Document
... • Cell Membrane is composed of – Phospholipid bilayer: forms the basic unit of the cell membrane – Proteins: help transport large molecules through the membrane – Carbohydrates: help cells send and receive chemical messages ...
... • Cell Membrane is composed of – Phospholipid bilayer: forms the basic unit of the cell membrane – Proteins: help transport large molecules through the membrane – Carbohydrates: help cells send and receive chemical messages ...
APPLIED BIOLOGY MID-TERM STUDY GUIDE
... Cell membrane composition (bilayer of phospholipids) Function of cell membrane Types of microscope (electron and compound) Surface area to volume ratio Three parts of cytoskeleton Parts of a microscope – and functions of these parts (use microscope diagram) Organelles of the plant and ...
... Cell membrane composition (bilayer of phospholipids) Function of cell membrane Types of microscope (electron and compound) Surface area to volume ratio Three parts of cytoskeleton Parts of a microscope – and functions of these parts (use microscope diagram) Organelles of the plant and ...
for cell
... The extracellular matrix of animal cells functions in support, movement, and regulation Cells synthesize and secrete the extracellular matrix (ECM) that is essential to cell function The ECM is composed of strong fibers of collagen, which holds cells together and protects the plasma membrane E ...
... The extracellular matrix of animal cells functions in support, movement, and regulation Cells synthesize and secrete the extracellular matrix (ECM) that is essential to cell function The ECM is composed of strong fibers of collagen, which holds cells together and protects the plasma membrane E ...
Cell Boundaries - Duplin County Schools
... • As water diffuses toward the hypertonic side of a membrane, this produces OSMOTIC PRESSURE acting on the hypertonic side of the membrane • Cells have salts, sugars, proteins, and other solutes dissolved in the cytoplasm, making the inside of cells hypertonic to fresh/distilled water; if not checke ...
... • As water diffuses toward the hypertonic side of a membrane, this produces OSMOTIC PRESSURE acting on the hypertonic side of the membrane • Cells have salts, sugars, proteins, and other solutes dissolved in the cytoplasm, making the inside of cells hypertonic to fresh/distilled water; if not checke ...
Quiz- Cells/ Photosynthesis/ Respiration
... What is the function of a cell membrane? a. to suPPortthe cell b. to perform different functions in each cell c. to control what entersand leavesthe cell d. to form a hard outer covering for the cell Which of the followingbest describesthe function of mitochondria? use' a. They convert energyfrom fo ...
... What is the function of a cell membrane? a. to suPPortthe cell b. to perform different functions in each cell c. to control what entersand leavesthe cell d. to form a hard outer covering for the cell Which of the followingbest describesthe function of mitochondria? use' a. They convert energyfrom fo ...
Cells - Junctions and Transport
... between adjacent cells – Cells are connected by hollow cylinders called connexons. – Small molecules pass through the water filled channels from one cell to the next. – Present in electrically excitable tissues like heart and smooth muscle ...
... between adjacent cells – Cells are connected by hollow cylinders called connexons. – Small molecules pass through the water filled channels from one cell to the next. – Present in electrically excitable tissues like heart and smooth muscle ...
Apoptosis—Programmed Cell Death
... -Because the plasma and interstitial fluids are separated only by highly permeable capillary membranes , their ionic compositions are similar and they are often considered together as one large compartment of homogeneous fluid . ...
... -Because the plasma and interstitial fluids are separated only by highly permeable capillary membranes , their ionic compositions are similar and they are often considered together as one large compartment of homogeneous fluid . ...
Cells Unit - Warren County Public Schools
... • Eukaryotes: Have nucleus, larger, more complex, more organelles, evolutionarily more modern. ...
... • Eukaryotes: Have nucleus, larger, more complex, more organelles, evolutionarily more modern. ...
Carrier Proteins
... • How and why is the plasma membrane (structure & function) essential in maintaining the homeostasis for the cell in reference to transport, hypertonic solutions, hypotonic solutions, and isotonic solutions? ...
... • How and why is the plasma membrane (structure & function) essential in maintaining the homeostasis for the cell in reference to transport, hypertonic solutions, hypotonic solutions, and isotonic solutions? ...
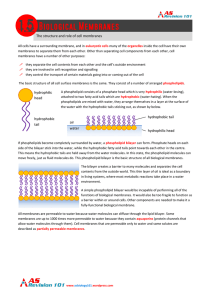
The structure and role of cell membranes hydrophilic head
... move freely, just as fluid molecules do. This phospholipid bilayer is the basic structure of all biological membranes. The bilayer creates a barrier to many molecules and separates the cell contents from the outside world. This thin layer of oil is ideal as a boundary in living systems, where most m ...
... move freely, just as fluid molecules do. This phospholipid bilayer is the basic structure of all biological membranes. The bilayer creates a barrier to many molecules and separates the cell contents from the outside world. This thin layer of oil is ideal as a boundary in living systems, where most m ...
Cells * The building blocks of life
... Storage of water, nutrients (food), waste Plants generally have one large vacuole while animal cells have several smaller vacuoles ...
... Storage of water, nutrients (food), waste Plants generally have one large vacuole while animal cells have several smaller vacuoles ...
