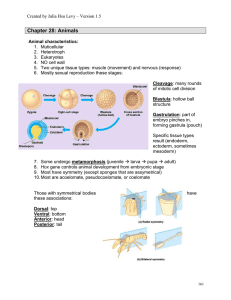
Cell Theory Cell Structure, Cell Transport and Mitosis
... It is the fastest mode of transport. Fig 3-9, Na-K pump It always consumes ATP directly or indirectly. It always needs one or more transport proteins. For example absorption of minerals by plant roots, absorption of nutrients when their concentration is already higher inside the cells. Vesicular Tra ...
... It is the fastest mode of transport. Fig 3-9, Na-K pump It always consumes ATP directly or indirectly. It always needs one or more transport proteins. For example absorption of minerals by plant roots, absorption of nutrients when their concentration is already higher inside the cells. Vesicular Tra ...
CHAPTER 3: CELLS
... Movement Into and Out of the Cell (Membrane Transport) The passage of a substance through the cell membrane may be physical (passive, requires no energy expenditure) or physiologic (active process, requires energy expenditure). In physical (passive) transport processes, substances move from where th ...
... Movement Into and Out of the Cell (Membrane Transport) The passage of a substance through the cell membrane may be physical (passive, requires no energy expenditure) or physiologic (active process, requires energy expenditure). In physical (passive) transport processes, substances move from where th ...
Passive Transport WS
... 1. ________ The swelling and bursting of animal cells when water enters is called? 2. ________ A cell bursts happens when the cell is placed in this type of tonic solution? 3. ________ The shrinking of ...
... 1. ________ The swelling and bursting of animal cells when water enters is called? 2. ________ A cell bursts happens when the cell is placed in this type of tonic solution? 3. ________ The shrinking of ...
Diffusion Quiz - cloudfront.net
... ATP is most likely being used for a) substance A to enter the cell b) substance B to enter the cell c) both substances to enter the cell d) neither substance to enter the cell _____ 10. When most proteins, fats, and carbohydrates are digested ...
... ATP is most likely being used for a) substance A to enter the cell b) substance B to enter the cell c) both substances to enter the cell d) neither substance to enter the cell _____ 10. When most proteins, fats, and carbohydrates are digested ...
Tissue Types in the human body
... Always has one free (apical) surface open to outside the body or inside (cavity) an internal organ. Always had one fixed (basal) section attached to underlying connective tissue. ...
... Always has one free (apical) surface open to outside the body or inside (cavity) an internal organ. Always had one fixed (basal) section attached to underlying connective tissue. ...
Section 8 - DigitalWebb.com
... 5. Oxygenated blood back to heart into left atrium, left ventricle (repeat #1). Arteries away from heart Veins back to heart Blood pressure: hydrostatic force that blood exerts against a vessel wall Capillary exchange: exchange of materials between blood through capillary walls and interstitial flui ...
... 5. Oxygenated blood back to heart into left atrium, left ventricle (repeat #1). Arteries away from heart Veins back to heart Blood pressure: hydrostatic force that blood exerts against a vessel wall Capillary exchange: exchange of materials between blood through capillary walls and interstitial flui ...
The Visual System: Retinal Anatomy and Physiology
... Duplex theory of vision There are two types of photoreceptor, rods and cones, in the retina. The rods contain the visual pigment rhodopsin sensitive to blue-green light. Rods are highly sensitive photoreceptors exclusively active during scotopic vision. They are completely inactivated during photop ...
... Duplex theory of vision There are two types of photoreceptor, rods and cones, in the retina. The rods contain the visual pigment rhodopsin sensitive to blue-green light. Rods are highly sensitive photoreceptors exclusively active during scotopic vision. They are completely inactivated during photop ...
Arthropods - About Miss Brougham
... ones can only live in water because it helps support the weight Heavy Limits movement They have to molt to grow – leaves them vulnerable ...
... ones can only live in water because it helps support the weight Heavy Limits movement They have to molt to grow – leaves them vulnerable ...
Chapter 01 Study Guide
... organs, tissues, and systems. The four primary tissues of the body — muscle, nerve, epithelium, and connective tissues — are all present in skin, an example of an organ. As you read the descriptions of how these tissues function independently, remember that they also perform in concert with other ti ...
... organs, tissues, and systems. The four primary tissues of the body — muscle, nerve, epithelium, and connective tissues — are all present in skin, an example of an organ. As you read the descriptions of how these tissues function independently, remember that they also perform in concert with other ti ...
Lectures 6 & 7: Powerpoint
... gradients (as for simple diffusion), but… Transport proteins assist these molecules in crossing the membrane No net energy expenditure! (This is a type of diffusion…) ...
... gradients (as for simple diffusion), but… Transport proteins assist these molecules in crossing the membrane No net energy expenditure! (This is a type of diffusion…) ...
Mechanosensitive ion channel studies by atomic force microscopy
... 1211 Geneva 4, Switzerland tel: +41 22 379 3134 email: [email protected] ...
... 1211 Geneva 4, Switzerland tel: +41 22 379 3134 email: [email protected] ...
Solar Technology Innovation Cycles
... Thin film PV on rolled substrate lends itself to large cell sizes, however today there are manufacturing limitations ...
