable internal structures. For this reason, biological stains are used to facilitate visualization ...
Hoechst 33342 Staining for Cell Cycle Analysis of Live Cells
... The optimal Hoechst 33342 dye concentration and staining time may vary between different cell types, as dye uptake depends on cellular metabolic rates; therefore, both have to be determine ...
... The optimal Hoechst 33342 dye concentration and staining time may vary between different cell types, as dye uptake depends on cellular metabolic rates; therefore, both have to be determine ...
File
... Stain with basic dye [dye+Cl-] Toluidine blue, methylene blue, hematoxylin, alcian blue ...
... Stain with basic dye [dye+Cl-] Toluidine blue, methylene blue, hematoxylin, alcian blue ...
Chapter 4: Microscopy, Staining, and Classification
... -cells have large amounts of waxy lipid, do not readily stain with simple water-based dye. The steps for acid-fast staining: ...
... -cells have large amounts of waxy lipid, do not readily stain with simple water-based dye. The steps for acid-fast staining: ...
Staining

Staining is an auxiliary technique used in microscopy to enhance contrast in the microscopic image. Stains and dyes are frequently used in biology and medicine to highlight structures in biological tissues for viewing, often with the aid of different microscopes. Stains may be used to define and examine bulk tissues (highlighting, for example, muscle fibers or connective tissue), cell populations (classifying different blood cells, for instance), or organelles within individual cells.In biochemistry it involves adding a class-specific (DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates) dye to a substrate to qualify or quantify the presence of a specific compound. Staining and fluorescent tagging can serve similar purposes. Biological staining is also used to mark cells in flow cytometry, and to flag proteins or nucleic acids in gel electrophoresis.Simple staining is staining with only one stain/dye. There are various kinds of multiple staining, many of which are examples of counterstaining, differential staining, or both, including double staining and triple staining. Staining is not limited to biological materials, it can also be used to study the morphology of other materials for example the lamellar structures of semi-crystalline polymers or the domain structures of block copolymers.