Cells of the Respiratory System
... Oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses from the alveoli to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells. In order to do so, it has to diffuse through the alveolar epithelial cell, the capillary endothelial cell, plasma in the capillary, and into the red blood cell. ...
... Oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses from the alveoli to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells. In order to do so, it has to diffuse through the alveolar epithelial cell, the capillary endothelial cell, plasma in the capillary, and into the red blood cell. ...
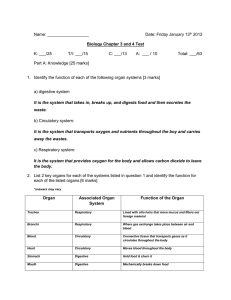
Name: Date: Friday January 13th 2012 Biology Chapter 3 and 4 Test
... 1. Describe the path an apple takes as it goes through your digestive system [5 marks] Food enters the body through the mouth and exits through the anus. In between, it undergoes digestion (from the mouth to the stomach), absorption (from the stomach to the small intestines), and elimination (from t ...
... 1. Describe the path an apple takes as it goes through your digestive system [5 marks] Food enters the body through the mouth and exits through the anus. In between, it undergoes digestion (from the mouth to the stomach), absorption (from the stomach to the small intestines), and elimination (from t ...
Structure and Function in Living Systems Chapter 8: Systems in
... Because multicellular organisms are large, many of their cells are far away from one another or from the outside of the organism where oxygen can be obtained and wastes such as carbon dioxide can be released. Therefore, multicellular organisms must have specialized cells to efficiently perform the t ...
... Because multicellular organisms are large, many of their cells are far away from one another or from the outside of the organism where oxygen can be obtained and wastes such as carbon dioxide can be released. Therefore, multicellular organisms must have specialized cells to efficiently perform the t ...
Kingdom Protista
... name. This 2-part name is also the species name. The first part is the Genus which is capitalized, and the second, which is the species, part of the scientific name is never capitalized. • Scientific names are used because the same plant or animal in different places may have different common names. ...
... name. This 2-part name is also the species name. The first part is the Genus which is capitalized, and the second, which is the species, part of the scientific name is never capitalized. • Scientific names are used because the same plant or animal in different places may have different common names. ...
Laboratory 4: Cells Structure and Function
... enormously in size, shape, and function. Some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovably fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells exchange materials with their immediate environment and therefore have a plasma membrane that controls which substances are ...
... enormously in size, shape, and function. Some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovably fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells exchange materials with their immediate environment and therefore have a plasma membrane that controls which substances are ...
The Lymphatic System A. 1.
... D. The Lymphatic System and Homeostasis 1. The lymphatic system helps maintain homeostasis by regulating buildup around cells. ...
... D. The Lymphatic System and Homeostasis 1. The lymphatic system helps maintain homeostasis by regulating buildup around cells. ...
Cells - St. Ambrose School
... They are organized structures that help living things carry on the activities of life, such as digestion, movement, growth and reproduction ...
... They are organized structures that help living things carry on the activities of life, such as digestion, movement, growth and reproduction ...
Cells & Systems Review - St. James
... • Can go “uphill” • Often uses CARRIER PROTEINS” – special gate like structures • SMALL or LARGE molecules ...
... • Can go “uphill” • Often uses CARRIER PROTEINS” – special gate like structures • SMALL or LARGE molecules ...
The Tiny Living World Around Us
... What your “blood type” means • Antibodies mark pathogens once they are discovered in the body so the immune system can find and destroy them • We are born with or without certain sets of antibodies (A and B) • If you have type O, you have neither A or B antibodies • The plus or minus means you have ...
... What your “blood type” means • Antibodies mark pathogens once they are discovered in the body so the immune system can find and destroy them • We are born with or without certain sets of antibodies (A and B) • If you have type O, you have neither A or B antibodies • The plus or minus means you have ...
Document
... • Mice lacking a copy of an important metabolism gene live to the human equivalent of a century, according to new research on induced longevity • The gene encodes a protein called insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) • Mice which had been genetically changed to lack one copy of this gene live on avera ...