... Thin film PV on rolled substrate lends itself to large cell sizes, however today there are manufacturing limitations ...
Circulatory System * General Aspects
... later becomes incorporated into capillary bed of liver. Some anatomical bypass of liver capillary network in birds and reptiles, but not in mammals. – Associated with nutritional role of chorioallantoic membrane of the placenta in mammals. Functions solely in respiration in birds and reptiles. ...
... later becomes incorporated into capillary bed of liver. Some anatomical bypass of liver capillary network in birds and reptiles, but not in mammals. – Associated with nutritional role of chorioallantoic membrane of the placenta in mammals. Functions solely in respiration in birds and reptiles. ...
A1. All of the following are characteristics of ventilation EXCEPT: A
... pO2 of expired air is greater than alveolar air pO2 of interstitial fluids is less than pO2 in blood leaving the lungs pO2 in the blood is greater than alveolar air pCO2 of blood returning from the lungs equals that found in the alveoli C&D ...
... pO2 of expired air is greater than alveolar air pO2 of interstitial fluids is less than pO2 in blood leaving the lungs pO2 in the blood is greater than alveolar air pCO2 of blood returning from the lungs equals that found in the alveoli C&D ...
Biology Mid-term Review Notes
... Put a cell in salt water and water is drawn out of the cell into the surrounding medium. This happened when we put concentrated salt solution on our onion cells. Cells adapt to the conditions they exist in. For example, FROG egg cells are adapted to exist in fresh water environments without taking u ...
... Put a cell in salt water and water is drawn out of the cell into the surrounding medium. This happened when we put concentrated salt solution on our onion cells. Cells adapt to the conditions they exist in. For example, FROG egg cells are adapted to exist in fresh water environments without taking u ...
Ability
... 11. The city’s first commercial blood bank opened last week with blood samples from one hundred men stored in refrigerated units. with: imprecise; stored in refrigerated units: unclear modifier The city’s first commercial blood bank opened last week. One hundred samples were collected from men were ...
... 11. The city’s first commercial blood bank opened last week with blood samples from one hundred men stored in refrigerated units. with: imprecise; stored in refrigerated units: unclear modifier The city’s first commercial blood bank opened last week. One hundred samples were collected from men were ...
Control of the Internal Environment
... while regulating water and ion concentrations in body fluids Kidneys filter blood to extract filtrate which contains H2O, urea, glucose, AA’s, ions, and vitamins Filtrate is processed so valuable solutes not lost in urine ...
... while regulating water and ion concentrations in body fluids Kidneys filter blood to extract filtrate which contains H2O, urea, glucose, AA’s, ions, and vitamins Filtrate is processed so valuable solutes not lost in urine ...
Text S1 Combined screening approach identifies functional
... After fusion of viral and cellular membranes, incoming viral capsids are known to be transported to nuclear pores via the microtubule organizing centre (MTOC). Transport is mediated by the capsid proteins VP26 (UL35) and UL46 binding to the dynein light chains DYNLT1 (Tctex1) and DYNLT3 (rp3) [1,2], ...
... After fusion of viral and cellular membranes, incoming viral capsids are known to be transported to nuclear pores via the microtubule organizing centre (MTOC). Transport is mediated by the capsid proteins VP26 (UL35) and UL46 binding to the dynein light chains DYNLT1 (Tctex1) and DYNLT3 (rp3) [1,2], ...
Cell Organelle Research Worksheet
... Cell Organelle Research Worksheet Please use the websites on my SCIENCE WIKISPACES website to get the information you need to complete the following organelle functions. Please tell me where the organelle is found, what it does, and an analogy used from the website. ...
... Cell Organelle Research Worksheet Please use the websites on my SCIENCE WIKISPACES website to get the information you need to complete the following organelle functions. Please tell me where the organelle is found, what it does, and an analogy used from the website. ...
A brief paragraph for PSC Partners members and for the lay public
... Lay Summary of Research Progress: Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a multifactorial disease with genetic, microbial, and environmental components. Emerging evidence suggests that cholangiocytes, i.e. the cells that line the bile ducts in the liver, may not only be affected in PSC, but may act ...
... Lay Summary of Research Progress: Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a multifactorial disease with genetic, microbial, and environmental components. Emerging evidence suggests that cholangiocytes, i.e. the cells that line the bile ducts in the liver, may not only be affected in PSC, but may act ...
PowerPoint
... Examples of models could include simulations and mathematical models.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the specific chemical steps of photosynthesis and respiration.] WHST.9‐12.7 Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self genera ...
... Examples of models could include simulations and mathematical models.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the specific chemical steps of photosynthesis and respiration.] WHST.9‐12.7 Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self genera ...
Effect of stimulants health and life.
... Lungs and Bronchi Moving down to your chest, smoke passes through the bronchi, or breathing tubes. Hydrogen cyanide and other chemicals in the smoke attack the lining of the bronchi, inflaming them and causing that chronic smoker's cough. Because the bronchi are weakened, you're more likely to get b ...
... Lungs and Bronchi Moving down to your chest, smoke passes through the bronchi, or breathing tubes. Hydrogen cyanide and other chemicals in the smoke attack the lining of the bronchi, inflaming them and causing that chronic smoker's cough. Because the bronchi are weakened, you're more likely to get b ...