Cell Cycle
... organisms produces one or more new organisms that are identical to itself and that live independently of it ...
... organisms produces one or more new organisms that are identical to itself and that live independently of it ...
Biochemistry: Chemicals of Life
... Allows some small, non-polar molecules through, but blocks large or charged molecules. ...
... Allows some small, non-polar molecules through, but blocks large or charged molecules. ...
Cell Structure - Anoka-Hennepin School District
... • Function: converts food into energy • Analogy: powerhouse • Made of: 2 membranes • Both ...
... • Function: converts food into energy • Analogy: powerhouse • Made of: 2 membranes • Both ...
Cell Structure and Function/ Cellular Transport Study Guide
... In the Venn Diagram below, write down the differences and similarities between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells: ...
... In the Venn Diagram below, write down the differences and similarities between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells: ...
File
... terminally (at one end), subtermillally (near one end, or celltrally inside the vegetative cell. When the endospore matures, the vegetative cell wall ruptures (lyses), killing the cell, and the endospore is freed. Most of the water present in the forespore cytoplasm is eliminated by the time sporula ...
... terminally (at one end), subtermillally (near one end, or celltrally inside the vegetative cell. When the endospore matures, the vegetative cell wall ruptures (lyses), killing the cell, and the endospore is freed. Most of the water present in the forespore cytoplasm is eliminated by the time sporula ...
Cell Membranes: Chapt. 6 - College Heights Secondary
... • Vesicles (lysosomes, other secretory vesicles) can fuse with the membrane and open up the the outside… ...
... • Vesicles (lysosomes, other secretory vesicles) can fuse with the membrane and open up the the outside… ...
For fertilized eggs to form complex animal structures, cells have to
... We aim to understand the molecular mechanisms that control dynamic cellular behaviors by using state-ofthe-arts technologies of high-resolution live-imaging microscopy and manipulation of gene functions. We will visualize cytoskeletal proteins and their regulators in live C. elegans embryos and anal ...
... We aim to understand the molecular mechanisms that control dynamic cellular behaviors by using state-ofthe-arts technologies of high-resolution live-imaging microscopy and manipulation of gene functions. We will visualize cytoskeletal proteins and their regulators in live C. elegans embryos and anal ...
Plant Cells and Tissues
... stretches as the cell grows – A secondary cell wall may then be produced, inside the primary wall • Strong, thick – Secondary cell walls set limits to cell growth • Middle Lamella is the area between adjacent plant cells and is made of pectin ...
... stretches as the cell grows – A secondary cell wall may then be produced, inside the primary wall • Strong, thick – Secondary cell walls set limits to cell growth • Middle Lamella is the area between adjacent plant cells and is made of pectin ...
What to know Chap 11
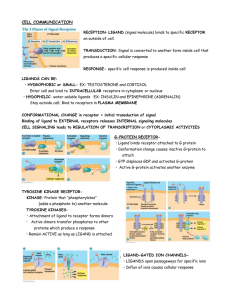
... RECEPTION- LIGAND (signal molecule) binds to specific RECEPTOR on outside of cell. TRANSDUCTION- Signal is converted to another form inside cell that produces a specific cellular response RESPONSE- specific cell response is produced inside cell LIGANDS CAN BE: • HYDROPHOBIC or SMALL- EX: TESTOSTERON ...
... RECEPTION- LIGAND (signal molecule) binds to specific RECEPTOR on outside of cell. TRANSDUCTION- Signal is converted to another form inside cell that produces a specific cellular response RESPONSE- specific cell response is produced inside cell LIGANDS CAN BE: • HYDROPHOBIC or SMALL- EX: TESTOSTERON ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... Common features of cells: Most cells have… A cell membrane: encloses cell, separates interior Cytoplasm: the fluid in which interior cell structures are suspended, also called cytosol Cytoskeleton: for cellular structure Ribosomes: make proteins DNA: all cells have DNA which contains in ...
... Common features of cells: Most cells have… A cell membrane: encloses cell, separates interior Cytoplasm: the fluid in which interior cell structures are suspended, also called cytosol Cytoskeleton: for cellular structure Ribosomes: make proteins DNA: all cells have DNA which contains in ...