... • Mice lacking a copy of an important metabolism gene live to the human equivalent of a century, according to new research on induced longevity • The gene encodes a protein called insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) • Mice which had been genetically changed to lack one copy of this gene live on avera ...
File - The Stem Cell Controversy
... 7. After two weeks, cells organize into 3 layers. Please describe what these layers will develop into: Cell Layers ...
... 7. After two weeks, cells organize into 3 layers. Please describe what these layers will develop into: Cell Layers ...
Cells and Basketball
... When you shoot a basketball many parts of your body work together to help you make the shot! These different parts are made up of different tissues and cells. Each type of cell is specialized to perform its job in shooting a basketball. Cells can be specialized in their shape and the organelles that ...
... When you shoot a basketball many parts of your body work together to help you make the shot! These different parts are made up of different tissues and cells. Each type of cell is specialized to perform its job in shooting a basketball. Cells can be specialized in their shape and the organelles that ...
Key Idea #9 - Mona Shores Blogs
... small cluster of cells that then differentiate by appearance and function to form the basic tissues, organs, and organ systems of multicellular organisms. ...
... small cluster of cells that then differentiate by appearance and function to form the basic tissues, organs, and organ systems of multicellular organisms. ...
Multicellular Organisms National 5 Biology Overview Multicellular
... cerebellum and medulla. Neurons are of three types, sensory, relay and motor. Receptors detect sensory input/stimuli. Electrical impulses carry messages along neurons. A synapse occurs between neurons. Chemicals transfer these messages across synapses. ii. Structure and function of reflex arc. b. Ho ...
... cerebellum and medulla. Neurons are of three types, sensory, relay and motor. Receptors detect sensory input/stimuli. Electrical impulses carry messages along neurons. A synapse occurs between neurons. Chemicals transfer these messages across synapses. ii. Structure and function of reflex arc. b. Ho ...
Adult neural stem cells, which are commonly thought of as
... Broad Center of Regeneration Medicine and Stem Cell Research. “It may be unwelcome news for those who thought of adult neural stem cells as having a wide potential for neural repair. Instead, it looks as if that potential is narrowed down very early during embryonic development. It’s almost as if th ...
... Broad Center of Regeneration Medicine and Stem Cell Research. “It may be unwelcome news for those who thought of adult neural stem cells as having a wide potential for neural repair. Instead, it looks as if that potential is narrowed down very early during embryonic development. It’s almost as if th ...
Epithelial Tissues
... Simple columnar- single layer of elongated cells, nucleus is located near bottom of cell Contains microvilli- helps with absorption Contains goblet cells- secretes mucus Found: uterus, digestive tract ...
... Simple columnar- single layer of elongated cells, nucleus is located near bottom of cell Contains microvilli- helps with absorption Contains goblet cells- secretes mucus Found: uterus, digestive tract ...
April 22, 2009
... Will derived cells be histocompatible with each individual? ✤ short term: immune suppression or tolerance induction ✤ solution: ✤ therapeutic cloning: isolate somatic nucleus from patient and grow in oocyte. embryo is genetically identical to patient ✤ stem cell line modified by homologous recombina ...
... Will derived cells be histocompatible with each individual? ✤ short term: immune suppression or tolerance induction ✤ solution: ✤ therapeutic cloning: isolate somatic nucleus from patient and grow in oocyte. embryo is genetically identical to patient ✤ stem cell line modified by homologous recombina ...
Immortality, Of a Sort, Beckons To Biologists
... differentiation, cycling indefinitely from embryonic stem cell to embryonic germ cell, to oocyte or sperm, to fertilized egg and embryonic stem cell again. At each cycle the cells spin off a new body as the temporary vehicle to carry them forward on their unending journey. Geron's second amazing adv ...
