unit 4 – syllabus - Effingham County Schools
... 6. ____________________a tool scientist use to predict all of the possible combinations of alleles that offspring can inherit from 2 parents 7. ____________________hereditary material found in the nucleus of a cell that controls all the activities of the cell 8. ____________________the inherited com ...
... 6. ____________________a tool scientist use to predict all of the possible combinations of alleles that offspring can inherit from 2 parents 7. ____________________hereditary material found in the nucleus of a cell that controls all the activities of the cell 8. ____________________the inherited com ...
KINGDOMS OF ORGANISMS
... Chromosome—usually a single, circular piece of DNA Ribosome—used for making proteins Plasmid—small circular piece of DNA Cell membrane (a.k.a. plasma membrane)— separates the cell from its external environment Pili—short, hairlike structures involved in reproduction and cell-to-cell contact Cell wal ...
... Chromosome—usually a single, circular piece of DNA Ribosome—used for making proteins Plasmid—small circular piece of DNA Cell membrane (a.k.a. plasma membrane)— separates the cell from its external environment Pili—short, hairlike structures involved in reproduction and cell-to-cell contact Cell wal ...
7 3-1DR - Groupfusion.net
... c. Multiply the area of each side times the number of sides. d. Multiply the surface area times the volume. PARTS OF A CELL Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. ...
... c. Multiply the area of each side times the number of sides. d. Multiply the surface area times the volume. PARTS OF A CELL Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. ...
90451 Describe physical factors of the environment and techniques
... Bigger molecules can pass across the membrane via active transport (uses energy). This is controlled by the cell using proteins embedded in the membrane. ...
... Bigger molecules can pass across the membrane via active transport (uses energy). This is controlled by the cell using proteins embedded in the membrane. ...
cells come from other cells - holyoke
... *A vesicle forms with Golgi to transport substances outside cell. ...
... *A vesicle forms with Golgi to transport substances outside cell. ...
Section 7-1 and 7-2 of textbook objectives - holyoke
... *A vesicle forms with Golgi to transport substances outside cell. ...
... *A vesicle forms with Golgi to transport substances outside cell. ...
Diapositiva 1
... cells or eukaryotic cells. The main differences between the two kinds of cells are in their structure: • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus defined by a membrane, while prokaryotic cells have no nucleus. • In eukaryotic cells, the DNA, or genetic information, is found in the nucleus. In prokaryotic cel ...
... cells or eukaryotic cells. The main differences between the two kinds of cells are in their structure: • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus defined by a membrane, while prokaryotic cells have no nucleus. • In eukaryotic cells, the DNA, or genetic information, is found in the nucleus. In prokaryotic cel ...
Lec.2
... composition the cell membrane. While the phospholipids of the outer leaflet are replaced by lipopolysaccharides molecules. Thus this bilayer differs from the bilayer of cell membrane. The outer membrane protects the cell from hydrophobic as well as hydrophilic molecules. The outer membrane has spe ...
... composition the cell membrane. While the phospholipids of the outer leaflet are replaced by lipopolysaccharides molecules. Thus this bilayer differs from the bilayer of cell membrane. The outer membrane protects the cell from hydrophobic as well as hydrophilic molecules. The outer membrane has spe ...
CELLS-Chapter 2 - St. Thomas the Apostle School
... -RIBOSOMES make protiens for all cell activities -some ribosomes attach to the rough part of the ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM- moves material around in a cell ...
... -RIBOSOMES make protiens for all cell activities -some ribosomes attach to the rough part of the ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM- moves material around in a cell ...
Diffusion
... because it is the concentration to areas of movement of molecules LOW concentration; so from areas of LOW it DOES NOT require concentration to areas of ...
... because it is the concentration to areas of movement of molecules LOW concentration; so from areas of LOW it DOES NOT require concentration to areas of ...
REading Assignment: Chapter 12 Membrane Transport pgs. 389
... Channel Proteins Forms a hydrophilic water-filled pores that extends across the lipid bilayer Specific for inorganic ions of the appropriate size and charge allowing them to cross the membrane Transport through channel proteins occurs at a much faster rate than transport through carrier pro ...
... Channel Proteins Forms a hydrophilic water-filled pores that extends across the lipid bilayer Specific for inorganic ions of the appropriate size and charge allowing them to cross the membrane Transport through channel proteins occurs at a much faster rate than transport through carrier pro ...
