Unit 2 - Notes
... If something does not have these characteristics (cells, biogenesis growth and development, metabolism, water requirements, organic compound production, reproduction with inheritance and adaptations), then it is not considered a living thing. A fox would be a living thing whereas a rock would not (i ...
... If something does not have these characteristics (cells, biogenesis growth and development, metabolism, water requirements, organic compound production, reproduction with inheritance and adaptations), then it is not considered a living thing. A fox would be a living thing whereas a rock would not (i ...
Circulation and Respiration Chapter 22
... • Contraction decreases thoracic cavity volume more than passive exhalation ...
... • Contraction decreases thoracic cavity volume more than passive exhalation ...
Chapter 16: Cardiovascular System
... 14. List two facts about each of the following: artery—carry blood away from heart; largest blood vessel (aorta); measures the highest blood pressure; thickest blood vessels; contain a layer of smooth muscle vein—carry blood to the heart; contains valves; contain a layer of smooth muscle; example = ...
... 14. List two facts about each of the following: artery—carry blood away from heart; largest blood vessel (aorta); measures the highest blood pressure; thickest blood vessels; contain a layer of smooth muscle vein—carry blood to the heart; contains valves; contain a layer of smooth muscle; example = ...
6 Kingdoms
... functions of archaebacteria, eubacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals, including humans. Main concepts include: • how structures and functions vary between and within the kingdoms; • comparisons of metabolic activities; • analyses of responses to the environment; • maintenance of homeostasis ...
... functions of archaebacteria, eubacteria, protists, fungi, plants, and animals, including humans. Main concepts include: • how structures and functions vary between and within the kingdoms; • comparisons of metabolic activities; • analyses of responses to the environment; • maintenance of homeostasis ...
Topic: Disease: How does our body come under attack?
... WBCs to form and defeat the pathogen. The second response to the same pathogen triggers a quicker and stronger response. ** After the first response, the immune system “remembers” specific pathogens by leaving behind WBCs that protect the body for years (memory cells). ...
... WBCs to form and defeat the pathogen. The second response to the same pathogen triggers a quicker and stronger response. ** After the first response, the immune system “remembers” specific pathogens by leaving behind WBCs that protect the body for years (memory cells). ...
Animations - Growth in Plants - teachers notes
... Both organisms need to grow, to reach maturity so that they can reproduce. They both depend on an external source of raw materials to grow, and much growth is concerned with increasing their access to these raw materials. Their growth involves an increase in the number of cells, rather than the si ...
... Both organisms need to grow, to reach maturity so that they can reproduce. They both depend on an external source of raw materials to grow, and much growth is concerned with increasing their access to these raw materials. Their growth involves an increase in the number of cells, rather than the si ...
Chapter 10
... Unipolar—Unipolar neurons have a single nerve fiber extending from the cell body. From there it branches in two directions; one branch extends into a peripheral body part and serves as a dendrite. The other extends into the CNS and acts like an axon. Multipolar—Multipolar neurons have one axon and ...
... Unipolar—Unipolar neurons have a single nerve fiber extending from the cell body. From there it branches in two directions; one branch extends into a peripheral body part and serves as a dendrite. The other extends into the CNS and acts like an axon. Multipolar—Multipolar neurons have one axon and ...
Cell–Cell Interactions in Bacterial Populations
... that a bacterial population is a community of interacting cells with possible differentiation in this supracellular “organism” succeeds the old view on bacterial culture as a homogeneous soup in which individual cells live and proliferate independently of each other [1]. So, bacterial populations ca ...
... that a bacterial population is a community of interacting cells with possible differentiation in this supracellular “organism” succeeds the old view on bacterial culture as a homogeneous soup in which individual cells live and proliferate independently of each other [1]. So, bacterial populations ca ...
Chapter 10
... Unipolar—Unipolar neurons have a single nerve fiber extending from the cell body. From there it branches in two directions; one branch extends into a peripheral body part and serves as a dendrite. The other extends into the CNS and acts like an axon. Multipolar—Multipolar neurons have one axon and m ...
... Unipolar—Unipolar neurons have a single nerve fiber extending from the cell body. From there it branches in two directions; one branch extends into a peripheral body part and serves as a dendrite. The other extends into the CNS and acts like an axon. Multipolar—Multipolar neurons have one axon and m ...
fully automated madin-darby canine kidney (mdck)
... Permeability assays elucidate the structure-activity relationships in the hit-to-lead stage, rank order compounds for in vivo pharmacokinetics studies and predict the potential for oral absorption. Reliability, accuracy and precision are critical for these assays, particularly when they are used in ...
... Permeability assays elucidate the structure-activity relationships in the hit-to-lead stage, rank order compounds for in vivo pharmacokinetics studies and predict the potential for oral absorption. Reliability, accuracy and precision are critical for these assays, particularly when they are used in ...
Gene Section DDIT4 (DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... REDD1 is developmentally regulated. Redd1 expression has a similar pattern as p63, being expressed at early stages in the apical ectodermal ridge and later on, at ectoderm-derived tissues (Ellisen et al., 2002). Interestingly, p63-/- embryos have lower Redd1 levels suggesting that p63 is an importan ...
... REDD1 is developmentally regulated. Redd1 expression has a similar pattern as p63, being expressed at early stages in the apical ectodermal ridge and later on, at ectoderm-derived tissues (Ellisen et al., 2002). Interestingly, p63-/- embryos have lower Redd1 levels suggesting that p63 is an importan ...
