Review of cells
... a eukaryotic cell, on the inner surface of the inner nuclear membrane (INM). It is composed of intermediate filaments and membrane associated proteins. Besides providing mechanical support, the nuclear lamina regulates important cellular events such as DNA replication and cell division. It organizes ...
... a eukaryotic cell, on the inner surface of the inner nuclear membrane (INM). It is composed of intermediate filaments and membrane associated proteins. Besides providing mechanical support, the nuclear lamina regulates important cellular events such as DNA replication and cell division. It organizes ...
The Cell
... Membrane-Bound organelles only found in Eukaryotes Localize Chemical Reactions making the cell far more efficient ...
... Membrane-Bound organelles only found in Eukaryotes Localize Chemical Reactions making the cell far more efficient ...
The Cell - Biology Junction
... Membrane-Bound organelles only found in Eukaryotes Localize Chemical Reactions making the cell far more efficient ...
... Membrane-Bound organelles only found in Eukaryotes Localize Chemical Reactions making the cell far more efficient ...
The Cell Cycle and Cancer
... The centromere splits and the two chromatids separate to opposite ends; 9. What happens in telophase? The chromosomes stretch and lose their rod like appearance; a nuclear membrane forms around each region of chromosomes; ...
... The centromere splits and the two chromatids separate to opposite ends; 9. What happens in telophase? The chromosomes stretch and lose their rod like appearance; a nuclear membrane forms around each region of chromosomes; ...
Solution - Glencoe
... 3. fluid-filled space within the cytoplasm; temporarily stores food ______________________ ...
... 3. fluid-filled space within the cytoplasm; temporarily stores food ______________________ ...
the-cell-factory Excellent
... Proteins are assembled ON Ribosomes Ribosomes are small particles of protein & RNA (what’s RNA?) They follow instructions from the nucleus to make proteins…follow the orders from the “head haunchos” in the main office Scattered throughout the cell They are like little factories If a cell ...
... Proteins are assembled ON Ribosomes Ribosomes are small particles of protein & RNA (what’s RNA?) They follow instructions from the nucleus to make proteins…follow the orders from the “head haunchos” in the main office Scattered throughout the cell They are like little factories If a cell ...
File
... How are prokaryotes and eukaryotes different? How do plant, animal, and bacterial cells compare in size? How are plant, animal, and bacterial cells alike and different? What organelles are found only in plants? Only in animals? How are bacterial and plant cell walls different? How are ...
... How are prokaryotes and eukaryotes different? How do plant, animal, and bacterial cells compare in size? How are plant, animal, and bacterial cells alike and different? What organelles are found only in plants? Only in animals? How are bacterial and plant cell walls different? How are ...
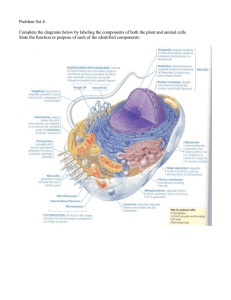
Problem Set 4:
... both of which are cations. How does this exchange generate a membrane potential? 3 Na+out for 2 K+ in, resulting in a net + charge outside the cell membrane 8.10 A. How is cholesterol, which is used for the synthesis of other steroids and membranes, transported into human cells? Receptor-mediated en ...
... both of which are cations. How does this exchange generate a membrane potential? 3 Na+out for 2 K+ in, resulting in a net + charge outside the cell membrane 8.10 A. How is cholesterol, which is used for the synthesis of other steroids and membranes, transported into human cells? Receptor-mediated en ...
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Introduction to Cells
... 13. The cell theory makes several fascinating statements about cells! What are three statements mentioned in the video that are included in the cell theory? ...
... 13. The cell theory makes several fascinating statements about cells! What are three statements mentioned in the video that are included in the cell theory? ...
Monkemeier - Madison Public Schools
... a. This is the outer boundary of a bacteria (prokaryote). It provides structure and support. b. This is the area in the cytoplasm that contains the chromosome (DNA) c. This is the only membrane that the bacteria (prokaryote) is allowed to have. It lies just inside the cell wall. d. This is the fluid ...
... a. This is the outer boundary of a bacteria (prokaryote). It provides structure and support. b. This is the area in the cytoplasm that contains the chromosome (DNA) c. This is the only membrane that the bacteria (prokaryote) is allowed to have. It lies just inside the cell wall. d. This is the fluid ...
CELLS
... Surrounds the cell to separate it from its external environment; it gives support and protection to the cell Composed of a double layer of phospholipids called the lipid bilayer; it also has proteins embedded in it The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling what substances enter and lea ...
... Surrounds the cell to separate it from its external environment; it gives support and protection to the cell Composed of a double layer of phospholipids called the lipid bilayer; it also has proteins embedded in it The membrane acts as a selective barrier by controlling what substances enter and lea ...
CK12 Nucleus
... The nucleus is only found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the genetic material, or the DNA ( Deoxy-ribonucleic acid) of the cell. This genetic material inside the nucleus is like a set of instructions. These instructions tell the cell how to build protein molecules needed for the cell to fu ...
... The nucleus is only found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the genetic material, or the DNA ( Deoxy-ribonucleic acid) of the cell. This genetic material inside the nucleus is like a set of instructions. These instructions tell the cell how to build protein molecules needed for the cell to fu ...
BIO 105 Summer 2013 Chapter 3 Part I – The Cell Cell Theory
... Objectives: By the end of lecture today you should be able to address the following points: 1. What is cell theory? 2. Identify the cellular organelles and their functions. 3. What is the difference between a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell? 4. What are the major parts of a eukaryotic cell? 5. Descr ...
... Objectives: By the end of lecture today you should be able to address the following points: 1. What is cell theory? 2. Identify the cellular organelles and their functions. 3. What is the difference between a eukaryotic and prokaryotic cell? 4. What are the major parts of a eukaryotic cell? 5. Descr ...
AP Biology
... 2. How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference between a scanning and transmission electron microscope? ...
... 2. How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference between a scanning and transmission electron microscope? ...
No Slide Title
... nucleus & other membrane-bound organelles 2 or more linear DNA molecules located in nucleus plasma membrane, cytoplasm & ribosomes some have a cell wall (cellulose or chitin) Ex. plants, animals, fungi, protista ...
... nucleus & other membrane-bound organelles 2 or more linear DNA molecules located in nucleus plasma membrane, cytoplasm & ribosomes some have a cell wall (cellulose or chitin) Ex. plants, animals, fungi, protista ...
All About Cells - Exploring Nature
... Each cell has a protective outside layer called the plasma membrane. The plasma membrane lets certain things into the cell that it needs, but keeps other things out. This is called semipermeable. Inside the cell is a watery medium that everything floats in called cytoplasm. The cytoplasm contains al ...
... Each cell has a protective outside layer called the plasma membrane. The plasma membrane lets certain things into the cell that it needs, but keeps other things out. This is called semipermeable. Inside the cell is a watery medium that everything floats in called cytoplasm. The cytoplasm contains al ...
Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
... Cell Structure and Function Worksheet 1. Construct a Venn diagram of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells and give at least one example of each type of cell. ...
... Cell Structure and Function Worksheet 1. Construct a Venn diagram of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells and give at least one example of each type of cell. ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.