The Endosymbiotic relationship of Leguminosae (Fabaceae) and
... fixation starts with the formation of a nodule. A common soil bacterium, Rhizobium, invades the root and multiplies within the cortex cells. Rhizobium enters the roots of the legumes either through root hair or directly at the point of emergence of lateral roots. Curling or controlled growth and bra ...
... fixation starts with the formation of a nodule. A common soil bacterium, Rhizobium, invades the root and multiplies within the cortex cells. Rhizobium enters the roots of the legumes either through root hair or directly at the point of emergence of lateral roots. Curling or controlled growth and bra ...
Unit 2 Lecture 5
... The purpose of respiration is to supply cells of the body with O2 and to remove excess CO2. In pulmonary ventilation (breathing), gases are exchanged between the atmosphere and alveoli as a result of differences in pressure gradients. Air moves into the lungs by bulk flow when pressure inside the lu ...
... The purpose of respiration is to supply cells of the body with O2 and to remove excess CO2. In pulmonary ventilation (breathing), gases are exchanged between the atmosphere and alveoli as a result of differences in pressure gradients. Air moves into the lungs by bulk flow when pressure inside the lu ...
An efficient immunodetection method for histone modifications in
... To test the reproducibility of our method, several tissues of different plant species of economical and agronomical interest, such as Agave, chili pepper, coffee, cedar and Arabidopsis were collected and treated under the procedures summarized in Figure 1. Tissues of several plant species from both ...
... To test the reproducibility of our method, several tissues of different plant species of economical and agronomical interest, such as Agave, chili pepper, coffee, cedar and Arabidopsis were collected and treated under the procedures summarized in Figure 1. Tissues of several plant species from both ...
Introduction to Cell fate and plasticity Introduction, fate maps
... identical twins can be obtained, provided that both fragments retain Spemann’s organizer tissue. Thus a half-embryo can regenerate the missing half. In humans, identical twins are found in three out of 1000 live births, and usually arise from the spontaneous separation of the inner cell mass of the ...
... identical twins can be obtained, provided that both fragments retain Spemann’s organizer tissue. Thus a half-embryo can regenerate the missing half. In humans, identical twins are found in three out of 1000 live births, and usually arise from the spontaneous separation of the inner cell mass of the ...
Comparison of an immortalized human corneal epithelial cell line
... blindness, is a sight threatening ocular infection often requiring a specific and prompt laboratory diagnosis [1]. A variety of techniques have been employed for the rapid diagnosis of HSK [2–5]. Isolation of Herpes simplex virus1(HSV-1) in culture provides the most reliable and specific method and ...
... blindness, is a sight threatening ocular infection often requiring a specific and prompt laboratory diagnosis [1]. A variety of techniques have been employed for the rapid diagnosis of HSK [2–5]. Isolation of Herpes simplex virus1(HSV-1) in culture provides the most reliable and specific method and ...
Lab Procedure (External and Internal Anatomy)
... 9. Spleen: a flattened organ that lies across the stomach and toward the extreme left side of the pig. The spleen stores blood and is not part of the digestive system. On the underside of the spleen, locate the splenic artery. 10. At the end of the ileum, where it widens to become the large intestin ...
... 9. Spleen: a flattened organ that lies across the stomach and toward the extreme left side of the pig. The spleen stores blood and is not part of the digestive system. On the underside of the spleen, locate the splenic artery. 10. At the end of the ileum, where it widens to become the large intestin ...
Cytosolic DNA Triggers Mitochondrial Apoptosis via DNA Damage
... With respect to microbial non-CpG DNA, which has long been proposed to act as a PAMP, the situation is less clear. It has been shown that transfected non-CpG DNA or DNA viruses such as modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) strain can trigger production of IFNs via a pathway involving IFN regulatory f ...
... With respect to microbial non-CpG DNA, which has long been proposed to act as a PAMP, the situation is less clear. It has been shown that transfected non-CpG DNA or DNA viruses such as modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) strain can trigger production of IFNs via a pathway involving IFN regulatory f ...
