Cell unit vocab - Allen County Schools
... Budding—a type of asexual repro. That involves a portion of an organism breaking off to form a completely new organism that is identical. hydra Fission—the splitting of a cell (organism) into 2 identical cells (2 organisms) bacteria Spores—the splitting of a cell into many identical cells. Mushroom ...
... Budding—a type of asexual repro. That involves a portion of an organism breaking off to form a completely new organism that is identical. hydra Fission—the splitting of a cell (organism) into 2 identical cells (2 organisms) bacteria Spores—the splitting of a cell into many identical cells. Mushroom ...
Cells - My CCSD
... 7. Microtubules and Microfilaments a. Shape and support cell (cytoskeleton) b. Move cellular material. 8. Centrosome a. Two hollow cylinders at right angles to one another. b. Help distribute chromosomes to newly forming cells. ...
... 7. Microtubules and Microfilaments a. Shape and support cell (cytoskeleton) b. Move cellular material. 8. Centrosome a. Two hollow cylinders at right angles to one another. b. Help distribute chromosomes to newly forming cells. ...
TFSD Unwrapped Standard 3rd Math Algebra sample
... National Standards C.1.a Cells have particular structures that underlie their functions. C.1.c. Cells store and use information to guide their functions. C.1.d. Cell functions are regulated. C.1.e Plant cells contain chloroplasts, the site of photosynthesis C.2.a In all organisms, the instructions f ...
... National Standards C.1.a Cells have particular structures that underlie their functions. C.1.c. Cells store and use information to guide their functions. C.1.d. Cell functions are regulated. C.1.e Plant cells contain chloroplasts, the site of photosynthesis C.2.a In all organisms, the instructions f ...
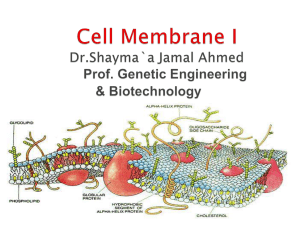
Plasma membrane Dr.Shayma`a Jamal Ahmed
... Recognize to the mechanisms of transport. Compare between the Exocytosis & Endocytosis ...
... Recognize to the mechanisms of transport. Compare between the Exocytosis & Endocytosis ...
Cells: Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
... Eukaryote cells can be multicellular The whole cell can be specialized for ...
... Eukaryote cells can be multicellular The whole cell can be specialized for ...
Ch 3 – Cell Structure The Cell Theory
... large cells. If a cell’s surface area–to-volume ratio is too low, substances cannot enter and leave the cell well enough to meet the cell’s needs. ...
... large cells. If a cell’s surface area–to-volume ratio is too low, substances cannot enter and leave the cell well enough to meet the cell’s needs. ...
Biological Membranes
... to orient itself with tails toward the center of the bilayer and heads out The embedded proteins in the bilayer are free to move about like icebergs floating on the sea This can be thought of as a liquid crystal ...
... to orient itself with tails toward the center of the bilayer and heads out The embedded proteins in the bilayer are free to move about like icebergs floating on the sea This can be thought of as a liquid crystal ...
Cell organelles
... Cell Wall - Outer covering of most cells that protects the bacterial cell and gives it shape. Cytoplasm - A gel-like substance composed mainly of water that also contains enzymes, salts, cell components, and various organic molecules. Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane Surrounds the cell's cytoplasm ...
... Cell Wall - Outer covering of most cells that protects the bacterial cell and gives it shape. Cytoplasm - A gel-like substance composed mainly of water that also contains enzymes, salts, cell components, and various organic molecules. Cell Membrane or Plasma Membrane Surrounds the cell's cytoplasm ...
KS3 Biology MCQs Cells, Tissues, Sexual Reproduction
... What does a ‘normal’ plant cell contain that an onion cell does not? ...
... What does a ‘normal’ plant cell contain that an onion cell does not? ...
Chapter 6 – A Tour of the Cell
... chloroplast. The nucleus is enclosed in the nuclear envelope (Figure 6.9). The nuclear pores of the nuclear membrane allows for passage of materials into and out of the nucleus. The nuclear side of the envelope is lined by the nuclear lamina, protein filaments that maintain the shape of the nucleus. ...
... chloroplast. The nucleus is enclosed in the nuclear envelope (Figure 6.9). The nuclear pores of the nuclear membrane allows for passage of materials into and out of the nucleus. The nuclear side of the envelope is lined by the nuclear lamina, protein filaments that maintain the shape of the nucleus. ...
File
... The table gives one difference between a plant cell and an animal cell. Complete the table to give two more differences. Plant cell ...
... The table gives one difference between a plant cell and an animal cell. Complete the table to give two more differences. Plant cell ...
Document
... increase in volume, but the surface area would only increase 4 fold. Therefore, there is not enough membrane for nutrients to flow through to keep the cell alive. ...