The Ultrastructure Of A Typical Bacterial Cell
... strength and rigidity. It is permeable to solutes. ...
... strength and rigidity. It is permeable to solutes. ...
1.2 Looking Inside Cells Guided Reading
... Bacterial Cells 12. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about bacterial cells. a. Bacterial cells are larger than plant or animal cells. b. Bacterial cells have a cell wall and a cell membrane. c. Bacterial cells do not have a nucleus. d. Bacterial cells do not have genetic material. ...
... Bacterial Cells 12. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about bacterial cells. a. Bacterial cells are larger than plant or animal cells. b. Bacterial cells have a cell wall and a cell membrane. c. Bacterial cells do not have a nucleus. d. Bacterial cells do not have genetic material. ...
What are cells?
... • consists of primarily of water • Site of chemical activities ie. dissolved gasses and nutrients • Allow transportation between structures • Store waste until depose ...
... • consists of primarily of water • Site of chemical activities ie. dissolved gasses and nutrients • Allow transportation between structures • Store waste until depose ...
Cell Function – Cells and their Environment
... Water moves into and out of cells because of the different concentrations of the solutes. Different kinds of cells react differently to osmosis, depending on the solution they are in: ...
... Water moves into and out of cells because of the different concentrations of the solutes. Different kinds of cells react differently to osmosis, depending on the solution they are in: ...
Cell Membranes
... Review of three types of endocytosis: Pinocytosis – pinching off of a small amount of the fluid around the cell. Receptor-mediated endocytosis – this is the process where the cell selectively bind to and engulf material found outside the cell. Phagocytosis – process by which cells pick up large part ...
... Review of three types of endocytosis: Pinocytosis – pinching off of a small amount of the fluid around the cell. Receptor-mediated endocytosis – this is the process where the cell selectively bind to and engulf material found outside the cell. Phagocytosis – process by which cells pick up large part ...
Chapter 5
... which specifically bind to receptors on the target cells c) Some ligand-receptor complexes bind to and activate specific integral membrane proteins: the G proteins Transport to target cells Reception of the information by target cells a) This is typically composed of a transmembrane protein with a f ...
... which specifically bind to receptors on the target cells c) Some ligand-receptor complexes bind to and activate specific integral membrane proteins: the G proteins Transport to target cells Reception of the information by target cells a) This is typically composed of a transmembrane protein with a f ...
hapter: Membrane Structure and Function You must know: 1. Why
... endocytosis. In exocytosis, vesicles from the cell’s interior fuse with the cell membrane, expelling their contents. In endocytosis, the cell forms new vesicles from the plasma membrane; this is basically the reverse of exocytosis, and the process allows the cell to take in macromolecules. There are ...
... endocytosis. In exocytosis, vesicles from the cell’s interior fuse with the cell membrane, expelling their contents. In endocytosis, the cell forms new vesicles from the plasma membrane; this is basically the reverse of exocytosis, and the process allows the cell to take in macromolecules. There are ...
Ribosomes
... Ribosomes are small organelles where protein synthesis occurs , it is composed of two subunits , one large and one small . Ribosomes can be found free in the cytoplasm either singly or in groups called poly ribosomes, also can be found attached to endoplasmic reticulum and can be found stored in nuc ...
... Ribosomes are small organelles where protein synthesis occurs , it is composed of two subunits , one large and one small . Ribosomes can be found free in the cytoplasm either singly or in groups called poly ribosomes, also can be found attached to endoplasmic reticulum and can be found stored in nuc ...
Lab Quiz 4 Study Guide Know the Domain, Kingdom and cellular
... 5. Selectively permeable: the plasma membrane and other non-biological membranes (dialysis tubing) are selective as to what particles/molecules/substance can pass across them. The plasma membrane (a phospholipid bilayer) is permeable to nonpolar molecules and small molecules like water, carbon dioxi ...
... 5. Selectively permeable: the plasma membrane and other non-biological membranes (dialysis tubing) are selective as to what particles/molecules/substance can pass across them. The plasma membrane (a phospholipid bilayer) is permeable to nonpolar molecules and small molecules like water, carbon dioxi ...
Cell Membrane II
... , the plasma membrane engulfs an extracellular substance (often a large protein). • The engulfing portion of the membrane pinches off in a membranous sac known as a with the substance inside. • During , a membrane-enclosed vesicle carrying material to be expelled from the cell moves to the cell surf ...
... , the plasma membrane engulfs an extracellular substance (often a large protein). • The engulfing portion of the membrane pinches off in a membranous sac known as a with the substance inside. • During , a membrane-enclosed vesicle carrying material to be expelled from the cell moves to the cell surf ...
8-2: Cell Transport
... The cell’s membrane is a little like a country’s border. It both barriers regulate who or what enters (imports/ immigration) and who or what leaves (exports/ emigration/ deportation). ...
... The cell’s membrane is a little like a country’s border. It both barriers regulate who or what enters (imports/ immigration) and who or what leaves (exports/ emigration/ deportation). ...
Plant and Animal Cell Parts
... substance that chromosomes are composed of that makes up the ___________________. ...
... substance that chromosomes are composed of that makes up the ___________________. ...