Cells - Avon Community School Corporation
... and delivers final proteins Arrive to Golgi enclosed in vesicles Vesicles fuse with Golgi As move through Golgi, the proteins are modified chemically When reach outermost layer, packaged again in vesicles and shipped ...
... and delivers final proteins Arrive to Golgi enclosed in vesicles Vesicles fuse with Golgi As move through Golgi, the proteins are modified chemically When reach outermost layer, packaged again in vesicles and shipped ...
21. Membranes
... effectively like a larger version of Van Der Waals forces, a membrane’s component parts are not locked in place; lateral motion is quite common. b. Those same hydrophobic forces, however, prevent molecules from cutting through the entire membrane – pieces and molecules tend to stay where they are co ...
... effectively like a larger version of Van Der Waals forces, a membrane’s component parts are not locked in place; lateral motion is quite common. b. Those same hydrophobic forces, however, prevent molecules from cutting through the entire membrane – pieces and molecules tend to stay where they are co ...
Origins - Stosich Science
... lipids, some RNA, some DNA…. That’s a cell! The first cells would have been Prokaryotes They would have given rise to ancient bacteria. ...
... lipids, some RNA, some DNA…. That’s a cell! The first cells would have been Prokaryotes They would have given rise to ancient bacteria. ...
Cholera as a prokaryote1.61 MB
... • Bacteria belong to a large group of organisms called prokaryotes which lack a nucleus. • All organisms that have a well defined membrane - bound nucleus are called eukaryotes e.g. animals, plants, fungi and some single-celled organisms. ...
... • Bacteria belong to a large group of organisms called prokaryotes which lack a nucleus. • All organisms that have a well defined membrane - bound nucleus are called eukaryotes e.g. animals, plants, fungi and some single-celled organisms. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Golgi Bodies and Lysosomes Golgi body • A folded membrane containing enzymes that finish polypeptides and lipids delivered by the ER • Packages finished products in vesicles that carry them to the plasma membrane or to lysosomes ...
... Golgi Bodies and Lysosomes Golgi body • A folded membrane containing enzymes that finish polypeptides and lipids delivered by the ER • Packages finished products in vesicles that carry them to the plasma membrane or to lysosomes ...
Membranes Reading Guide
... 1. What does selective permeability mean and why is that important to cells? Selective permeability means that it is a selective barrier, which allows passage of certain materials (waste, water, oxygen, nutrients, etc.) but not others, or at least some may pass more easily. It allows a cell to discr ...
... 1. What does selective permeability mean and why is that important to cells? Selective permeability means that it is a selective barrier, which allows passage of certain materials (waste, water, oxygen, nutrients, etc.) but not others, or at least some may pass more easily. It allows a cell to discr ...
1st Nine Weeks Bundle
... Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Examine and compare different types of cells. Each part of the cell is designed to complete specific functions. The structure of the part is directly related to its function. ...
... Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Examine and compare different types of cells. Each part of the cell is designed to complete specific functions. The structure of the part is directly related to its function. ...
The Cell
... are bounded by a double membrane. Each of these membranes is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The outermost membrane is smooth while the inner membrane has many folds. These folds are called cristae. The folds enhance the "productivity" of cellular respiration by increasing the availab ...
... are bounded by a double membrane. Each of these membranes is a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. The outermost membrane is smooth while the inner membrane has many folds. These folds are called cristae. The folds enhance the "productivity" of cellular respiration by increasing the availab ...
Document
... Following Voc words: tissues, organ systems, organs, organism, community, cells. Difference between animal and plant cells. Be able to label and describe the function of the following organelles: Chlorophyll, chloroplast, cell wall, lysosomes, vacuole, cell membrane, nucleolus, ribosome, mitochondri ...
... Following Voc words: tissues, organ systems, organs, organism, community, cells. Difference between animal and plant cells. Be able to label and describe the function of the following organelles: Chlorophyll, chloroplast, cell wall, lysosomes, vacuole, cell membrane, nucleolus, ribosome, mitochondri ...