Keystone Biology Cram Sheet: MODULE 1 1. Because carbon has 4
... = amino acid amino acid amino acid amino acid … 14. mRNA takes the code from the DNA in the nucleus to ER in the cytoplasm. 15. The ER is like a protein assembly line. The workers along it are ribosomes, which actually line up the amino acids in the right order (according to the DNA code) 16. The pr ...
... = amino acid amino acid amino acid amino acid … 14. mRNA takes the code from the DNA in the nucleus to ER in the cytoplasm. 15. The ER is like a protein assembly line. The workers along it are ribosomes, which actually line up the amino acids in the right order (according to the DNA code) 16. The pr ...
Chapter Three Review #2 KEY - Mr. Lesiuk
... Allow for motile structures and key process like cell division. ...
... Allow for motile structures and key process like cell division. ...
b. Section 1.2 Cells
... • Multicellular: describes a living thing made up of many cells. • Both unicellular and multicellular things are called organisms. • Two main types of cells: Plant Cells Animal Cells ...
... • Multicellular: describes a living thing made up of many cells. • Both unicellular and multicellular things are called organisms. • Two main types of cells: Plant Cells Animal Cells ...
Distinguishing cell types with masks
... There is mounting evidence that protein synthesis and its regulation play a pivotal role in numerous neural processes such as the formation of new synaptic contacts and long-lasting forms of synaptic plasticity. These processes, which are necessary for learning and memory, involve changes in the cel ...
... There is mounting evidence that protein synthesis and its regulation play a pivotal role in numerous neural processes such as the formation of new synaptic contacts and long-lasting forms of synaptic plasticity. These processes, which are necessary for learning and memory, involve changes in the cel ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... V. Two very different cell types have evolved – prokaryotic and eukaryotic A. Prokaryotic cells – small and structurally simple – bacteria and archaea 1. Small - .5 to 10um in length (.0005 to .01mm or 1/100th of mm) 2. No nucleus – DNA is in the cytoplasm in a distinct “nucleoid” region 3. Ribosome ...
... V. Two very different cell types have evolved – prokaryotic and eukaryotic A. Prokaryotic cells – small and structurally simple – bacteria and archaea 1. Small - .5 to 10um in length (.0005 to .01mm or 1/100th of mm) 2. No nucleus – DNA is in the cytoplasm in a distinct “nucleoid” region 3. Ribosome ...
pdf full text
... a TF. The researchers describe a simple regulatory circuit in which a TF represses a reporter to measure the relationship between TF and various reporter copy numbers in the absence or presence of competing TF-binding sites. The resulting model will help fine-tune the output of a genetic circuit wit ...
... a TF. The researchers describe a simple regulatory circuit in which a TF represses a reporter to measure the relationship between TF and various reporter copy numbers in the absence or presence of competing TF-binding sites. The resulting model will help fine-tune the output of a genetic circuit wit ...
NAME DATE ______ PERIOD _____
... C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids and proteins The nucleus includes all of the following EXCEPT ____________________ A. cytoplasm ...
... C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids and proteins The nucleus includes all of the following EXCEPT ____________________ A. cytoplasm ...
Chapter 4 – A Tour of the Cell
... Smallest units of Life (therefore has the characteristics of life Chapter 1!) Requires energy (to run metabolic reactions of life) Grows and develops ...
... Smallest units of Life (therefore has the characteristics of life Chapter 1!) Requires energy (to run metabolic reactions of life) Grows and develops ...
Angiosperms III - University of Nebraska Omaha
... – all have thick secondary cell walls of LIGNIN (and stain red in prepared slides) – all are DEAD at maturity – include: fibers, sclereids, tracheids, and ...
... – all have thick secondary cell walls of LIGNIN (and stain red in prepared slides) – all are DEAD at maturity – include: fibers, sclereids, tracheids, and ...
The Cell Theory Notes
... Name__________________________________ period _____ date assigned_____________ date due ______________ date returned _____________ ...
... Name__________________________________ period _____ date assigned_____________ date due ______________ date returned _____________ ...
Chapter 4 Exam Review
... 17. Plants cells are generally easy to differentiate from an animal cell by their large central____________. 18. Cells with a high energy demand will have many _______________________ to power the cell. 19. The organelle that aids in digestion of intracellular materials is the _____________________. ...
... 17. Plants cells are generally easy to differentiate from an animal cell by their large central____________. 18. Cells with a high energy demand will have many _______________________ to power the cell. 19. The organelle that aids in digestion of intracellular materials is the _____________________. ...
