Cell Organelles
... Composed of protein of lipid (fat) molecules. Acts as a boundary to contain cytoplasm Selectively permeable membrane to select chemicals that can pass in and out of cells. ...
... Composed of protein of lipid (fat) molecules. Acts as a boundary to contain cytoplasm Selectively permeable membrane to select chemicals that can pass in and out of cells. ...
Biology- ch. 7
... • Used a microscope to study nature in 1600’s in Holland • He was the first person to see living organisms in a drop of ...
... • Used a microscope to study nature in 1600’s in Holland • He was the first person to see living organisms in a drop of ...
CELL FLIP NOTES - blog part 1
... •Some live as single cells •Examples: Plants, animals, fungi, etc. ...
... •Some live as single cells •Examples: Plants, animals, fungi, etc. ...
Cell membrane – boundary that separates the interior of
... Cytoplasm – the cytosol (gel like substance) and organelles; cytosol: 70% of the cell volume, made of water, salts, and organic molecules ...
... Cytoplasm – the cytosol (gel like substance) and organelles; cytosol: 70% of the cell volume, made of water, salts, and organic molecules ...
Biology Chapter 7 Notes I. Cell Theory A. Discovered since 1600 by
... Biology Chapter 7 Notes I. ...
... Biology Chapter 7 Notes I. ...
END OF CHAPTER QUESTIONS
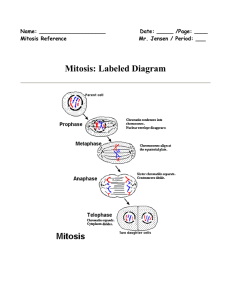
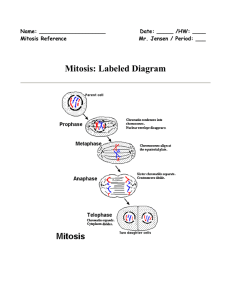
... Mitosis stages: In Prophase, chromosomes appear after chromatin coils; the nucleolus breaks down; elongated microtubules grow from centrioles; and the nuclear envelope disappears. In Metaphase, chromosomes align in the equatorial middle of the cell. In Anaphase, microtubule strands pull sister chrom ...
... Mitosis stages: In Prophase, chromosomes appear after chromatin coils; the nucleolus breaks down; elongated microtubules grow from centrioles; and the nuclear envelope disappears. In Metaphase, chromosomes align in the equatorial middle of the cell. In Anaphase, microtubule strands pull sister chrom ...
(null): Can You Identify These Cell Structures.doc, filename=Can
... I’m a series of tubes Found throughout the cell. I transport proteins And other things as well What am I?__________________ I’m full of holes, Flexible, and thin I control what gets out As well as what comes in. What am I?__________________ ...
... I’m a series of tubes Found throughout the cell. I transport proteins And other things as well What am I?__________________ I’m full of holes, Flexible, and thin I control what gets out As well as what comes in. What am I?__________________ ...
Cells
... nucleus membrane enclosed organelle chromosomes in pairs streaming in the cytoplasm cell division by mitosis complex flagella larger ribosomes complex cytoskeleton cellulose in cell walls DNA bound to histone proteins ...
... nucleus membrane enclosed organelle chromosomes in pairs streaming in the cytoplasm cell division by mitosis complex flagella larger ribosomes complex cytoskeleton cellulose in cell walls DNA bound to histone proteins ...
Major Cell Parts and Organelles
... cell - keeps contents separated from surroundings Has protein channels & pores which let things in and out ...
... cell - keeps contents separated from surroundings Has protein channels & pores which let things in and out ...
Cells Organelle Practice
... Name:_____________________________________P:_________________Date:____________________ ...
... Name:_____________________________________P:_________________Date:____________________ ...
Cell Structure Worksheet /25
... 3. Why would cells found lining the stomach have large numbers of golgi bodies and ribosomes? (2 marks) ...
... 3. Why would cells found lining the stomach have large numbers of golgi bodies and ribosomes? (2 marks) ...
THE EUKARYOTIC CELL
... the genetic material is carried. Most eukaryotic cells also contain other membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. ...
... the genetic material is carried. Most eukaryotic cells also contain other membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. ...
Cell Labeling Worksheet Instructions: Using the Organelle List
... Instructions: Using the Organelle List below, write each organelle term next to its function description. By doing so, you will also be labeling the cell parts in your model. “DNA,” “nucleus,” and “flagellum” are already filled in for you as an example. Organelle List: DNA, nucleus, flagellum, cell ...
... Instructions: Using the Organelle List below, write each organelle term next to its function description. By doing so, you will also be labeling the cell parts in your model. “DNA,” “nucleus,” and “flagellum” are already filled in for you as an example. Organelle List: DNA, nucleus, flagellum, cell ...
The Cell - CCRI Faculty Web
... bilayer (with pores) Bilayers surround the fluid part of nucleus (nucleoplasm) Continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum ...
... bilayer (with pores) Bilayers surround the fluid part of nucleus (nucleoplasm) Continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum ...
Cell Quiz - Catawba County Schools
... a. stores DNA b. controls most of the cell’s processes c. contains the information needed to make proteins d. all of the above 9. Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton? a. helps a cell keep its shape b. contains DNA c. surrounds the cell d. helps make proteins 10. Which organelle ...
... a. stores DNA b. controls most of the cell’s processes c. contains the information needed to make proteins d. all of the above 9. Which of the following is a function of the cytoskeleton? a. helps a cell keep its shape b. contains DNA c. surrounds the cell d. helps make proteins 10. Which organelle ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.