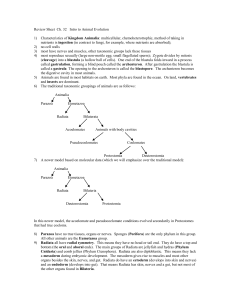
lecture notes ch32 Intro Animal Evolution
... individual embyonic cells is not set; i.e. a split embryo may develop into twins) 16) The coelom (“sea-lum”) is the body cavity, a fluid filled space separating the gut from the outer body wall. This is where our viscera (heart, lungs, kidneys), muscles, etc. are located. Some bilateria, like the fl ...
... individual embyonic cells is not set; i.e. a split embryo may develop into twins) 16) The coelom (“sea-lum”) is the body cavity, a fluid filled space separating the gut from the outer body wall. This is where our viscera (heart, lungs, kidneys), muscles, etc. are located. Some bilateria, like the fl ...
Eukaryotic cells
... – Only eukaryotic cells have organelles, membrane-bound structures that perform specific functions. – The most important organelle is the nucleus, which houses most of a eukaryotic cell’s DNA. ...
... – Only eukaryotic cells have organelles, membrane-bound structures that perform specific functions. – The most important organelle is the nucleus, which houses most of a eukaryotic cell’s DNA. ...
§ 58-10-90
... to other income, gains or losses of the protected cell company, including income, gains or losses of other protected cells. Amounts attributed to any protected cell and accumulations on the attributed amounts may be invested and reinvested without regard to any requirements or limitations of this Ch ...
... to other income, gains or losses of the protected cell company, including income, gains or losses of other protected cells. Amounts attributed to any protected cell and accumulations on the attributed amounts may be invested and reinvested without regard to any requirements or limitations of this Ch ...
Circulatory System
... o Single layer of endothelial cells (8 µm). o Interconnected networks called capillary beds. o Contact tissue cells and directly serve cellular needs. Capillary Anatomy ...
... o Single layer of endothelial cells (8 µm). o Interconnected networks called capillary beds. o Contact tissue cells and directly serve cellular needs. Capillary Anatomy ...
Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetases (AARS) Inventor: Overview Invention
... as a pro-angiogenic chemokine-like protein. In cell models, TARS efficiently stimulates new blood vessel formation. The use of TARS and TARS activators is different from existing technologies, as this pathway was unknown before our discovery. Secondly, A class of compounds (borrelidin and its deriva ...
... as a pro-angiogenic chemokine-like protein. In cell models, TARS efficiently stimulates new blood vessel formation. The use of TARS and TARS activators is different from existing technologies, as this pathway was unknown before our discovery. Secondly, A class of compounds (borrelidin and its deriva ...
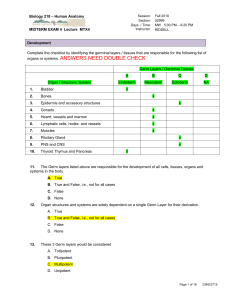
biol 218 mtx 4 qa 200 101130.3 draft
... At 10 weeks' gestation, the intestines have begun moving back into the coelomic cavity, after they initially pushed outward into the umbilical stalk. A. True B. True and False, i.e., not for all cases C. False D. None ...
... At 10 weeks' gestation, the intestines have begun moving back into the coelomic cavity, after they initially pushed outward into the umbilical stalk. A. True B. True and False, i.e., not for all cases C. False D. None ...
ExamView Pro - Human Body Review 5.tst
... 45. The type of neurons known as ____________________ neurons pick up stimuli from the external or internal environment and convert those stimuli to nerve impulses. 46. The part of the brain that controls balance is the ____________________. 47. In order for a nerve impulse to pass from an axon tip ...
... 45. The type of neurons known as ____________________ neurons pick up stimuli from the external or internal environment and convert those stimuli to nerve impulses. 46. The part of the brain that controls balance is the ____________________. 47. In order for a nerve impulse to pass from an axon tip ...
Hypertrophy
... and obviously both result in an enlarged (hypertrophic) organ. Thus, the massive physiologic enlargement of the uterus during pregnancy occurs as a consequence of estrogen-stimulated smooth muscle hypertrophy and smooth muscle hyperplasia . In contrast, the striated muscle cells in both the skeletal ...
... and obviously both result in an enlarged (hypertrophic) organ. Thus, the massive physiologic enlargement of the uterus during pregnancy occurs as a consequence of estrogen-stimulated smooth muscle hypertrophy and smooth muscle hyperplasia . In contrast, the striated muscle cells in both the skeletal ...
Accepted version
... Regulation of cell proliferation and motility is essential for normal development. The Rho family of GTPases plays a critical role in the control of cell polarity and migration through effects upon the cytoskeleton, membrane trafficking and cell adhesion. We investigated a recognized developmental d ...
... Regulation of cell proliferation and motility is essential for normal development. The Rho family of GTPases plays a critical role in the control of cell polarity and migration through effects upon the cytoskeleton, membrane trafficking and cell adhesion. We investigated a recognized developmental d ...
SIXTH FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME
... (CZTS, Eg ≈ 1.5 eV) [1-2]. Despite a rapid progress achieved by different groups in a short time, many aspects are not well understood yet in terms of material properties and working mechanisms of the device. Optical and electrical modelling and simulations can be a powerful tool to overcome this ga ...
... (CZTS, Eg ≈ 1.5 eV) [1-2]. Despite a rapid progress achieved by different groups in a short time, many aspects are not well understood yet in terms of material properties and working mechanisms of the device. Optical and electrical modelling and simulations can be a powerful tool to overcome this ga ...