Tissues and Membranes
... o Neurons—generate and carry electrochemical impulses o Has a direct role in almost every body function o 2 structural divisions CNS—brain and spinal cord • Neurons and neuroglial cells PNS—peripheral nerves • Neurons and Schwann cells (produce myelin sheath) o Neuron structure Cell body—conta ...
... o Neurons—generate and carry electrochemical impulses o Has a direct role in almost every body function o 2 structural divisions CNS—brain and spinal cord • Neurons and neuroglial cells PNS—peripheral nerves • Neurons and Schwann cells (produce myelin sheath) o Neuron structure Cell body—conta ...
EPC (Skin, Fish)
... This cell line known as Epithelioma papulosum cyprini (EPC) was originally reported to be from Carp (Cyprinus carpio) epidermal herpes virus-induced hyperplastic lesions. More recently EPC was found to be derived from Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas) see Winton et al., 2010. This has been confir ...
... This cell line known as Epithelioma papulosum cyprini (EPC) was originally reported to be from Carp (Cyprinus carpio) epidermal herpes virus-induced hyperplastic lesions. More recently EPC was found to be derived from Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas) see Winton et al., 2010. This has been confir ...
Author: Guan-Jong Chen, MIT ©SCICOM MIT Stem Cells and Its
... Ideally, scientists would like to be able to grow a particular type of cell in the laboratory and then inject it into a patient, where it would replace diseased tissue. But stem cells are not yet being used to treat disease because scientists still haven't learned how to direct a stem cell to diffe ...
... Ideally, scientists would like to be able to grow a particular type of cell in the laboratory and then inject it into a patient, where it would replace diseased tissue. But stem cells are not yet being used to treat disease because scientists still haven't learned how to direct a stem cell to diffe ...
Histology
... Merocrine glands secrete fluid without loss of cytoplasm Apocrine glands lose portions of cells during secretion Holocrine glands release cells filled with secretory products ...
... Merocrine glands secrete fluid without loss of cytoplasm Apocrine glands lose portions of cells during secretion Holocrine glands release cells filled with secretory products ...
Spermatogonial stem cells (A Basic Concept)
... Spermatogenic process can be reinitiated in the patients those who have lost their spermatogonial cells during the treatment for such diseases. Transplantation of spermatogonial stem cells in the recipient’s seminiferous tubules for reinitiation of spermatozoa production in injury and other cytotoxi ...
... Spermatogenic process can be reinitiated in the patients those who have lost their spermatogonial cells during the treatment for such diseases. Transplantation of spermatogonial stem cells in the recipient’s seminiferous tubules for reinitiation of spermatozoa production in injury and other cytotoxi ...
Stem cell research
... Once cell lines are established, or even before that stage, batches of them can be frozen and stored or shipped to other laboratories for further culture and experimentation. Q3. Why not use human adult somatic stem cells instead of human embryonic stem cells in research? A. Embryonic stem cells are ...
... Once cell lines are established, or even before that stage, batches of them can be frozen and stored or shipped to other laboratories for further culture and experimentation. Q3. Why not use human adult somatic stem cells instead of human embryonic stem cells in research? A. Embryonic stem cells are ...
Chapter 2 Cells to Systems
... cells - nerve cells, can connect several parts of the body at once. 2) Flat cells cells, join to overlap and cover a surface. Like shingles on a house. 3) Round cells blood cells, round with 2 two dimples. Gives extra surface area for picking up O2. ...
... cells - nerve cells, can connect several parts of the body at once. 2) Flat cells cells, join to overlap and cover a surface. Like shingles on a house. 3) Round cells blood cells, round with 2 two dimples. Gives extra surface area for picking up O2. ...
STAAR Review Day Five Independent Practice 3. In humans, the
... neuron affects its function. In one of her experiments, she uses a microscalpel to cut off a neurons dendrites. How do you think this experiment will change the function of a neuron? The neuron will no longer be able to receive messages because it is missing its dendrites therefore it will not be ab ...
... neuron affects its function. In one of her experiments, she uses a microscalpel to cut off a neurons dendrites. How do you think this experiment will change the function of a neuron? The neuron will no longer be able to receive messages because it is missing its dendrites therefore it will not be ab ...
