Cell Structure and Membrane Transport Study Guide
... Cell Theory: Know the three parts of the theory. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Bacteria are prokaryotic, do not have nucleus or other membranebound organelles. Do have cell membrane and ribosomes. Importance of Surface Area: Limits how much can enter or leave the cell. Ratio of surface area to v ...
... Cell Theory: Know the three parts of the theory. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells: Bacteria are prokaryotic, do not have nucleus or other membranebound organelles. Do have cell membrane and ribosomes. Importance of Surface Area: Limits how much can enter or leave the cell. Ratio of surface area to v ...
Cells - cloudfront.net
... Help support cell Maintains its shape Helps materials move within the cell ...
... Help support cell Maintains its shape Helps materials move within the cell ...
Cells
... plant and animal cells have a thin outer covering which defines the boundary of the cell and regulates the traffic of chemicals between the cell and its surroundings. You would have to stack 8,000 cell membranes to reach the thickness of a piece of paper. ...
... plant and animal cells have a thin outer covering which defines the boundary of the cell and regulates the traffic of chemicals between the cell and its surroundings. You would have to stack 8,000 cell membranes to reach the thickness of a piece of paper. ...
The Biology of Anatomy
... • These make up the “steps” of the “ladder”. • Everyone has errors or mutations in their DNA, some are minor and have no impact while others can give rise to major disease and illness. ...
... • These make up the “steps” of the “ladder”. • Everyone has errors or mutations in their DNA, some are minor and have no impact while others can give rise to major disease and illness. ...
chapter 7 a tour of the cell
... Produce proteins for export out of cell protein secreting cells packaged into transport vesicles for export ...
... Produce proteins for export out of cell protein secreting cells packaged into transport vesicles for export ...
Bacteria Jeopardy
... What is the slimy coating on the outside of the cell wall of some bacteria? ...
... What is the slimy coating on the outside of the cell wall of some bacteria? ...
Eukaryotic Cells
... 1. What is the purpose of the cell wall? a. To make a plant droop. b. To support the cell c. To carry DNA d. To digest cellulose. 2. What is the purpose of a cell membrane? a. To make lipids b. To make phospholipids c. To protect the cell d. To support the cell wall 3. What is the genetic material i ...
... 1. What is the purpose of the cell wall? a. To make a plant droop. b. To support the cell c. To carry DNA d. To digest cellulose. 2. What is the purpose of a cell membrane? a. To make lipids b. To make phospholipids c. To protect the cell d. To support the cell wall 3. What is the genetic material i ...
Chapter 3 Powerpoint
... • Intermediate in size between actin filaments and microtubules • Functions: – Support nuclear envelope – Cell-cell junctions, such as those holding skin cells tightly together ...
... • Intermediate in size between actin filaments and microtubules • Functions: – Support nuclear envelope – Cell-cell junctions, such as those holding skin cells tightly together ...
2nd 6 weeks review notes 2014
... 1. All living things contain at least cell 2. Cells are the smallest structural and functional units of life 3. Cells can only come from pre-existing life Names to know: Redi, Leeuwenhoek, Hooke, Spallanzani, Pastuer, Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow GENETICS The study of how traits are inherited through ...
... 1. All living things contain at least cell 2. Cells are the smallest structural and functional units of life 3. Cells can only come from pre-existing life Names to know: Redi, Leeuwenhoek, Hooke, Spallanzani, Pastuer, Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow GENETICS The study of how traits are inherited through ...
CELLS-A STUDY GUIDE CHECKLIST
... C. Which cell is more complex and which cell was most likely the cell of the earliest life forms? D. Advantage of having a cell compartmentalized by membranes E. Which kingdoms or domains are made from eukaryotic cells and which kingdoms or domains are made from prokaryotic cells? ...
... C. Which cell is more complex and which cell was most likely the cell of the earliest life forms? D. Advantage of having a cell compartmentalized by membranes E. Which kingdoms or domains are made from eukaryotic cells and which kingdoms or domains are made from prokaryotic cells? ...
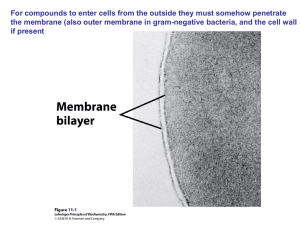
Slide 1
... the membrane (also outer membrane in gram-negative bacteria, and the cell wall if present ...
... the membrane (also outer membrane in gram-negative bacteria, and the cell wall if present ...
Cell membrane Chromatin Nuclear membrane
... 2. Replace worn out cells- every cell dies at some point 3. Repair damaged cells – allows damaged areas of organisms to be fixed Cells that do not go through cell cycle: Muscle & Nerve ...
