april 21, 2016 - DeSales University
... definitive prognosis or successful treatment. MARY-X is an IBC model that, in vitro, forms tight, compact aggregates of cells called spheroidsMARY-X. The spheroidsMARY-X mimic in vivo tumor emboli as they contain proliferative cells on the periphery and dormant/hypoxic cells in the center. This make ...
... definitive prognosis or successful treatment. MARY-X is an IBC model that, in vitro, forms tight, compact aggregates of cells called spheroidsMARY-X. The spheroidsMARY-X mimic in vivo tumor emboli as they contain proliferative cells on the periphery and dormant/hypoxic cells in the center. This make ...
WELCOME
... Process of disposing urine from urinary bladdder through the urethra to outside the body The process of urination is usually under voluntary control ...
... Process of disposing urine from urinary bladdder through the urethra to outside the body The process of urination is usually under voluntary control ...
Chapter 25 - Teacher Pages
... Heat exchange with the environment may occur by – conduction—the transfer of heat by direct contact, – convection—the transfer of heat by movement of air or liquid past a surface, – radiation—the emission of electromagnetic waves, or – evaporation—the loss of heat from the surface of a liquid that ...
... Heat exchange with the environment may occur by – conduction—the transfer of heat by direct contact, – convection—the transfer of heat by movement of air or liquid past a surface, – radiation—the emission of electromagnetic waves, or – evaporation—the loss of heat from the surface of a liquid that ...
3.4 Circulatroy System
... A. The heart is a strong muscular organ that constantly pumps blood throughout the body. a. It is a the size of a fist b. It is located in the corner of the chest behind the sternum bone. c. It has a protective sac of tissue called the pericardium surrounding it. B. The heart has two sides separated ...
... A. The heart is a strong muscular organ that constantly pumps blood throughout the body. a. It is a the size of a fist b. It is located in the corner of the chest behind the sternum bone. c. It has a protective sac of tissue called the pericardium surrounding it. B. The heart has two sides separated ...
Homeostasis
... Heat exchange with the environment may occur by – conduction—the transfer of heat by direct contact, – convection—the transfer of heat by movement of air or liquid past a surface, – radiation—the emission of electromagnetic waves, or – evaporation—the loss of heat from the surface of a liquid that ...
... Heat exchange with the environment may occur by – conduction—the transfer of heat by direct contact, – convection—the transfer of heat by movement of air or liquid past a surface, – radiation—the emission of electromagnetic waves, or – evaporation—the loss of heat from the surface of a liquid that ...
Evaluation of Wet Mount and KOH Preparations
... appearance of the cell and can mimic bacterial adhesion. 3. To determine the percentage of clue cells in your field: a. Count the number of clue cells and divide that number by the total number of distinguishable epithelial cells. ...
... appearance of the cell and can mimic bacterial adhesion. 3. To determine the percentage of clue cells in your field: a. Count the number of clue cells and divide that number by the total number of distinguishable epithelial cells. ...
chapt05_lecture
... – Allow the passage of ions – Gated channels – open or close in response to stimulus (chemical or electrical) – 3 conditions determine direction • Relative concentration on either side of membrane • Voltage differences across membrane • Gated channels – channel open or closed ...
... – Allow the passage of ions – Gated channels – open or close in response to stimulus (chemical or electrical) – 3 conditions determine direction • Relative concentration on either side of membrane • Voltage differences across membrane • Gated channels – channel open or closed ...
Body Cavity and Joint Effusions: Why They Form and How to
... but hypoproteinemia alone often will not cause effusion unless it developed rapidly ◦ Usually multifactorial (e.g. hypoproteinemia and liver fibrosis resulting in portal hypertension) ...
... but hypoproteinemia alone often will not cause effusion unless it developed rapidly ◦ Usually multifactorial (e.g. hypoproteinemia and liver fibrosis resulting in portal hypertension) ...
Effective Indicator of Preterm Labor
... • Would ideally be a standard procedure for doctors to do • Would allow for the existence of a baseline to compare levels to ...
... • Would ideally be a standard procedure for doctors to do • Would allow for the existence of a baseline to compare levels to ...
KS4 What is Blood
... body, they are travelling through tiny capillaries similar to those found in the alveolus. capillary ...
... body, they are travelling through tiny capillaries similar to those found in the alveolus. capillary ...
Respiratory System 9.1-9.2
... oxygen dislodges the H+ from the hemoglobin sites • Free hydrogen and bicarbonate ions combine to form CO2 and H2O • The CO is eliminated during ___________ ...
... oxygen dislodges the H+ from the hemoglobin sites • Free hydrogen and bicarbonate ions combine to form CO2 and H2O • The CO is eliminated during ___________ ...
DNA aptamers as molecular probes for colorectal cancer study
... The ability of a probe to selectively differentiate tumor cells from the adjoining normal cells is important for tumor detection as well as targeted therapy. It is therefore necessary to determine if the individual aptamers generated by cell-SELEX, which commonly bind to unknown targets, also bind t ...
... The ability of a probe to selectively differentiate tumor cells from the adjoining normal cells is important for tumor detection as well as targeted therapy. It is therefore necessary to determine if the individual aptamers generated by cell-SELEX, which commonly bind to unknown targets, also bind t ...
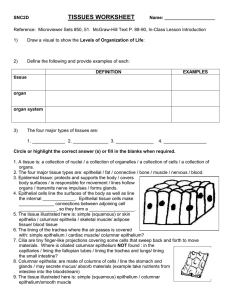
SNC2D TISSUES WORKSHEET Name: Reference: Microviewer
... 12. Which of the following are NOT connective tissues: blood /fingernails / ligaments / bone / saliva / adipose tissue / cartilage? 13. Muscle tissues are designed to change their shape. A muscle cell is ___________ inches long. They are in one of two states, either they contract and are __________ ...