Getting to Know: Cell Theory
... of the circulatory system. The circulatory system works with the muscular system, the digestive system, the immune system, and others to make your body function properly. Each of these systems is made of specialized cells that perform special functions. ...
... of the circulatory system. The circulatory system works with the muscular system, the digestive system, the immune system, and others to make your body function properly. Each of these systems is made of specialized cells that perform special functions. ...
Chapter 20 – Pregnancy, Growth, and Development
... Other hormonal changes during pregnancy include increased secretions of _____________ (promotes fluid retention) and parathyroid hormone (to maintain a high calcium level in the blood). C. Embryonic Stage (p. 526; Figs. 20.7-20.14; Table 20.2) ...
... Other hormonal changes during pregnancy include increased secretions of _____________ (promotes fluid retention) and parathyroid hormone (to maintain a high calcium level in the blood). C. Embryonic Stage (p. 526; Figs. 20.7-20.14; Table 20.2) ...
Levels of Organization-Plants
... Throughout your body, tissues are grouped together so they can work together. An organ is a group of tissues that work together doing certain jobs. ...
... Throughout your body, tissues are grouped together so they can work together. An organ is a group of tissues that work together doing certain jobs. ...
4- Blood
... all organelles shortly before the cells are released by bone marrow into the circulation. Lacking mitochondria, mature erythrocytes depend on anaerobic glycolysis for their minimal energy needs. Lacking nuclei, they cannot replace defective proteins. Human erythrocytes normally survive in the circul ...
... all organelles shortly before the cells are released by bone marrow into the circulation. Lacking mitochondria, mature erythrocytes depend on anaerobic glycolysis for their minimal energy needs. Lacking nuclei, they cannot replace defective proteins. Human erythrocytes normally survive in the circul ...
5.16.05 Development and Aging
... • Processing and Transporting Cardiovascular disorders are the leading cause of death among the elderly; the heart shrinks with age, and fatty deposits clog arteries. Lungs lose elasticity, so ventilation is reduced. A reduced blood supply to the kidneys results in the kidneys becoming smaller and l ...
... • Processing and Transporting Cardiovascular disorders are the leading cause of death among the elderly; the heart shrinks with age, and fatty deposits clog arteries. Lungs lose elasticity, so ventilation is reduced. A reduced blood supply to the kidneys results in the kidneys becoming smaller and l ...
Key Idea #9 - Mona Shores Blogs
... Whether doctors, teachers, builders, engineers, farmers, etc, everyone learns a specific skill which they can then use to help everyone else. Just like people, cells specialize in important jobs. ...
... Whether doctors, teachers, builders, engineers, farmers, etc, everyone learns a specific skill which they can then use to help everyone else. Just like people, cells specialize in important jobs. ...
Stem cells
... type of cell, it is not specialised • All animal cells originate from embryo stem cells. During the development of an embryo, most of these cells become specialised. They cannot later change to become a different type of cell. This process is called cell differentiation. • Adult stem cells can grow ...
... type of cell, it is not specialised • All animal cells originate from embryo stem cells. During the development of an embryo, most of these cells become specialised. They cannot later change to become a different type of cell. This process is called cell differentiation. • Adult stem cells can grow ...
Materials and Methods S1.
... identity. PCR-amplification of 16sRNA gene sequences from stool DNA, DNA sequencing and DGGE analyses were performed as previously described38, 39. The number of patients whose DGGE banding pattern changed was determined for each sampling interval in both the LR and placebo-treated control group. ...
... identity. PCR-amplification of 16sRNA gene sequences from stool DNA, DNA sequencing and DGGE analyses were performed as previously described38, 39. The number of patients whose DGGE banding pattern changed was determined for each sampling interval in both the LR and placebo-treated control group. ...
The respiratory system - Spark (e
... cells of the lungs. Each alveolus is formed by two different types of specialized cells. These cells are easily crossed by gases and that is why the exchange between blood and air is quite simple. ...
... cells of the lungs. Each alveolus is formed by two different types of specialized cells. These cells are easily crossed by gases and that is why the exchange between blood and air is quite simple. ...