Working paper - Complex Systems Lab
... (Theraulaz et al., 2003) and the spatial distribution of population densities in ecosystems (Solé and Bascompte, 2006). One particular scenario where living systems develop a spatial asymmetry is provided by single cells in morphogenesis. During early morphogenesis, cells often display a spatially ...
... (Theraulaz et al., 2003) and the spatial distribution of population densities in ecosystems (Solé and Bascompte, 2006). One particular scenario where living systems develop a spatial asymmetry is provided by single cells in morphogenesis. During early morphogenesis, cells often display a spatially ...
TOPIC 1. CELL CHARACTERISTICS AND DIGESTIBILITIES What
... the evidence for chemical inhibitors of digestion in plants has been available for over 30 years. Knowledge of the effects of different inhibitors on diet digestibilities are not yet well understood, however. Fraenkal (1959) called attention to the role of secondary plant compounds as defense mechan ...
... the evidence for chemical inhibitors of digestion in plants has been available for over 30 years. Knowledge of the effects of different inhibitors on diet digestibilities are not yet well understood, however. Fraenkal (1959) called attention to the role of secondary plant compounds as defense mechan ...
protists2
... produce motile (moving) cells during part of their like cycle. Also, these protists surround and engulf bacteria as food. Slime molds live as separate cells most of their lives, feeding on bacteria. When conditions get harsh, they aggregate into a multicellular slug, which migrates to a new location ...
... produce motile (moving) cells during part of their like cycle. Also, these protists surround and engulf bacteria as food. Slime molds live as separate cells most of their lives, feeding on bacteria. When conditions get harsh, they aggregate into a multicellular slug, which migrates to a new location ...
The Control of Patterning and Morphogenesis during Root
... species, there are only two cell types in the root epidermis: cells that produce long hairlike extensions (i.e., root hair cells, which are derived from trichoblasts) and cells that do not &e., hairless cells, which are derived from atrichoblasts; Cormack, 1949, 1962; Cutter, 1978). The arrangement ...
... species, there are only two cell types in the root epidermis: cells that produce long hairlike extensions (i.e., root hair cells, which are derived from trichoblasts) and cells that do not &e., hairless cells, which are derived from atrichoblasts; Cormack, 1949, 1962; Cutter, 1978). The arrangement ...
chapter3_part1 Membrane lecture
... thermally induced random motion • Net movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration • Equilibrium is reached when there is no concentration gradient and no net diffusion ...
... thermally induced random motion • Net movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration • Equilibrium is reached when there is no concentration gradient and no net diffusion ...
Water Soluble Vit PPT
... – Vitamin C acts like an anti-histamine – May be beneficial during a cold ...
... – Vitamin C acts like an anti-histamine – May be beneficial during a cold ...
Three types of muscles
... There are three types of muscle tissue: Visceral, cardiac, and skeletal. Visceral Muscle. Visceral muscle is found inside of organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels. The weakest of all muscle tissues, visceral muscle makes organs contract to move substances through the organ. Because ...
... There are three types of muscle tissue: Visceral, cardiac, and skeletal. Visceral Muscle. Visceral muscle is found inside of organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels. The weakest of all muscle tissues, visceral muscle makes organs contract to move substances through the organ. Because ...
Genesis of Cardiac Arrhythmias
... Leading cause of death in patients with HF Contractile dysfunction Possibly due to prolonged AP: Change in ion currents and Ca+ signaling Is it deglycosylation? ...
... Leading cause of death in patients with HF Contractile dysfunction Possibly due to prolonged AP: Change in ion currents and Ca+ signaling Is it deglycosylation? ...
OPEN STOMATA1 opens the door to ABA signaling in Arabidopsis
... responses, modulation of stomatal aperture is unique in being the only response that does not involve irreversible developmental changes. Rather, reversible changes in the intracellular concentrations of the osmotically active solutes Kþ, Cl2 malate22 and sucrose drive guard cell swelling or shrinki ...