As Powerpoint Slide
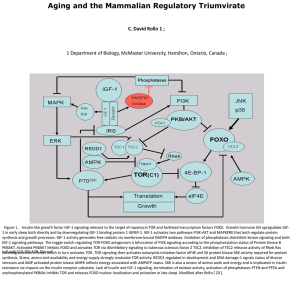
... Figure 1. Insulin-like growth factor IGF-1 signaling relevant to the target of rapamycin TOR and forkhead transcription factors FOXO. Growth hormone GH upregulates IGF1 in early sleep both directly and by downregulating IGF-1 binding protein 1 IGFBP-1. IGF-1 activates two pathways PI3K-AKT and MAPKE ...
... Figure 1. Insulin-like growth factor IGF-1 signaling relevant to the target of rapamycin TOR and forkhead transcription factors FOXO. Growth hormone GH upregulates IGF1 in early sleep both directly and by downregulating IGF-1 binding protein 1 IGFBP-1. IGF-1 activates two pathways PI3K-AKT and MAPKE ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
... less complex -DNA - Ribosomes larger -Cytoplasm and complex -DNA is circular -Ribosomes -DNA is linear ...
... less complex -DNA - Ribosomes larger -Cytoplasm and complex -DNA is circular -Ribosomes -DNA is linear ...
2.4 Mitosis Notes
... function as the parent sell, so they need the same number of chromosomes and the same combination of DNA to do that. ...
... function as the parent sell, so they need the same number of chromosomes and the same combination of DNA to do that. ...
Cell Specialization - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... specialists. Each cell must carry out all the functions of life. Multicellular ...
... specialists. Each cell must carry out all the functions of life. Multicellular ...
The Origin of Life
... be similar to earliest cells. • Unicellular organisms that thrive in harsh environmental conditions. –Anaerobic metabolism. –Inorganic energy sources. ...
... be similar to earliest cells. • Unicellular organisms that thrive in harsh environmental conditions. –Anaerobic metabolism. –Inorganic energy sources. ...
pH - Elmwood Park Public Schools
... Animal cells and Plant cells have some organelles in common, and some that are different. We are going to start with the ones they have in common. ...
... Animal cells and Plant cells have some organelles in common, and some that are different. We are going to start with the ones they have in common. ...
Parts of Plant and Animal Cells By
... the cell's growth and reproduction. Found usually in the center of plant and animal cells. • Its function: o Regulates all cell activity o Involved in cell division o Controls the transfer and replication of hereditary molecules o Controls cell growth ...
... the cell's growth and reproduction. Found usually in the center of plant and animal cells. • Its function: o Regulates all cell activity o Involved in cell division o Controls the transfer and replication of hereditary molecules o Controls cell growth ...
Cells - Ector County ISD.
... surface of cells – When they are present in large numbers on a cell they are called cilia – When they are less numerous and longer they are called flagella – Both organelles are composed of nine pairs of microtubules arranged around a central pair. Function: cell motility ...
... surface of cells – When they are present in large numbers on a cell they are called cilia – When they are less numerous and longer they are called flagella – Both organelles are composed of nine pairs of microtubules arranged around a central pair. Function: cell motility ...
Active Transport
... External materials are enclosed by part of the cell, forming a pouch The pouch pinches off cell membrane & becomes a membrane bound organelle called a vesicle Vesicles can fuse with lysosomes to digests contents. Two kinds of Endocytosis: ...
... External materials are enclosed by part of the cell, forming a pouch The pouch pinches off cell membrane & becomes a membrane bound organelle called a vesicle Vesicles can fuse with lysosomes to digests contents. Two kinds of Endocytosis: ...
Cells Alive – Internet Lesson - Ms. Kim`s Honors Biology Site
... parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are ...
... parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are ...
Course outline cell biology 2016 2017 (2) modified (1)
... topics such as endocytosis, intramembrane transport, protein targeting, organelle biosynthesis, protein sorting, exocytosis, cell shape, motility, and cell-to-cell interaction. In addition, lectures will deal with signal transduction processes, cell cycle, mitosis, cancer and cellular functions that ...
... topics such as endocytosis, intramembrane transport, protein targeting, organelle biosynthesis, protein sorting, exocytosis, cell shape, motility, and cell-to-cell interaction. In addition, lectures will deal with signal transduction processes, cell cycle, mitosis, cancer and cellular functions that ...