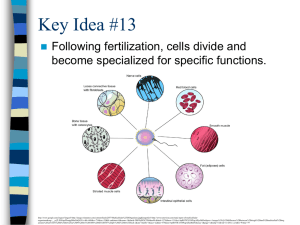
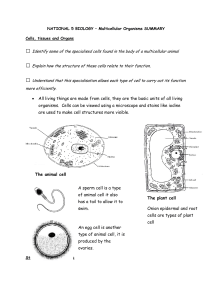
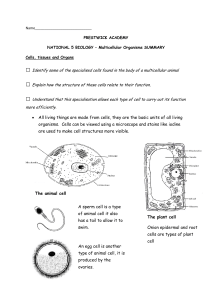
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... Red blood cells transport the oxygen in the blood and deliver it to cells in the body. They have a biconcave shape that ensures that the cell has a large surface area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at t ...
... Red blood cells transport the oxygen in the blood and deliver it to cells in the body. They have a biconcave shape that ensures that the cell has a large surface area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at t ...
• All living things are made from cells, they are the basic units of all
... Red blood cells transport the oxygen in the blood and deliver it to cells in the body. They have a biconcave shape that ensures that the cell has a large surface area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at t ...
... Red blood cells transport the oxygen in the blood and deliver it to cells in the body. They have a biconcave shape that ensures that the cell has a large surface area for the absorption of oxygen. Red blood cells contain the pigment haemoglobin which combines with oxygen at high concentrations (at t ...
2017 Year 8 Term3 Programme
... Cells are the basic units of living things; they have specialised structures and functions (ACSSU149) ...
... Cells are the basic units of living things; they have specialised structures and functions (ACSSU149) ...
2nd Semester Final Exam Review 2016
... 32. Give an example of selective breeding. You have two different kinds of roses. One is prettier than the other while the second smells better. You cross the two flowers hoping for a flower that is both beautiful and smells pretty. 33. Define natural selection. The process by which organisms better ...
... 32. Give an example of selective breeding. You have two different kinds of roses. One is prettier than the other while the second smells better. You cross the two flowers hoping for a flower that is both beautiful and smells pretty. 33. Define natural selection. The process by which organisms better ...
Induced pluripotent stem cell
Induced pluripotent stem cells (also known as iPS cells or iPSCs) are a type of pluripotent stem cell that can be generated directly from adult cells. The iPSC technology was pioneered by Shinya Yamanaka’s lab in Kyoto, Japan, who showed in 2006 that the introduction of four specific genes encoding transcription factors could convert adult cells into pluripotent stem cells. He was awarded the 2012 Nobel Prize along with Sir John Gurdon ""for the discovery that mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent."" Pluripotent stem cells hold great promise in the field of regenerative medicine. Because they can propagate indefinitely, as well as give rise to every other cell type in the body (such as neurons, heart, pancreatic, and liver cells), they represent a single source of cells that could be used to replace those lost to damage or disease.The most well-known type of pluripotent stem cell is the embryonic stem cell. However, since the generation of embryonic stem cells involves destruction (or at least manipulation) of the pre-implantation stage embryo, there has been much controversy surrounding their use. Further, because embryonic stem cells can only be derived from embryos, it has so far not been feasible to create patient-matched embryonic stem cell lines.Since iPSCs can be derived directly from adult tissues, they not only bypass the need for embryos, but can be made in a patient-matched manner, which means that each individual could have their own pluripotent stem cell line. These unlimited supplies of autologous cells could be used to generate transplants without the risk of immune rejection. While the iPSC technology has not yet advanced to a stage where therapeutic transplants have been deemed safe, iPSCs are readily being used in personalized drug discovery efforts and understanding the patient-specific basis of disease.Depending on the methods used, reprogramming of adult cells to obtain iPSCs may pose significant risks that could limit their use in humans. For example, if viruses are used to genomically alter the cells, the expression of oncogenes (cancer-causing genes) may potentially be triggered. In February 2008, scientists announced the discovery of a technique that could remove oncogenes after the induction of pluripotency, thereby increasing the potential use of iPS cells in human diseases. In April 2009, it was demonstrated that generation of iPS cells is possible without any genetic alteration of the adult cell: a repeated treatment of the cells with certain proteins channeled into the cells via poly-arginine anchors was sufficient to induce pluripotency. The acronym given for those iPSCs is piPSCs (protein-induced pluripotent stem cells).