... 12. Which of the following are NOT connective tissues: blood /fingernails / ligaments / bone / saliva / adipose tissue / cartilage? 13. Muscle tissues are designed to change their shape. A muscle cell is ___________ inches long. They are in one of two states, either they contract and are __________ ...
CHAPTER 7 - HCC Learning Web
... • Diffusion is the tendency for molecules to spread out evenly into the available space • Although each molecule moves randomly, diffusion of a population of molecules may be directional • At dynamic equilibrium, as many molecules cross the membrane in one direction as in the other ...
... • Diffusion is the tendency for molecules to spread out evenly into the available space • Although each molecule moves randomly, diffusion of a population of molecules may be directional • At dynamic equilibrium, as many molecules cross the membrane in one direction as in the other ...
SOMATIC CELL FUSION
... or ‘hybrid’ protoplasts, particularly those resulting from fusion between one protoplast of each of the two fusion partners, are of interest. • However, they form only a small proportion of the population (usually 0.5-10%). Therefore, an effective strategy has to be employed for their identification ...
... or ‘hybrid’ protoplasts, particularly those resulting from fusion between one protoplast of each of the two fusion partners, are of interest. • However, they form only a small proportion of the population (usually 0.5-10%). Therefore, an effective strategy has to be employed for their identification ...
Chapter 31
... At the AV node, the impulses are conducted through the bundle of His and then travel to the Purkinje fibers that make the ventricles ...
... At the AV node, the impulses are conducted through the bundle of His and then travel to the Purkinje fibers that make the ventricles ...
What are Stem Cells? How can they be used in medicine?
... patient themselves or a donor) and transplanted into the patient to replace faulty blood cells. This is a very successful procedure to treat diseases such as leukaemia. CANCER: A. A disease characterised as unregulated cell growth in the body. Stem cell therapies are a method used to overcome this d ...
... patient themselves or a donor) and transplanted into the patient to replace faulty blood cells. This is a very successful procedure to treat diseases such as leukaemia. CANCER: A. A disease characterised as unregulated cell growth in the body. Stem cell therapies are a method used to overcome this d ...
Primary mediators
... (receptor activator of nuclear factor κβ) and M-CSF (Macrophage colony-stimulating factor). These membrane bound proteins are produced by neighbouring stromal cells and osteoblasts; thus requiring direct contact between these cells and osteoclast precursors. • M-CSF acts through its receptor on the ...
... (receptor activator of nuclear factor κβ) and M-CSF (Macrophage colony-stimulating factor). These membrane bound proteins are produced by neighbouring stromal cells and osteoblasts; thus requiring direct contact between these cells and osteoclast precursors. • M-CSF acts through its receptor on the ...
Activation of murine B lymphocytes by anti
... B cells in culture respond to anti-immunoglobulin reagents (anti-Ig) by blast transformation and DNA synthesis (1, 2). Anti-Ig activates by binding to and crosslinking cell surface Ig (3-5). Because surface Ig has been shown to function as the receptor for antigen, accounting for the specificity of ...
... B cells in culture respond to anti-immunoglobulin reagents (anti-Ig) by blast transformation and DNA synthesis (1, 2). Anti-Ig activates by binding to and crosslinking cell surface Ig (3-5). Because surface Ig has been shown to function as the receptor for antigen, accounting for the specificity of ...
Nanomechanics of superbugs and superdrugs
... and is key to their survival. The cell wall is a crosslinked peptidoglycan matrix that protects bacteria from harsh external forces and high internal osmotic pressures, and, importantly, it is not found in humans, making it an ideal drug target. However, there remains much to be learnt about its str ...
... and is key to their survival. The cell wall is a crosslinked peptidoglycan matrix that protects bacteria from harsh external forces and high internal osmotic pressures, and, importantly, it is not found in humans, making it an ideal drug target. However, there remains much to be learnt about its str ...
B2-Topic-3-notes - Greenacre Academy Trust
... Growth in animals also involves cell division…but unlike plants, animals stop growing when they become adults In an animal, cells that can differentiate to form many different types of specialised cells are called stem cells: o Embryonic stem cells can differentiate and form almost any type of cell ...
... Growth in animals also involves cell division…but unlike plants, animals stop growing when they become adults In an animal, cells that can differentiate to form many different types of specialised cells are called stem cells: o Embryonic stem cells can differentiate and form almost any type of cell ...
Neuroblastoma (NB) is the most common extra cranial solid tumor in
... DA and NE each have a variety of regulatory roles in the body. DA increases heart rate and blood pressure, it is also involved in memory, movement and mood. NE is the neurotransmitter responsible for the fight or flight response which increases heart rate, blood flow and glucose release in response ...
... DA and NE each have a variety of regulatory roles in the body. DA increases heart rate and blood pressure, it is also involved in memory, movement and mood. NE is the neurotransmitter responsible for the fight or flight response which increases heart rate, blood flow and glucose release in response ...
Cooperation Based Energy Efficiency Optimization Using Game
... Therefore, minimizing the power consumption of wireless platforms becomes a great challenge, for the entire Information and Communication technologies (ICTs), at all system levels. To deal with these two problems listed above, several researches have been launched. In [2] many examples were proposed ...
... Therefore, minimizing the power consumption of wireless platforms becomes a great challenge, for the entire Information and Communication technologies (ICTs), at all system levels. To deal with these two problems listed above, several researches have been launched. In [2] many examples were proposed ...