Lec.14 Dr:Buthaina Al-Sabawi Date:21/12/2016 Mitosis
... During mitosis one cell divides ONCE to form two identical cells. The major purpose of mitosis is for growth and to replace worn out cells. Mitosis is nuclear division plus cytokinesis, and produces two identical daughter cells during prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Inter ...
... During mitosis one cell divides ONCE to form two identical cells. The major purpose of mitosis is for growth and to replace worn out cells. Mitosis is nuclear division plus cytokinesis, and produces two identical daughter cells during prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Inter ...
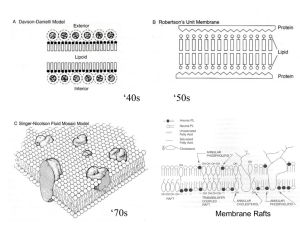
lecture 11
... Hydrophobic mismatch: if there is a mismatch between the length of the TMD and the hydrocarbon thickness, then the bilayer would need to deform to prevent exposure of the hydrophobic amino acids to water. This would be energetically unfavorable. So, if the protein can “move” to a “raft” of different ...
... Hydrophobic mismatch: if there is a mismatch between the length of the TMD and the hydrocarbon thickness, then the bilayer would need to deform to prevent exposure of the hydrophobic amino acids to water. This would be energetically unfavorable. So, if the protein can “move” to a “raft” of different ...
Class IX Chapter 5 – The Fundamental Unit of Life Science
... Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to observe cells in a cork slice. Question 2: Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life? Answer: Cells constitute various components of plants and animals. A cell is the smalles ...
... Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to observe cells in a cork slice. Question 2: Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life? Answer: Cells constitute various components of plants and animals. A cell is the smalles ...
Long Version
... What is a primary producer? What is a primary consumer? What is a heterotroph? autotroph? What is biological magnification? Explain the rule of 10% in regards to trophic levels. What are there not unlimited steps in the energy pyramid? What is primary productivity? What is Gross primary productivity ...
... What is a primary producer? What is a primary consumer? What is a heterotroph? autotroph? What is biological magnification? Explain the rule of 10% in regards to trophic levels. What are there not unlimited steps in the energy pyramid? What is primary productivity? What is Gross primary productivity ...
Let’s “Cell”-ebrate the cell!!
... All cells contain organelles The structures of a cell that perform a specific function are called organelles. Animal and plant cells have some organelles in common but there are also differences in the organelles each have. You will need to know the function of each organelle and how to draw a ...
... All cells contain organelles The structures of a cell that perform a specific function are called organelles. Animal and plant cells have some organelles in common but there are also differences in the organelles each have. You will need to know the function of each organelle and how to draw a ...
MITOSIS
... • Cell growth and synthesis of materials needed for proper cell function take place • Certain cells never leave G1 Known as G0 Red blood cells, neurons, skeletal muscle cells These cells will not divide or grow, but will continue to function until cell death ...
... • Cell growth and synthesis of materials needed for proper cell function take place • Certain cells never leave G1 Known as G0 Red blood cells, neurons, skeletal muscle cells These cells will not divide or grow, but will continue to function until cell death ...
Cell Structures
... other materials in cell • Recycles and decomposes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html ...
... other materials in cell • Recycles and decomposes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html ...
membrane - Lemon Bay High School
... Cytoplasm Cytoplasm is the material outside the nucleus and inside the plasma membrane ...
... Cytoplasm Cytoplasm is the material outside the nucleus and inside the plasma membrane ...
Cells Part 1 - Lemon Bay High School
... Cytoplasm Cytoplasm is the material outside the nucleus and inside the plasma membrane ...
... Cytoplasm Cytoplasm is the material outside the nucleus and inside the plasma membrane ...
slides
... that are present in low concentrations in their environment. Membrane proteins act as carriers and enzymes. They are specific for a single or a few molecules or ions. The end result is that a gradient is set up and maintained. These carriers can be saturated. Group translocation reactions move a sub ...
... that are present in low concentrations in their environment. Membrane proteins act as carriers and enzymes. They are specific for a single or a few molecules or ions. The end result is that a gradient is set up and maintained. These carriers can be saturated. Group translocation reactions move a sub ...
013368718X_CH10_143
... Regulatory proteins work both inside and outside of the cell. Internal regulators allow the cell cycle to proceed when certain events have occurred within a cell. External regulators called growth factors stimulate the cell cycle. Other external regulators cause the cell cycle to slow down or st ...
... Regulatory proteins work both inside and outside of the cell. Internal regulators allow the cell cycle to proceed when certain events have occurred within a cell. External regulators called growth factors stimulate the cell cycle. Other external regulators cause the cell cycle to slow down or st ...