... increase in volume, but the surface area would only increase 4 fold. Therefore, there is not enough membrane for nutrients to flow through to keep the cell alive. ...
Chapter 4
... 4.4 Eukaryotic cells are partitioned into functional compartments Structural support, movement, and communication involve the cytoskeleton, plasma membrane, and cell wall – An example of the importance of these is the response and movement of phagocytic cells to an infected area ...
... 4.4 Eukaryotic cells are partitioned into functional compartments Structural support, movement, and communication involve the cytoskeleton, plasma membrane, and cell wall – An example of the importance of these is the response and movement of phagocytic cells to an infected area ...
Study Guide - people.vcu.edu
... get to area of lower concentration so they can move and not collide, pioneers E to W) 1. H2O, O2, CO2, Amino Acids: move freely across the cell membrane because they are small molecules 2. Carbohydrates, Proteins, larger molecules: they are bigger molecules so they need help moving across the membra ...
... get to area of lower concentration so they can move and not collide, pioneers E to W) 1. H2O, O2, CO2, Amino Acids: move freely across the cell membrane because they are small molecules 2. Carbohydrates, Proteins, larger molecules: they are bigger molecules so they need help moving across the membra ...
A cell is the very smallest unit of living matter
... Inside the nucleus there is DNA which contains genetic information. The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance inside the cell where most of the cell's activities take place. It's made out of water and other chemicals. All cell parts, except the nucleus, are located in the cytoplasm. Basically, each ce ...
... Inside the nucleus there is DNA which contains genetic information. The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance inside the cell where most of the cell's activities take place. It's made out of water and other chemicals. All cell parts, except the nucleus, are located in the cytoplasm. Basically, each ce ...
Unit 1: The Cell & Organization of Life
... Leucoplasts: Store starches & lipids, give plants a white color ...
... Leucoplasts: Store starches & lipids, give plants a white color ...
Lab 4H -Characteristics of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... Lab #4H: Characteristics of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Pre Lab Discussion: Cells are the basic units of structure and function of all living things. There are two major divisions into which all cells fall – prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are cells that lack a nucleus a ...
... Lab #4H: Characteristics of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Pre Lab Discussion: Cells are the basic units of structure and function of all living things. There are two major divisions into which all cells fall – prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are cells that lack a nucleus a ...
Cell in its environment - Somerset Academy North Las Vegas
... Collisions cause molecules to move away from each other. The molecules will continue to spread out until they are eventually evenly spread out throughout the area. ...
... Collisions cause molecules to move away from each other. The molecules will continue to spread out until they are eventually evenly spread out throughout the area. ...
COMPARISON OF CHEEK AND ONION CELLS
... diagram onion cells and label the cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and chloroplast. measure the length and width of onion cells in micrometers. diagram human cheek cells and label the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus. measure the diameter of human cheek cells in micrometers. compar ...
... diagram onion cells and label the cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and chloroplast. measure the length and width of onion cells in micrometers. diagram human cheek cells and label the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus. measure the diameter of human cheek cells in micrometers. compar ...
BSCI 124: LECTURE 2
... What is a cell? • Basic building blocks of living organisms • Form tissues and organs • Each cell is functionally independent – it can live on its own under the right conditions – Uses sugars to get energy and stay alive – Contains all necessary info to replicate produce a multicellular organism ...
... What is a cell? • Basic building blocks of living organisms • Form tissues and organs • Each cell is functionally independent – it can live on its own under the right conditions – Uses sugars to get energy and stay alive – Contains all necessary info to replicate produce a multicellular organism ...
Cell nucleus

In cell biology, the nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin nucleus or nuculeus, meaning kernel) is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types have no nuclei, and a few others have many.Cell nuclei contain most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome. The function of the nucleus is to maintain the integrity of these genes and to control the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression—the nucleus is, therefore, the control center of the cell. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm, and the nucleoskeleton (which includes nuclear lamina), a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support, much like the cytoskeleton, which supports the cell as a whole.Because the nuclear membrane is impermeable to large molecules, nuclear pores are required that regulate nuclear transport of molecules across the envelope. The pores cross both nuclear membranes, providing a channel through which larger molecules must be actively transported by carrier proteins while allowing free movement of small molecules and ions. Movement of large molecules such as proteins and RNA through the pores is required for both gene expression and the maintenance of chromosomes. The interior of the nucleus does not contain any membrane-bound sub compartments, its contents are not uniform, and a number of sub-nuclear bodies exist, made up of unique proteins, RNA molecules, and particular parts of the chromosomes. The best-known of these is the nucleolus, which is mainly involved in the assembly of ribosomes. After being produced in the nucleolus, ribosomes are exported to the cytoplasm where they translate mRNA.