1. Describe two functions of centromere during mitosis. 2. a) Look at
... c) A cell in the G1 stage of interphase had 10 arbitrary units of DNA contained in six pairs of homologus chromosomes. If it divided by mitosis, how many units of DNA and how many chromosomes would there be, i) In the nucleus at the end of G2? ...
... c) A cell in the G1 stage of interphase had 10 arbitrary units of DNA contained in six pairs of homologus chromosomes. If it divided by mitosis, how many units of DNA and how many chromosomes would there be, i) In the nucleus at the end of G2? ...
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
... eukaryotic cells as additional proteins that play cytoskeletal roles. Actin homologs perform a variety of functions, helping to determine cell shape, segregate chromosomes, and localize proteins with the cell. ...
... eukaryotic cells as additional proteins that play cytoskeletal roles. Actin homologs perform a variety of functions, helping to determine cell shape, segregate chromosomes, and localize proteins with the cell. ...
Lecture Outline (in PDF format)
... Questions you should be able to answer: • What are some key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? • Why do the specialized organelles of a eukaryotic cell allow for greater size and complexity? • How did mitochondria probably originate? • Describe the structures of Gram-positive and ...
... Questions you should be able to answer: • What are some key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? • Why do the specialized organelles of a eukaryotic cell allow for greater size and complexity? • How did mitochondria probably originate? • Describe the structures of Gram-positive and ...
Glossary - FOSSweb
... Excerpt from DSM Small Things and Microscopes Teacher’s Guide, © Copyright by Delta Education, a member of the School Specialty Family. Not for resale, redistribution, or use other than classroom use without further permission. ...
... Excerpt from DSM Small Things and Microscopes Teacher’s Guide, © Copyright by Delta Education, a member of the School Specialty Family. Not for resale, redistribution, or use other than classroom use without further permission. ...
Parts of a Cell Note Sheet:
... Surrounds the nucleus. Controls what enters and exits the nucleus. ...
... Surrounds the nucleus. Controls what enters and exits the nucleus. ...
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... Ribosomes Where proteins are made. Has no membrane. Formed of RNA and proteins. During protein synthesis, ribosomes and RNA translated from DNA leave the nucleus through the nuclear envelope and enter the cytoplasm ...
... Ribosomes Where proteins are made. Has no membrane. Formed of RNA and proteins. During protein synthesis, ribosomes and RNA translated from DNA leave the nucleus through the nuclear envelope and enter the cytoplasm ...
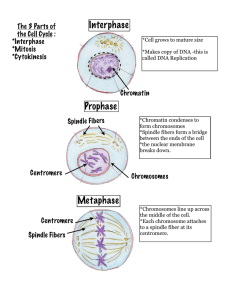
Interphase Prophase Metaphase
... form chromosomes *Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell *the nuclear membrane breaks down. ...
... form chromosomes *Spindle fibers form a bridge between the ends of the cell *the nuclear membrane breaks down. ...
Cells AP Bio Test Review ANSWERS
... 32. Explain which intracellular structures make up the endomembrane system and their functions. 33. Compare & contrast prokaryotes & eukaryotes. Know examples of each. 34. Illustrate a plant & animal cell, and know how to identify the different structures. ...
... 32. Explain which intracellular structures make up the endomembrane system and their functions. 33. Compare & contrast prokaryotes & eukaryotes. Know examples of each. 34. Illustrate a plant & animal cell, and know how to identify the different structures. ...
“cells”. - Biggs` Biology
... multicellular organisms •Includes plants, animals, fungi, & protists ...
... multicellular organisms •Includes plants, animals, fungi, & protists ...
Cell Organelles and Their Functions
... materials. Animal cell vacuoles form and reform over and over again. ...
... materials. Animal cell vacuoles form and reform over and over again. ...
LB145-lecture4
... What does animal cell have that plants don’t? A. A single plasma membrane surrounding it B. Mitochondria C. A true Nucleus D. The cell wall surrounding it E. None of the above ...
... What does animal cell have that plants don’t? A. A single plasma membrane surrounding it B. Mitochondria C. A true Nucleus D. The cell wall surrounding it E. None of the above ...
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Answer the following questions on your
... Answer the following questions on your own paper. (25 points) Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) ...
... Answer the following questions on your own paper. (25 points) Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) ...
organellesNed2013 35.5 KB
... E: central vacuole: fluid-filled, can store enzymes and wastes. Very large in plant cells. E: contractile vacuole: (another type of vacuole). As in Paramecia, can excrete water; appears as a star-shaped pump. E: vesicles: membrane-bound sacs pinch in (perform endocytosis) or out (perform exocytosis) ...
... E: central vacuole: fluid-filled, can store enzymes and wastes. Very large in plant cells. E: contractile vacuole: (another type of vacuole). As in Paramecia, can excrete water; appears as a star-shaped pump. E: vesicles: membrane-bound sacs pinch in (perform endocytosis) or out (perform exocytosis) ...
CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY
... Isolating Organelles by Cell Fractionation Cell fractionation – Takes cells apart and separates the major organelles from one another The centrifuge – Is used to fractionate cells into their component parts ...
... Isolating Organelles by Cell Fractionation Cell fractionation – Takes cells apart and separates the major organelles from one another The centrifuge – Is used to fractionate cells into their component parts ...
Ranking-of-Cell
... ______ A. A window screen in your home allows air to pass through while keeping insects out. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane has pretty much the same job. The cell membrane is the thin, flexible boundary between the cell and its watery environment. Nutrients enter the cell and w ...
... ______ A. A window screen in your home allows air to pass through while keeping insects out. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane has pretty much the same job. The cell membrane is the thin, flexible boundary between the cell and its watery environment. Nutrients enter the cell and w ...
Year 8 Science
... Mitosis is the name given to the process of cell division that produces two identical cells. Mitosis consists of four phases. In the diagram below, indicate which phase of mitosis is represented by each of the letters: Prophase a) A ______________ The nucleus membrane breaks down. The chromosomes t ...
... Mitosis is the name given to the process of cell division that produces two identical cells. Mitosis consists of four phases. In the diagram below, indicate which phase of mitosis is represented by each of the letters: Prophase a) A ______________ The nucleus membrane breaks down. The chromosomes t ...
File - need help with revision notes?
... membrane bound sacs called cisternae, which are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. Rough endoplasmic reticulum is studded with ribosomes for making proteins, and the RER acts as a method of storage and transportation of the proteins that have been synthesised on the attached ribosomes. Smoo ...
... membrane bound sacs called cisternae, which are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. Rough endoplasmic reticulum is studded with ribosomes for making proteins, and the RER acts as a method of storage and transportation of the proteins that have been synthesised on the attached ribosomes. Smoo ...
Cell Organelle Flipbook How-to (1)
... You will need 6 different color pieces of paper to fold flipbook style. Your flipbook will have 12 pages (to include all 10 organelles and a title and complete diagram of the cell) – Include a picture (Draw as best you can) of the organelle on the page where you are describing its structure and ...
... You will need 6 different color pieces of paper to fold flipbook style. Your flipbook will have 12 pages (to include all 10 organelles and a title and complete diagram of the cell) – Include a picture (Draw as best you can) of the organelle on the page where you are describing its structure and ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.