... differentiation, cycling indefinitely from embryonic stem cell to embryonic germ cell, to oocyte or sperm, to fertilized egg and embryonic stem cell again. At each cycle the cells spin off a new body as the temporary vehicle to carry them forward on their unending journey. Geron's second amazing adv ...
PP text version
... IGF for skeletal system) receptors for growth factors are present or active on some cells and not on others. e.g. Speeman & Mangold’s organizer ...
... IGF for skeletal system) receptors for growth factors are present or active on some cells and not on others. e.g. Speeman & Mangold’s organizer ...
Solutions - jfindlay.ca
... 25.Explain how each plant tissue has a similar function to the organ or organ system in the human body. a) Dermal tissue and human skin cover the outside of the organism and protect it b) Vascular tissue and the circulatory system transport nutrients and other things around the organism c) Groun ...
... 25.Explain how each plant tissue has a similar function to the organ or organ system in the human body. a) Dermal tissue and human skin cover the outside of the organism and protect it b) Vascular tissue and the circulatory system transport nutrients and other things around the organism c) Groun ...
How does the food you eat provide energy to cells in
... Imagine von are a microSCopiC, unicellular organism. lour whole body is one cell. This one cell must carry out all the functions needed to keep you alive. It must be able to move, obtain food, reproduce, and respond to the environment. "There are many living organisms that consist of only one cell. ...
... Imagine von are a microSCopiC, unicellular organism. lour whole body is one cell. This one cell must carry out all the functions needed to keep you alive. It must be able to move, obtain food, reproduce, and respond to the environment. "There are many living organisms that consist of only one cell. ...
6.2 Respiration gas exchange - HIS-IGSci-Bio
... The plant makes an insecticide called nicotine Nicotine acts as an addictive drug in our body ...
... The plant makes an insecticide called nicotine Nicotine acts as an addictive drug in our body ...
Induced pluripotent stem cell
Induced pluripotent stem cells (also known as iPS cells or iPSCs) are a type of pluripotent stem cell that can be generated directly from adult cells. The iPSC technology was pioneered by Shinya Yamanaka’s lab in Kyoto, Japan, who showed in 2006 that the introduction of four specific genes encoding transcription factors could convert adult cells into pluripotent stem cells. He was awarded the 2012 Nobel Prize along with Sir John Gurdon ""for the discovery that mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent."" Pluripotent stem cells hold great promise in the field of regenerative medicine. Because they can propagate indefinitely, as well as give rise to every other cell type in the body (such as neurons, heart, pancreatic, and liver cells), they represent a single source of cells that could be used to replace those lost to damage or disease.The most well-known type of pluripotent stem cell is the embryonic stem cell. However, since the generation of embryonic stem cells involves destruction (or at least manipulation) of the pre-implantation stage embryo, there has been much controversy surrounding their use. Further, because embryonic stem cells can only be derived from embryos, it has so far not been feasible to create patient-matched embryonic stem cell lines.Since iPSCs can be derived directly from adult tissues, they not only bypass the need for embryos, but can be made in a patient-matched manner, which means that each individual could have their own pluripotent stem cell line. These unlimited supplies of autologous cells could be used to generate transplants without the risk of immune rejection. While the iPSC technology has not yet advanced to a stage where therapeutic transplants have been deemed safe, iPSCs are readily being used in personalized drug discovery efforts and understanding the patient-specific basis of disease.Depending on the methods used, reprogramming of adult cells to obtain iPSCs may pose significant risks that could limit their use in humans. For example, if viruses are used to genomically alter the cells, the expression of oncogenes (cancer-causing genes) may potentially be triggered. In February 2008, scientists announced the discovery of a technique that could remove oncogenes after the induction of pluripotency, thereby increasing the potential use of iPS cells in human diseases. In April 2009, it was demonstrated that generation of iPS cells is possible without any genetic alteration of the adult cell: a repeated treatment of the cells with certain proteins channeled into the cells via poly-arginine anchors was sufficient to induce pluripotency. The acronym given for those iPSCs is piPSCs (protein-induced pluripotent stem cells).