... 2. Replace worn out cells- every cell dies at some point 3. Repair damaged cells – allows damaged areas of organisms to be fixed Cells that do not go through cell cycle: Muscle & Nerve ...
Cell structures & Functions
... • Location: Surrounding the cell • Function: Controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell – “Selectively permeable” ...
... • Location: Surrounding the cell • Function: Controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell – “Selectively permeable” ...
Gene Regulation
... Would the proteins for a given cell always be “required” though? Cells can respond to environmental cues to regulate which proteins are actually needed We have seen this in people living in high altitudes ...
... Would the proteins for a given cell always be “required” though? Cells can respond to environmental cues to regulate which proteins are actually needed We have seen this in people living in high altitudes ...
Eukaryotic cells .................................... and
... The cytoskeleton is …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… and it acts as both a ……………………………. and a skeleton. It keeps the cell membrane from collapsing and also helps some cells move. The cytoskeleton is made of ……………. Types of proteins. One protein is ………………………………. The other two are ………………… ...
... The cytoskeleton is …………………………………………………………………………………………………………… and it acts as both a ……………………………. and a skeleton. It keeps the cell membrane from collapsing and also helps some cells move. The cytoskeleton is made of ……………. Types of proteins. One protein is ………………………………. The other two are ………………… ...
Cytology 20 Questions - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 12) Which of the following statements about internal membranes in eukaryotic cells is false? A) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes form membranous compartments called organelles. B) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes provide an additional area for many metabolic processes to occur. C) In e ...
... 12) Which of the following statements about internal membranes in eukaryotic cells is false? A) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes form membranous compartments called organelles. B) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes provide an additional area for many metabolic processes to occur. C) In e ...
Cell theory + structure
... Describe the contributions of the following scientists: Robert Hooke – Anton van Leeuwenhoek – Matthias Schleiden – Theodor Schwann – Rudolph Virchow – All cells come from pre-existing cells The Cell Theory State the three components of the cell theory: 1. ___________________________________________ ...
... Describe the contributions of the following scientists: Robert Hooke – Anton van Leeuwenhoek – Matthias Schleiden – Theodor Schwann – Rudolph Virchow – All cells come from pre-existing cells The Cell Theory State the three components of the cell theory: 1. ___________________________________________ ...
Life Science Preview Vocabulary Terms Vocabulary Quiz 1. Cells
... 4. The lysosome is a section of a cell in which waste removed. 5. The ribosome is a section of a cell that changes amino acids into proteins. 6. The nucleus is the largest structure of the cell that controls all of the cells activities. 7. The packaging of proteins for shipment is called the golgi b ...
... 4. The lysosome is a section of a cell in which waste removed. 5. The ribosome is a section of a cell that changes amino acids into proteins. 6. The nucleus is the largest structure of the cell that controls all of the cells activities. 7. The packaging of proteins for shipment is called the golgi b ...
Define Cell Parts
... mitochondrion provides energy for the cell vacuole contains the waste golgi apparatus packs protein nucleus controls the cell rhibosomes synthesizes (transforms) protein cytoplasm holds the cell’s organelles in place cell membrane separates the inside of the cell from the outside microvilli involved ...
... mitochondrion provides energy for the cell vacuole contains the waste golgi apparatus packs protein nucleus controls the cell rhibosomes synthesizes (transforms) protein cytoplasm holds the cell’s organelles in place cell membrane separates the inside of the cell from the outside microvilli involved ...
Cell Structure and Genetic Control
... A. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is covered with ribosomes and is involved in protein synthesis. B. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum provides a site for many enzymatic reactions and, in skeletal muscles, serves to store Ca2+. Cell Nucleus and Nucleic Acids ...
... A. The rough endoplasmic reticulum is covered with ribosomes and is involved in protein synthesis. B. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum provides a site for many enzymatic reactions and, in skeletal muscles, serves to store Ca2+. Cell Nucleus and Nucleic Acids ...
element Any substance that cannot be broken down into simpler
... The building blocks of proteins ...
... The building blocks of proteins ...
Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell 1. Cell Basics Limits to Cell Size
... Storage of water, waste, & nutrients Source of “turgor pressure” that maintains rigidity of plant cells • swells when water is plentiful due to osmosis • cell wall provides support, prevents lysis ...
... Storage of water, waste, & nutrients Source of “turgor pressure” that maintains rigidity of plant cells • swells when water is plentiful due to osmosis • cell wall provides support, prevents lysis ...
Endoplasmic Reticulum - Brandywine School District
... •Has openings where items may enter and exit cell (aided by ...
... •Has openings where items may enter and exit cell (aided by ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.