... responses, modulation of stomatal aperture is unique in being the only response that does not involve irreversible developmental changes. Rather, reversible changes in the intracellular concentrations of the osmotically active solutes Kþ, Cl2 malate22 and sucrose drive guard cell swelling or shrinki ...
A Pseudomonas aeruginosa Type VI Secretion Phospholipase D Effector Targets Both Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... widespread T6SS-mediated mechanism, which deploys a single phospholipase effector to influence both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic hosts. ...
... widespread T6SS-mediated mechanism, which deploys a single phospholipase effector to influence both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic hosts. ...
Open and closed circulatory systems
... more efficient system to overcome their low surface area to volume ratio • In insects, the open circulatory system is supplemented with another separate open system of gas exchange ...
... more efficient system to overcome their low surface area to volume ratio • In insects, the open circulatory system is supplemented with another separate open system of gas exchange ...
File
... – May damage the cells and tissues of infected organisms directly by breaking down its living cells to use for food – May release toxins that travel throughout the body, interfering with the host Many ...
... – May damage the cells and tissues of infected organisms directly by breaking down its living cells to use for food – May release toxins that travel throughout the body, interfering with the host Many ...
THE ROLE OF MHC GENE PRODUCTS IN IMMUNE REGULATION AND
... cell immunity and of T cell immune regulation has evolved with particular emphasis on the genes of the MHC and the molecules for which they code that regulate essential immune mechanisms. Carrier Function and the Specificity of T Lymphocytes The pioneering experiments of Landsteiner (21) established ...
... cell immunity and of T cell immune regulation has evolved with particular emphasis on the genes of the MHC and the molecules for which they code that regulate essential immune mechanisms. Carrier Function and the Specificity of T Lymphocytes The pioneering experiments of Landsteiner (21) established ...
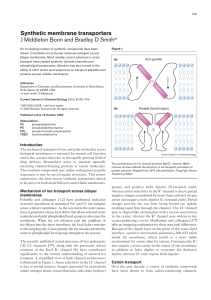
Synthetic membrane transporters J Middleton Boon and Bradley D
... Pohorille and colleagues [1,2] have performed molecular dynamics simulations of unassisted Na+ and Cl– ion transport across a bilayer membrane. As the ion enters the outer monolayer, it generates a deep, local defect that allows solvated water molecules and polar phospholipid head-groups to also ent ...
... Pohorille and colleagues [1,2] have performed molecular dynamics simulations of unassisted Na+ and Cl– ion transport across a bilayer membrane. As the ion enters the outer monolayer, it generates a deep, local defect that allows solvated water molecules and polar phospholipid head-groups to also ent ...
2006 Renal exam questions
... 12. A 35-year-old woman comes to see you for a physical exam. She is mildly obese, the blood pressure is 138/82, and the rest of the exam is normal. Over two ensuing visits, her blood pressure is 136/84 and 132/88. She has a normal electrocardiogram and urine analysis and the BUN is 11 mg/dL with a ...
... 12. A 35-year-old woman comes to see you for a physical exam. She is mildly obese, the blood pressure is 138/82, and the rest of the exam is normal. Over two ensuing visits, her blood pressure is 136/84 and 132/88. She has a normal electrocardiogram and urine analysis and the BUN is 11 mg/dL with a ...
Cue-Signal-Response Analysis of TNF-Induced
... Cue–signal–response relationships in cell signaling are ripe for applying multivariate analysis techniques, such as PLS, to tease out the key biochemical changes associated with critical cell decisions. However, assaying cell signaling involves the measurement of a wide range of parameters including ...
... Cue–signal–response relationships in cell signaling are ripe for applying multivariate analysis techniques, such as PLS, to tease out the key biochemical changes associated with critical cell decisions. However, assaying cell signaling involves the measurement of a wide range of parameters including ...